![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
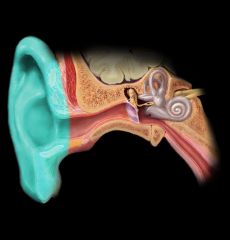
Auricle of ear
|
|
|
|
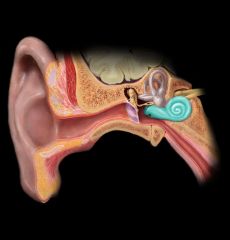
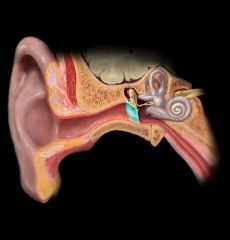
Cochlea
|
|
|
|
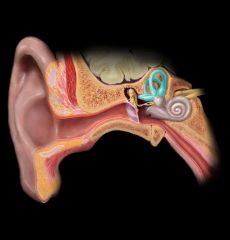
Semicircular ducts
|
|
|
|
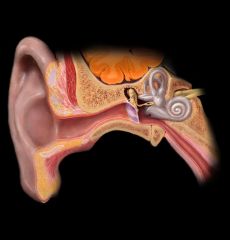
Temporal lobe
|
|
|
|
Tempanic membrane
|
|
|
|
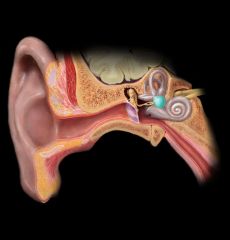
Utricle of ear
|
|
|
|
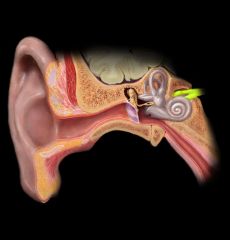
Vestibulocochlear n. CNVIII
|
|
|
|
Are the external auditory meatus and the external acoustic meatus the same thing?
|
I don't know.
|
|
|
What is the external acoustic meatis?
|
the external ear canal
|
|
|
What is the function of the auricle of the ear?
|
Acts like a funnel to collect and modify sound waves
|
|
|
What is the location of the cochlea?
|
temporal bone - petrous part
|
|
|
Describe the cochlea
|
coiled membranous tube surrounded by bone
contains three fluid-filled chambers |
|
|
how many fluid-filled chambers does a cochlea have?
|
three
|
|
|
Is the cochlea an organ? if so, of what?
|
yes; hearing
|
|
|
What is the location of the tympanic membrane?
|
temporal bone - petrous part
|
|
|
What separates the external acoustic meatus from the tympanic cavity?
|
tympanic membrane
|
|
|
Thin, semi-transparent, oval membrane
|
tympanic membrane
|
|
|
What is the other name for ear drum?
|
tympanic membrane
|
|
|
What is the other name for the tympanic membrane?
|
ear drum
|
|
|
What is the tympanic membrane attached to?
|
malleus (ossicle)
|
|
|
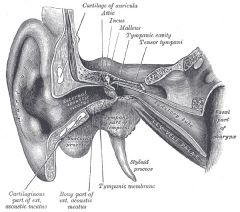
Tensor tympani m.
|
|
|
|
eustachian tube
|
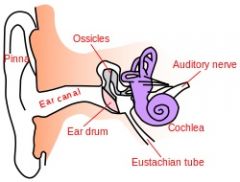
|
|
|
malleus
|
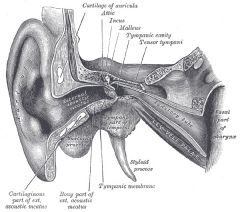
attached to tympanic membrane and the incus
looks like a hammer transmits sound vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the incus part of the middle ear |
|
|
transmits sound vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the incus
|
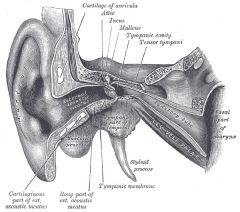
malleus
|
|
|
incus
|
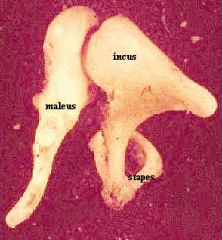
connects the malleus to the stapes
transmits sound vibrations from the malleus to the stapes part of the middle ear |
|
|
middle ear parts
|
malleus, incus, stapes
|
|
|
stapes
|
part of the inner ear
connects to the incus via the incudostapedial joint smallest bone in the human body transmits sound vibrations from the incus to the membrane of the inner ear |
|
|
the footplate of the stapes rests where?
|
the oval (vestibular) window
|
|
|
what is the smallest bone in the human body?
|
stapes
|
|
|
which muscle controls the stapes?
|
stapedius muscle, which is innervated by the facial nerve VII
|
|
|
which nerve innervates the stapes
|
facial nerve VII
|
|
|
Where is the spiral organ (of corti) located?
|
in the cochlear duct
|
|
|
what is contained in the cochlear duct?
|
spiral organ (of Corti)
|
|
|
in which part of the ear is the cochlea?
|
inner ear
|
|
|
vestibular apparatus
|
the structures of the inner ear concerned with stimuli of equilibrium, including the semicircular canals, saccule, and utricle.
|
|
|
the structures of the inner ear concerned with stimuli of equilibrium, including the semicircular canals, saccule, and utricle.
|
vestibular apparatus
|
|
|
organ of equilibrium
|
semicircular ducts
|
|
|
utricle
|
part of vestibular apparatus
involved with balance |
|
|
saccule
|
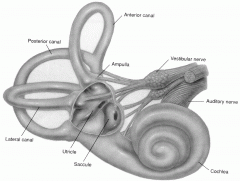
part of the vestibular apparatus
involved with balance |
|
|
ampulla
|
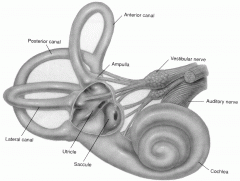
part of vestibular apparatus
involved with balance |
|
|
vestibulochoclear nerv
|
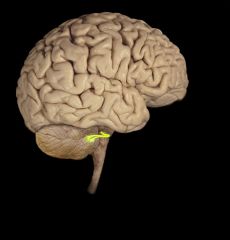
CN VIII
posterior cranial fossa petrous portion of temporal bone composition - special sensation |
|
|
CN VIII
|
vestibulocochlear nerve
|
|
|
post semicircular canal
|
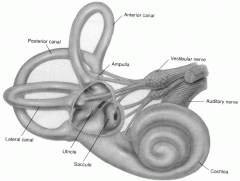
organ of equilibrium
|
|
|
internal carotid artery
|
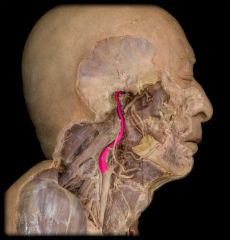
|
|
|
what artery feeds the ear?
|
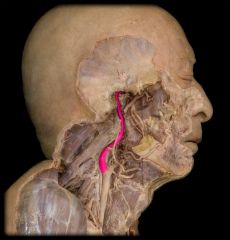
internal carotid artery
|

