![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
107 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define marketing
|
Identifying and meeting human and social needs
|
|
|
Define a market
|
A merket is described as a collection of buyers and sellers who transact over a particular product or product class
|
|
|
Identify and define the three levels of marketing
|
1) Macro-marketing - Marketing's role in society 2) Meso-marketing - Marketing's role in supply chain and industry 3) Micro-marketing - Marketing's role in individual organizations |
|
|
Define: Needs
|
Needs are the basic human requirements
|
|
|
What are the hollistic marketing dimensions?
|
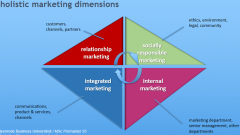
Relationsship marketing Socially responsible marketing Internal marketing Integrated marketing |
|
|
Marketing Mix
|
Product (what products to make and sell) Promotion (Advertising personal selling, sales promotion, publicity) Price (How much your product is going to cost) Place (Where to sell your product) |
|
|
Define: Wants
|
Directed to specific objects that might satisfy the needs
|
|
|
Identify four types of marketing in specific situations
|
- Consumer marketing - Retail marketing - Trade marketing - Non-profit marketing |
|
|
What does the marketing environment consist of?
|
1 Macro environment 2 Meso environment 3 Micro environment |
|
|
Define the microenvironment
|
Within the organization
|
|
|
Define the mesoenvironment
|
Within the supply chain, industry
|
|
|
Define the macroenvironment
|
Within society
|
|
|
Define: Demand
|
The wants for specific products backed by an ability to pay
|
|
|
Identify the types of competition
|
- Brand competition from various brands - Product form competition From products in various technical versions - Generic competition From suppliers in other product categories who solve the same needs - Need competition From products that satisfy different needs |
|
|
What are Porter's Five Forces?
|
- Threat of substitutes - Bargaining power of suppliers - Bargaining power of buyers - Threat of new entrants They all contribute to: - The rivalry among existing competitors |
|
|
What are the environments within the macro-environment and name at least two examples of forces.
|
- Demographic environment Population growth Population age mix - Economic environment Spendable income Income distribution Inflation/Deflation - Socio-Cultural environment Existence of subcultures Shift of secondary values over time - Technological environment Accelerating pace of change Varying R&D budgets - Natural environment Shortage of raw materials Anti-pollution pressure - Political-legal environment Increased in business legislation Growth of special interest groups |
|
|
What are the three kinds of marketing channels?
|
- Communication channels: deliver and receive messages from target buyers - Distribution channels: display, sell, or deliver the physical product or service - Service channels: (warehousing, banking, transport) |
|
|
Define: a suppy chain
|
From raw materials to components to finished products to final buyers
|
|
|
Define globalisation:
|
Increasing speed of delivery of products makes it increasingly easy for suppliers to supply their product around the world
|
|
|
Define: The production concept
|
Consumers prefer products that are widely available and inexpensive
|
|
|
Define: The product concept
|
consumers favour products offering the most quality, performance, or innovative features
|
|
|
Define: The selling concept
|
Consumers and business, if left alone, won't buy enough of the organisation's products
|
|
|
Define: The marketing concept
|
Find the product for your customers (instead of vice versa)
|
|
|
Define: The Holistic marketing concept
|
Based on development, design, and implementation of marketing programs, processes and activities that recognise their breadth and interdependencies.
'EVERYTHING IN MARKETING MATTERS' |
|
|
Define: Relationship marketing
|
Aims to build mutually satisfying long-term relationships with key constituents in order to earn and retain their business
|
|
|
Define: The Value Chain
|
Every firm is a synthesis of activities performed to design, produce, market, deliver, and support its products. Task of a firm: Examine costs and performance in each value-creating activity |
|
|
What are the three characteristics of core competencies?
|
- It is a source of competitive advantage and makes significant contribution to perceived customer benefits - It has application in a wide variety of markets - It is difficult for competitors to imitate |
|
|
What should a mission statement do?
|
A mission statement should provide a shared sense of purpose, direction, and opportunity.
Good mission statements focus on a limited number of goals, stress the firm's major policies and values, and define the major competitive spheres within which the firm will operate. |
|
|
What are the types of growth opportunities?
|
- Intensive growth - Integrative growth (backward integration, forward integration, horizontal integration) - Diversification growth, good opportunities ourside the present businesses. |
|
|
What is the Business Unit Strategic Planning Process?
|
Business mission SWOT Goals Strategy Program Implementation Feedback and Control |
|
|
Define strategy:
|
Strategy is the game plan for achieving the goals
|
|
|
Name the generic strategies:
|
- Overall cost-leadership (underprice competitors through minimizing cost) - Differentiation (Achieving superior performance in a customer benefit area) - Focus (Focus on one or more narrow market segments, persue cost-leadership or differentiation within these segments) |
|
|
What are the steps in a marketing plan?
|
- Executive summary and ToC - Situation analysis - Marketing strategy, mission and goals - Marketing tactics - Financial projections - Implementation controls, goals, and budget |
|
|
What is database marketing?
|
The process of building maintaining, and using customer databases and othe databases to contact, transact with, and build relationships with customers.
|
|
|
What is data wherehouse?
|
The place where marketers can capture, query and analyse data to draw interferences about individual customers' needs and responses
|
|
|
Define data mining
|
Data mining is used to extract from the mass of data useful insights about customer behaviour, trends, and segments.
|
|
|
What is a market intelligence system?
|
A set of procedures and sources that managers use to obtain everyday information about developments in the marketing environment.
|
|
|
What are variables in a marketing research plan?
|
Data sources: (primary vs. secondary) Research approaches: - Observational - Focus groups - Surveys - Behavioural data - Experimental research Research instruments Sampling plan - Unit - Size - Procedure Contact methods |
|
|
Identify and define the measures of market demand.
|
- The potential market (sufficient level of interest) - The available market (Consumers who have: interest, income, and access) - The target market: the part of the available market the company decided to persue - The penetrated market: The consumers who are buying the product/service |
|
|
What are the major macro-environmental forces?
|
AKA: DESTEP - Demographic - Economical - Social/Cultural - Technical - (Natural) Ecological - Political |
|
|
Define the customer benefit:
|
The perceived monetary value a customer expects from a given market offering
|
|
|
Define the total consumer cost:
|
The perceived bundle costs consumers expect to incur
|
|
|
Define quality:
|
Quality: The total of features and charateristics of a product/service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs.
|
|
|
Define CRM:
|
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is; the process of carefully managing detailed information about individual customers and all customer touch points to maximize loyalty |
|
|
Define customer behaviour:
|
Customer behaviour is the study of how individuals, groups, and organizations select, buy, use, and sipose of goods, services, ideas or experiences to satisfy their needs and wants
|
|
|
What are the factors influencing customer behaviour?
|
- Cultural factors - Social factors (cliques, family, roles and status) - Personal factors (age, occupation, lifestyle) |
|
|
Define perception:
|
Perception is the process by which we select, organise, and interpret information inputs to create a meaningful picture of the world.
|
|
|
What do brand associations consist of?
|
All brand-related thoughts, feelings, perceptions, images, etc., that become linked to the brand
|
|
|
What are the steps in the consumer buying process?
|
1. Problem recognition 2. Information search 3. Evaluation of alternatives 4. Purchase decision |
|
|
What are the steps involved in the Consumer Decision Making?
|
Total set → Awareness set → Consideration set → Choice set → Decision
|
|
|
What is a belief?
|
A belief is a discriptive thought that a person holds about something
|
|
|
What are the types of business buying decisions?
|
- Straight rebuy (reordering items on a routine basis) - Modified rebuy (the buyer wants to change terms) - New task (for the first time) |
|
|
What is the buying centre?
|
The buying centre includes all organisational members who play any role in the purchase decision process |
|
|
What are the buyphases of the Industrial buying process?
|
1. Problem recognition 2. General need description 3. Product specification 4. Supplier search 5. Proposal solicitation 6. Supplier selection 7. Order-routine selection 8. Performance review |
|
|
Major selection variables for Consumer markets
|
Anything really... Gender/climate/race/religion/loyalty status |
|
|
Major selection variables for business markets
|
Per DESTEP |
|
|
What are the steps in the segmentation process?
|
1. Needs-based segmentation (segment based on similar needs/benefits) 2. Segment identification (per need-base, determine demographics, lifestyle, and usage behaviours) 3. Segment attractiveness (based on market growth, competitive itensity , market access) 4. Segment profitability 5. Segment positioning (create a value proposition and product-price strategy) 6. Segment 'Acid test' Create a 'segment storyboard' to test the attractiveness of each segment's positioning strategy 7. Marketing-Mix strategy (Expand the product-price stategy to make sure it encorporates all 4 P's) |
|
|
What are the bases for selecting market segments?
|
- Full market coverage - Multiple segment specialisation - Single segment concentration - Individual marketing |
|
|
Define positioning:
|
Positioning is the act of designing a company's offering and image to occupy a distinvtive place in the minds of the target market.
|
|
|
Define: Value proposition
|
A value proposition is a cogent reason why the target market should buy a product or service
|
|
|
What are the criteria for determining if a company's brand association makes a difference:
|
- Desirable to consumer - Deliverable by the company - Differentiating from competitors |
|
|
Define brand equity:
|
Brand equity is the added value endowed to products and services with customers
|
|
|
Define: Brand Audit
|
A brand audit is a focussed series of procedures to assess the health of the brand, uncover its sources of brand equity, and suggest ways to improve and leverage its equity
|
|
|
Define: Branding strategy
|
A firm's branding strategy - often called a branding architecture - reflects the number and nature of both common and distinctive brand elements.
|
|
|
What are the available branding strategies?
|
- Individual or seperate family brand names - Corporate umbrella of company brand name - Sub-brand name |
|
|
What are the concepts of branding new products?
|
- Brand extension - Sub-brand - Parent brand - Master (or family) brand - Line extension - Category extension - Brand line - Brand mix - Branded variants - Licensed product |
|
|
What does it mean when you brand a new product through brand extension?
|
Using an established brand to launch a new product |
|
|
What does it mean when you brand a new product through a sub-brand?
|
Combining a new brand with an existing brand |
|
|
What does it mean when you brand a new product through Parent brand?
|
An existing brand that gives birth to a brand extension or sub-brand
|
|
|
What does it mean when you brand a new product through Master (or family) brand?
|
A parent brand that is already associated with multiple products through brand
|
|
|
What does it mean when you brand a new product through line extension?
|
Using a parent brand on a new product within a category it currently serves
|
|
|
What does it mean when you brand a new product through category extension?
|
Using a parent brand on a product to enter a new category, different from the one it currently serves
|
|
|
What does it mean when you brand a new product through brand line
|
All the products sold under a particular brand
|
|
|
What does it mean when you brand a new product through brand mix
|
The set of all brand lines sold under a particular brand
|
|
|
What does it mean when you brand a new product through branded variants?
|
Specific brand lines supplied to specific retailers or distribution channels
|
|
|
What does it mean when you brand a new product through Licensed product
|
Using the brand name licensed from one firm on a product made by another firm
|
|
|
What are the ways to classify products?
|
- Durability and tangibility - Consumer-goods vs. Industrial goods |
|
|
Define a company's product mix:
|
The set of all products and items a particular firm offers for sale
|
|
|
What does the width of a product mix refer to?
|
It refers to how many different product lines the company carries
|
|
|
What does the length of a product mix refer to?
|
The total number of products in the mix
|
|
|
What does the consistency of the product mix refer to?
|
How closely related the various product lines are
|
|
|
Define co-branding:
|
Two or more well-known brands are combined into a joint product. (Lays Joppie Saus) |
|
|
Define Ingrediënt branding
|
A special case of co-branding, here two or more well known brands are combined into a joint product or marketed together in some fashion. (VW + Blaupunkt) |
|
|
Describe the consumer adaptation process:
|
The mental steps through which an individual passes from first hearing about an innovation to final adoption: 1. Awareness 2. Interest 3. Evaluation 4. Trial 5. Adoption |
|
|
Draw the graph of adoption of innovations:
|
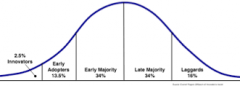
|
|
|
What are the categories of offerings?
|
- A pure tangible good (soap) - A tangible good with accompanying services (car) - A hybrid offering (restaurant) - A major service (Air travel) - A pure service (baby sitting) |
|
|
What are the types of marketing in the service industry?
|
- Internal marketing (company → employee) - External marketing (company → customer) - Interactive marketing (employee → customer) |
|
|
What are the steps in setting a price?
|
1. Selecting the pricing objective 2. Determining the demand 3. Estimating cost 4. Analyzing competitor's cost, prices, offers 5. Selecting a pricing method 6. Selecting the final price |
|
|
Define: Discount
|
A price reduction to buyers who pay bills promptly.
|
|
|
Define: Quantity discount
|
A price reduction to those who buy large volumes
|
|
|
Define: Functional discount
|
A discount provided by a manufacturer to trade-channel members if they perform certain functions, such as selling, storing, and record keeping.
|
|
|
Define: Seasonal discount
|
A price reduction to those who buy merchandise or services out of season.
|
|
|
Define: Allowance
|
An extra payment designed to gain reseller participation in special programs.
|
|
|
Define: First degree price discrimination
|
When the seller charges a seperate price to each customer depending on the intensity of his/her demand.
|
|
|
Define: Second degree price discrimination
|
When the seller charges different amounts to different classes of buyers
|
|
|
What are the conditions for price discrimination to work?
|
- The market is segmentable with different demand - Members in the lowest-price segment cannot resell - Competitors cannot undersell the firm - The cost of segmenting does not exceed the extra revenue - The practice does not breed customer resentment or ill will - The used form is not illegal |
|
|
What is an integrated multichannel marketing system?
|
In an integrated multichannel marketing system, the strategies and tactics of selling through one channel reflect the strategies and tactics of selling through one or more other channels. Adding one more channel gives companies three important benefits: - Increased market coverage - Lower channel cost - The ability to do more customized selling |
|
|
Define a vertical marketing system
|
A marketing system which includes the producer, wholesaler, and retailers acting as a unified system. (franchise, McDonalds)
|
|
|
Define a horizontal marketing system
|
In a horizontal marketing system, two or more unrelated companies put together resources or programs to exploit an emerging marketing opportunity
|
|
|
What is one of the most important marketing decisions for retailers?
|
LOCATION LOCATION LOCATION
|
|
|
Why use wholesalers?
|
In general, wholesalers can more efficiently perform one or more of the following functions: - Selling and promoting - Buying and assortment building - Bulk breaking - Warehousing, high inventory - Transportation - Financing - Risk bearing - Market information - Management services and counseling |
|
|
What are the common communication platforms?
|
- Advertising - Sales promotion - Events & Experiences - Public Relations & Publicity - Online and Social Media Marketing - Mobile Marketing - Direct and Database Marketing - Personal Selling |
|
|
What should be considered when setting the advertising budget?
|
- Stage in the product life cycle - Market share and consumer base - Competition and clutter - Advertising frequency - Product substitutability |
|
|
What are the steps for selecting media?
|
1. Reach, frequency and impact 2. Choosing among major media types 3. Place advertising options 4. Evaluate alternative media 5. Selecting specific media vehicles 6. Selecting media timing and allocation |
|
|
Types of major media types
|
- Newspaper - Television - Direct mail - Radio - Magazines - Outdoor - Yellow Pages - Newsletter - Brochures - Telephone |
|
|
Identify several major consumer promotion tools:
|
- Samples - Coupons - Cash refund offers - Price packs (two for one) - Premium (offering free merchandise) - Frequency Programs - Prizes (contests) - Patronage awards - Free trails - Product warranties - Tie-in promotions - Cross-promotions - Point-of-Purchase Displays (supermarktkassa) |
|
|
Identify major tools in marketing PR
|
- Publications - Events - Sponsorships - News - Speeches - Public Service Activities - Identity media |

