![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
the study of the nature, behavior, and uses of static electricity and related phenomena
|
electrostatics
|
|
|
Greek philosopher, mathematician and astronomer who observed that amber, when rubbed, attracts straw
|
Thales of Miletus
|
|
|
British scientist who discovered that many materials attract things after being rubbed as amber does
|
William Gilbert
|
|
|
American scientist who discovered that static electricity exists in two forms and that lightning is caused by static electricity
|
Benjamin Franklin
|
|
|
invisible fluids supposedly released by electrics
|
effluvia
|
|
|
a property possessed by subatomic particles that allows them to attract and repel other particles
|
electric charge
|
|
|
electric charge possessed by a proton
|
positive
|
|
|
electric charge possessed by an electron
|
negative
|
|
|
the interactions between electrons and other charged particles
|
electricity
|
|
|
an atom or object with an equal number of positive and electric charges
|
neutral
|
|
|
what happens when equal opposite charges come into contact
|
they neutralize each other
|
|
|
the simplest form of electricity, stationary on an object's surface
|
static electricity
|
|
|
what charges two objects have if they have been charged through friction
|
one is positive and the other negative
|
|
|
the region around a charged object in which the forces of attraction and repulsion are operating
|
electric field
|
|
|
lines that show the direction and strength of an electric field
|
lines of force
|
|
|
SI unit of electric charge
|
coulomb
|
|
|
law that says that opposite charges attract and like charges repel
|
law of electric charges
|
|
|
name for what the lines of force look like when two plates of opposite charge are near each other
|
uniform field
|
|
|
description of a uniform field
|
even lines between the two plates, direction from positive to negative
|
|
|
law that says the strength of the attraction or repulsion between 2 objects is directly related to the strength of the charges and inversely related to the distance between them
|
law of electric force
|
|
|
discovered the law of electric force
|
Charles de Coulomb
|
|
|
formula for law of electric force
|
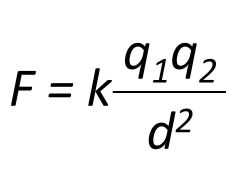
|
|
|
transferring of electric charge through direct contact
|
conduction
|
|
|
charge produced by conduction
|
same charge as the source's (positive is the source's charge was positive, negative if its was negative)
|
|
|
law that says the total charge after conduction or induction is the same before and after
|
law of conservation of charge
|
|
|
the process of diverting unwanted electric charge directly into the earth
|
grounding
|
|
|
occurs when an object with a negative charge suddenly releases electricity to another object with a positive or weaker negative charge
|
electrostatic discharge
|
|
|
transferring of electric charge over a distance without direct contact
|
induction
|
|
|
charge produced by induction
|
two charges—charge opposite the source's on the end nearest the source, and charge the same as the source's on the furthest end
|
|
|
how to produce a permanent charge through induction
|
induction plus grounding
|
|
|
atom or group of atoms with an electric charge
|
ion
|
|
|
negative ion
|
anion
|
|
|
positive ion
|
cation
|
|
|
flow of charge from one place to the next
|
current
|
|
|
ionized gas
|
plasma
|
|
|
liquids that readily conduct electricity because they contain freely moving ions
|
electrolytes and electrolytic solutions
|
|
|
oppositely charged wires placed in an electrolyte, causing a circular current
|
electrochemical cell
|
|
|
device that detects small electric charges
|
electroscope
|
|
|
device that produces static electricity
|
electrostatic generator
|
|
|
built the first electrostatic generator
|
Otto von Guericke
|
|
|
glowing caused by static electricity
|
electroluminescence
|
|
|
most commonly used electrostatic generator today
|
Van de Graaff generator
|
|
|
where electric charge always goes
|
the outside of a charged object
|
|
|
where a charged object has the most concentrated charge
|
on sharp curves or at corners and points
|
|
|
initial stream of electrons from cloud to ground in a thunderstorm
|
stepped leader
|
|
|
second stream of electrons from ground to cloud
|
positive streamer
|
|
|
upward flow of positive charged produced when the stepped leader and positive streamer meet in the air
|
return stroke
|
|
|
second leader which can form and cause a second return stroke
|
dart leader
|
|
|
which part is seen as lightning
|
return stroke
|
|
|
device that protects buildings from lightning by diverting electricity into the ground
|
lightning rod
|
|
|
eerie bluish glow that may appear around pointed objects during storms
|
St. Elmo's fire
|
|
|
the scientific name for what causes St. Elmo's fire
|
corona discharge
|
|
|
discovered that electric charges can be stored
|
Pieter van Musschenbroek
|
|
|
early device used to store electric charge
|
Leyden jar
|
|
|
any device used to store a static electric charge (of which the Leyden jar was one)
|
capacitor
|
|
|
purpose of a capacitor
|
to release all their charge at once, producing a short, intense burst of electricity
|
|
|
an electrostatic method of reproducing images on paper
|
xerography
|
|
|
dry powdered ink in a photocopier
|
toner
|
|
|
uses friction with the air to attract dust particles
|
electrostatic air filter
|

