![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Isotopes Definition |
Atoms with the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons. |
|
|
Isotopes- Chemical properties |
They have similar chemical properties (how it reacts) as, they have the same electronic structure. |
|
|
Isotopes- Physical Properties |
They may have a slight varying physical property due to the difference in masses. |
|
|
Mass (kg) of Protons |
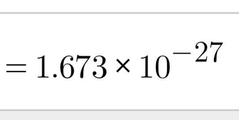
|
|
|
Charge (C) of Protons |
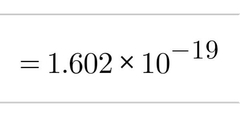
|
|
|
Position of Protons |
In the nucleus |
|
|
Mass (kg) of Neutrons |
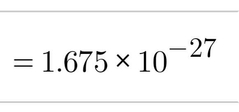
|
|
|
Charge (C) of Neutrons |
0 |
|
|
Position of neutrons |
In the nucleus |
|
|
Mass (kg) of Electrons |
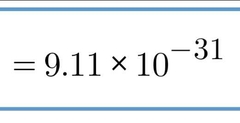
(very nearly 0) |
|
|
Charge (C) of Electrons |

|
|
|
Position of Electrons |
Around the nucleus in orbitals |
|
|
Relative Mass of Protons |
1 |
|
|
Relative Charge of Protons |
+1 |
|
|
Relative Mass of Neutrons |
1 |
|
|
Relative Charge of Neutrons |
0 |
|
|
Relative Mass of Electrons |
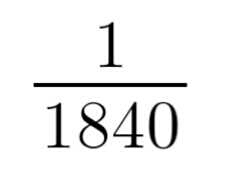
|
|
|
Relative Charge of Electrons |
-1 |
|
|
Strong nuclear force |
A force that holds together the protons and neutrons in the centre of the atom. It only acts over very short distances within the nucleus. |
|
|
Why is the 'strong nuclear force' much stronger than the 'electrostatic forces'? |
This is because nuclear force can bind many positively charged protons in a very short space that is in the nuclei of an atom despite the repulsions between them whereas the electrostatic forces holds the protons and electrons together in an atom. |
|
|
What are nucleons? |
Protons and neutrons. They are called this as, they are found in the nucleus. |
|
|
Atomic number (Z) Definition |
The number of protons in the nucleus. (The proton number) |
|
|
Why are atoms electrically neutral? |
The number of electrons in the atom is equal to the proton number, therefore, the charges balances out. |
|
|
Atomic numbers of elements |
Atoms of the same element have the same atomic number. Atoms of different elements have different atomic numbers. |
|
|
Mass Number (A) Definition |
The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. |
|
|
Mass of an atom |
The nucleons are responsible for almost all of the mass of an atom as, the electrons weigh virtually nothing (negligible). |
|
|
What happens when the isotopes are unstable? |
The nucleus of the atom breaks down giving off bits of the nucleus or energetic rays. |
|
|
Half-life Definition |
This is the time taken for half of its radioactivity to decay.
Each radioactive isotope decays at a rate measured by this. For example, a well-known radioactive isotope is carbon-14. |
|
|
How is carbon-14 produced in the atmosphere? |
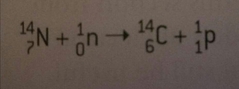
By a nuclear reaction in which a neutron (from a cosmic ray) hits a nitrogen atom and ejects a proton. |
|
|
Atomic model theories used to explain: |
Dalton's Model- Still used to explain the geometries of crystals. Bohr's Model- Used for a simple model of ionic and covalent bonding. The Charged Cloud Idea (J.J Thomson)- Explanation of bonding and the shapes of molecules. Simple model of electrons orbiting in shells- Used to work out bonding between atoms. |
|
|
The Mass Spectrometer Definition |
The mass spectrometer can be used to determine all the isotopes present in a sample of an element and to therefore identify elements.
Used to determine the relative atomic masses accurately. |

