![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How is mRNA processed in the nucleus?
|
5'-cap (methylated GTP), poly A tail (3' end), introns removed and exons spliced together
|
|
|
What is a holoenzyme?
|
bacterial core enzyme plus alpha factor
|
|
|
What is a cistron?
|
bacteria--region of DNA that encodes a single protein
|
|
|
What is the does polymerase 1, 2, and 3 encode for?
|
polymerase 1- makes rRNA, 2- mRNA 3- tRNA
|
|
|
How is the parental strand in DNA read?
|
3'-->5' direction
|
|
|
How is the new strand in DNA replication read?
|
5' to 3' direction
|
|
|
What is the function of primase?
|
Bacteria--RNA polymerase, copies parental strand and makes a RNA primer
|
|
|
What is the function of polymerase 3?
|
Bacteria
-major DNA polymerase, replicates both parenteral strands -proofreads -3' exonuclease activity, removes wrong nucleotides |
|
|
What is the function of sigma?
|
Humans
major DNA polymerase produces leading strand helicase activity (no proofreading, no exonculease activity) "sigma, special, makes leading" |
|
|
What is the function of alpha?
|
Humans
DNA polymerase produces lagging strand |
|
|
What minor DNA polymerases do DNA repair (3' exonuclease activity)?
|
Human
beta, epsilon |
|
|
What is the mitochondrial DNA polymerase?
|
Human
gamma |
|
|
What does endonuclease do?
|
in-cisions of DNA
|
|
|
What does exo-nuclease do?
|
removal of nucleotides form incised end
|
|
|
What derives from the ectoderm?
|
neural tube (CNS), neural crest (PNS), placodes (sensory organs), surface epithelium (skin)
|
|
|
What derives from the mesoderm?
|
somites (muscles, vertebral column)
|
|
|
What derives from the endoderm?
|
epithelium of the gut, liver, pancreas, thymus thyroid
|
|
|
What is Meckel's Diverticulum?
|
2-2-2
2% of people within 2 feet of the ileocecal jxn 2 cm long **may mimic appendicitis |
|
|
What is the action of the 1st arch?
|
chewing (muscles of mastication, facial artery, V3, malleus and incus)
|
|
|
What is the action of the 2nd arch?
|
moving face (muscles of facial expression, carotid artery, CN 7, stapes/hyoid/lesser horns of hyoid)
|
|
|
What is the action of 3rd arch?
|
stylopharyngeus (stylopharyngeal muscel, internal carotid artery, CN 9, hyoid)
|
|
|
What is the action of the 4th arch?
|
talking (pharyngeal muscles, larynx, CN 10, larynx)
|
|
|
What is the only pouch that remains throughout our lives?
|
first pouch--tympanic cavity and eustachian tube
|
|
|
What are the pharyngeal clefts (spaces)?
|
1- external auditory meatus 2-4: sinuses
|
|
|
What controls male differentiation?
|
1. Wolff is sustained by testosterone (from Leydig cells)
2. Muller suppressed by mullerian inhibitory factor (sertoli cells) |
|
|
What does the embrylogical structure does the allantois turn into?
|
urinary bladder and urachus
|
|
|
What does the embrylogical structure does the ureteric bud turn into?
|
bladder trigonum, ureter, collecting tubules
|
|
|
What does the embrylogical structure does the metanephros turn into?
|
kidney
|
|
|
What are the embryological features of the heart during fetal period?
|
ductus arteriosus (avoids blood from going to the lungs), foramen ovale (keeps the atria patent)
|
|
|
What are the embryological features of the heart during postnatal period?
|
ductus arterious-->ligamentum arteriosum, foramen ovale-->fossa ovalis
|
|
|
What goes through the superior orbital fissure?
|
Cranial nerves: 3, 4, 5, 6
sympathetic nerves opthalmic veins |
|
|
What goes through the foramen spinosum?
|
middle meningeal artery
|
|
|
What goes through the internal auditory meatus?
|
CN 7, 8
|
|
|
What goes through the hypoglossal canal?
|
CN 12
|
|
|
What nerve innervates the superior oblique muscle?
|
trochlear nerve
|
|
|
What happens when the abducens nerve is paralyzed?
|
unable to abduct eye, diplopia (double vision)
|
|
|
What happens when the trochlear nerve is paralyzed?
|
slight vertical double image, down and out
|
|
|
What is mydriasis?
|
dialation, controlled by the dilator pupillae (sympathetic control)
|
|
|
What raises the eye lid?
|
levator palpebrae and muller's muscle
|
|
|
What are the signs of horner's syndrome?
|
miosis (small pupils), ptosis (drooping eyelid), read and dry facial skin on affected side
**caused by neck injuries or tumors |
|
|
What are the three muscles controlled by CN 12 (hypoglossal nerve)?
|
genioglossus, styloglossus, hyoglossus
|
|
|
What happens when the hypoglossal nerve is damaged?
|
tongue deviates toward the side of damage
|
|
|
What controls taste and temp on the posterior 1/3 of the tongue?
|
CN 9
|
|
|
What controls taste on the ant 2/3 of the tongue?
|
CN 7
|
|
|
What controls touch and temp on the ant 2/3 of the tongue?
|
V3
|
|
|
What arch is the mandible adn the muscles that move it derived from?
|
first arch (chewing)
|
|
|
What does the lateral pterygoid control?
|
opens mouth, protrudes mandible, lateral displacement
|
|
|
What muscles open the mouth?
|
lateral pterygoid, digastri, geniohyoid
|
|
|
What muscle closes the mouth?
|
masseter
|
|
|
What muscle protrudes the mandible?
|
lateral pterygoid
|
|
|
What muscle retracts mandible?
|
temporalis
|
|
|
What lateral displaces the mandible?
|
lateral pterygoid
|
|
|
What are the muscles of the mandible?
|
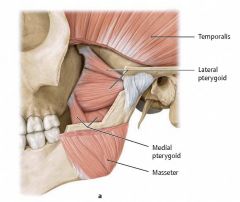
Temporalis: retracts mandible
Lateral pterygoid: opens mouth Masseter: closes mouth |
|
|
What are the 4 cartiladges that make up the larynx?
|
cricoid, thyroid, pair of arytenoid
|
|
|
What could cause the recurrent nerve to be injured?
|
thyroidectomy, carotid endarectomy, operations in anterior triangle of the neck
unilateral damage-->hoarse bilateral-->dyspnea |
|
|
Which nerve wraps around aortic arch?
|
left recurrent nerve
|
|
|
Which nerve wraps around right sublclavian artery?
|
right recurrent nerve
|
|
|
What are the 2 ways to initate the cough reflex?
|
above glottis-->superior laryngeal nerve
below glottis-->recurrent nerve |
|
|
What are the 4 muscles that make up the rotator cuff?
|
supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis (inward rotation, medial)
|
|
|
Damage to which nerve induces scapular winging?
|
long thoracic nerve
|
|
|
What muscles control AB-duction?
|
deltoid, (first 60 degrees), serratus anterior (long thoracic nerve)
|
|
|
What controls anteversion and retroversion of the shoulder?
|
anteversion-- deltoid, retroversion--pteres major
|
|
|
What controls outward rotation?
|
infraspinatus
|
|
|
What controls inward rotation of the shoulder?
|
subscapular muscle
|
|
|
What are the muscles that connect humerus to scapula?
|
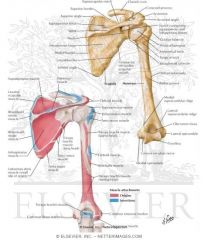
deltoid, supraspinatus, subscapularis, corobrachialis, infraspinatus, teres minor, teres major
|
|
|
What are the three trunks and associated spinal rami, terminal nerves?
|
UPPER TRUNK- C5-C6, musculocutanous nerve
MIDDLE TRUNK: C7, axillary/radial/median nerves LOWER TRUNK: C8-T1, ulnar nerve LOWER TRUNK |
|
|
What are the S/S of upper brachial plexus injury?
|
waiter's tip pxn (arm hangs in medial rotation)
|
|
|
What are the S/S of posterior cord injury?
|
wrist drop (radial nerve injury)
|
|
|
What are the S/S of lower brachial plexus injury?
|
"claw hand" ulnar nerve injury
|
|
|
What are the S/S of humerus fracture?
|
risk of radial nerve injury, spiral down near humerus
|
|
|
What causes wrist drop?
|
radial nerve injury
|
|
|
What causes claw hand?
|
ulnar nerve injury
|
|
|
What are the nerves that innervate the arm?
|
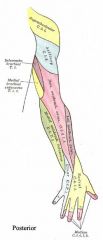
radial nerve (posterior, dorsal hand), median (2.5 fingers palms and tips), ulnar (1.5 fingers palms and tips), musculocutaneous (extensor part of the forearm)
|
|
|
What innervates biceps brachii?
|
musculocutaneous nerve
|
|
|
What innervates triceps brachii?
|
radial nerve
|
|
|
What innervates pronator teres?
|
median nerve
|
|
|
What flexes the thumb?
|
floxr pollicis (thumb) longus
|
|
|
What flexes the wrist and medial 4 digits?
|
flexor digitorum profundus
|
|
|
What flexes and adducts the wrist?
|
flexor carpi ulnaris
|
|
|
What flexes the wrist?
|
palmaris longus
|
|
|
What innervates the formearm flexors of wrists and fingers + digitalis profundus?
|
median nerve
|
|
|
What innervates all intrinsic hand muscles, carpi ulnaris, and dig profund besides those supplied by the median nerve?
|
ulnar nerve
|
|
|
What are the innervations of the hand?
|
radial: thumb, median: 2nd and 3rd digit tips and posterior, ulnar 4th and 5th digit tips and posterior
|
|
|
What muscle does the inferior gluteal nerve innervate?
|
gluteus maximus
|
|
|
What muscle does the superior gluteal nerve innervate?
|
gluteus medius and minimus
|
|
|
What gluteal muscles control outward and inward rotation of the hip?
|
outward--gluteus maximus, inward--gluteus minimus and medius
|
|
|
What controls extension of hip?
|
gluteus maximus (innervated by inferior gluteal nerve)
|
|
|
What controls ab-duction of the hip?
|
gluteus medius (innervated by superior gluteal nerve)
|
|
|
What are the medial thigh muscles?
|
pectineus, adductor brevis, adductor longus, adductor magnus, gracilis
|
|
|
What are the anterior thigh muscles?
|
sartorius, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis
|

