![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
140 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Reset CMOS |
Reseat battery mb jumper Default settings in configuration |
|
|
|
Install new component |
Have to enable in CMOS first sometimes, then driver |
|
|
|
Info on new device stored |
CMOS RAM Flash memory |
|
|
|
Windows utility to view basic info on BIOS |
Msinfo32.exe |
|
|
|
Flash BIOS w.o removing chip |
EEPROM Flash memory |
|
|
|
CPU socket types |
PGA, LGA, zif, pga2 |
|
|
|
RAM |
Mb slot type for primary storage modules |
|
|
|
PCIe v3.x x1 speed |
985 MB/s |
|
|
|
PCIe v2.x x1 speed |
500 MB/s |
|
|
|
PCIe v1.x x1 speed |
250 MB/s |
|
|
|
PCIe lane |
2 wires, one for receiving another for sending data |
|
|
|
PCIe replaces |
PCI, PCIX, AGP |
|
|
|
Expansion slots for dedicated graphics controller |
AGP & PCIe |
|
|
|
Form factors using riser cards |
LPX & NLX |
|
|
|
RTC |
Real time clock, keeps track of time Uses CMOS battery |
|
|
|
Permanent memory types |
ROM PROM |
|
|
|
Word (computer architecture) |
Groups of bits processed as unit SDR SDRAM- processes one word of data per clock cycle DDR- 2 words DDR2- 4 words |
|
|
|
DIMM bits |
64 bit |
|
|
|
eMMC |
Secondary storage for tablets and phones |
|
|
|
Tape drives |
High capacity, slow seek times, magnetic |
|
|
|
Lowest to highest capacity storage media |
Floppy, CD, DVD, BD, tape |
|
|
|
Video basics |
Video card/display adapter handles communication between CPU & display/monitor Drivers help os handle communication between CPU & video card |
|
|
|
Video displays |
LCD, projector, CRT(old), OLED(expensive, phones, small screens) |
|
|
|
Refresh rate |
Time to draw whole screen 60hz is standard 120hz-need dual link dvi Doesn't affect LCD, lower refresh rate in CRT meant flickering |
|
|
|
Display ratios |
Aspect ratio 4:3--640x480, 800x600, 1024x768 Wide screen aspect ratio 16:9 16:10--1366x768, 1600x900, 1920x1080 |
|
|
|
Static charging |
For basic numeric displays (calculators) Different shaped elements not connected, making a shape when charged Inflexible display |
|
|
|
(Dual scan) passive matrix vs active matrix/thin film transistor |
Passive matrix-slow, overlapped pixels (blurs), dual scan faster version Active matrix- each pixel controlled by 1+transistor, better than dual scan passive Active twisted nematic(TN) is basic Active in plane switching (IPS) best |
|
|
|
LCD backlights |
-Need inverter to convert back to AC power after transformer (ac to DC) -Usually CCFL (low power, lasts) -LED on edges -LED on entire back is better -LED monitors are LCD with LED backlights, less thick, less power usage
|
|
|
|
LCD ports |
DVI, HDMI both connected to logic circuit since digital VGA connected to analog/digital converter first |
|
|
|
LCD resolution |
Native resolution- can't change, displays sharpest image possible Control panel, task list (vista) or display/personalization Change DPI to make everything bigger/smaller |
|
|
|
Nits |
Measures brightness 100 nits low end LCD 1000 nits high end |
|
|
|
Response rate |
Time for all sub pixels to go from pure black to pure white to black 2-4 millisecond |
|
|
|
Contrast ratio |
Difference between lightest and darkest pixel can be displayed LCD = CRT in terms of color saturation, richness, contrast 450:1 good, 250:1 low end Dynamic contrast ratio is trick, doesn't affect monitor output |
|
|
|
Compare LCD |
Size Native resolution TN vs IPS CCFL(florescent) vs LED Brightness, response rate, contrast ratio |
|
|
|
Protectors |
-Rear view- self enclosed, like a big TV, no longer used -Front view used -CRT- 3 colors w separate CRT to project, big, heavy, expensive -LCD- light, cheaper, lower image quality -same issues as monitors (native resolution) -lumen: brightness, 1000(small, dark room)-10000(large rooms) -throw: min/max projection distance, long throw lens (1:2 ratio, 4ft screen, 8ft away), short throw lens(1:1) -bulb expensive, couple hundred |
|
|
|
PDP |
Plasma display panel Better picture, cheaper, heavier, more energy usage Burn in & over scan problems Use for movies not PC monitor |
|
|
|
HD15 |
high density 15 pin, 3 row d shape Aka D shell/subminiature, DB15, DE15, VGA |
|
|
|
RAMDAC |
Chip on video card RAM digital to analog converter for CRT monitor |
|
|
|
DVI |
DVI D-digital DVI A- analog DVI A/D aka DVI I- takes both Single link (1920x1080 at 60hz, can use dual link connector) or dual link (higher bandwidth, 2048x1536 at 60hz) |
|
|
|
Color depth |
Described in bits, 2 bits p pixel, more bits more colors 2 colors- 1 bit 4 colors- 2 bits 16 colors- 4 bits 256- 8 bits |
|
|
|
Video modes |
Combo of resolution and color depth settings VGA standard- 16 colors, 640x480, minimum for many software SXGA- 1280x1024, 5:4, LCD native resolution 4k ultra HD |
|
|
|
Display adaptor connections |
-PCI: 32 bit @ 33 mhz = 132 MBps, video would take all PCI bus power -PCIe- x16 connector -AGP: PCI 2 66mhz 32 bit standard, old -integrated: on CPU, mb, or north bridge, less electricity |
|
|
|
Graphics processor |
Device that processes video, takes commands from CPU and translates them so the monitor can display Nvidia, AMD, Intel make GPU for video card makers Huge (384 bit) bus between GPU and video RAM ex. XFX (video card maker) Radeon HD7970 (gpu) 3GB 384 bit GDDR5 (RAM & bus to GPU) PCIe 3.0(video card connection) |
|
|
|
Video RAM |
Throughput speed, access speed, capacity GPU handles video data processing with video RAM(can write and read data at same time unlike DRAM), faster access than system RAM & bigger bus GDDR5 standard, DDR3 lower end |
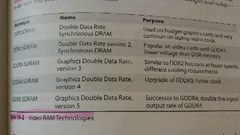
|
|
|
Monitor connectors |
VGA DVI (supports analog) DB15 display port (Mac, dell) Thunderbolt (Mac, good for multi monitors) HDMI (best, can use dual link DVI port) RCA (composite or component connection), BNC, mini DIN6 (S video cable), RJ45(TV, camcorders..) Several adapters and converters for all types |
|
|
|
Install display adapter |
Make sure room (slot, space for air) Power connection (usually need additional PCI power connector) Driver (website, installation media, don't use built in win driver) |
|
|
|
Improperly seated video card |
Dead PC Blank screen but fans running |
|
|
|
Monitor flickering |
Ccfl backlights dying |
|
|
|
Modern CPU speed measured in |
Ghz |
|
|
|
AMD virtualization support |
AMD-v |
|
|
|
Socket T |
775 contacts LGA Intel CPU socket |
|
|
|
Nx bit technology for intel |
Xd bit |
|
|
|
Socket h2 |
LGA 1155 contacts Intel cpu socket |
|
|
|
RISC |
CPU design based on instruction set that tries to improve speed by utilizing relatively few and simple instructions |
|
|
|
Socket h/h1 |
1156 contacts LGA packaging Intel CPU socket |
|
|
|
bus between the CPU and the internal memory cache (L2 cache) inside the CPU housing |
Back-side bus (BSB |
|
|
|
Intel virtualization support |
Vt-x |
|
|
|
Socket b |
LGA 1366 Intel |
|
|
|
Bus between CPU & north bridge |
Front side bus |
|
|
|
Socket h3 |
LGA 1150 Intel |
|
|
|
Intel CPU for desktop & workstation |
Celeron Pentium i3,5,7 |
|
|
|
AMD CPU for servers |
Opteron |
|
|
|
Socket r |
Intel 2011 contacts Lga |
|
|
|
Intel CPU for servers |
Xeon Itanium |
|
|
|
AMD Nx bit technology |
Evp |
|
|
|
AMD CPU for desktop & workstations |
Athlon Sempron Phenom FX |
|
|
|
NIC |
Network interface controllers -client & server need, labels machine on network(MAC address) -breaks down, sends, reassembles files discrete data units(frames) -used to be cards, now built in to mb |
|
|
|
Frames |
Discrete data chunks Packets are part of frame Many varieties Contains: 1. MAC address of where frame from/sent to 2. data (os knows what data is, not NIC), size varies on frame type 3. data check, verifies if received in good order, usually cyclic redundancy check (CRC, math algorithm) |
|
|
|
MAC address |
Media access control 48 bits long, represented w 12 hexadecimal Unique identifier, some NICs allow you to change -Show address: System information utility, NIC description "ipconfig /all" command, LAN, Ethernet, physical address category |
|
|
|
Ethernet |
Standard to get data from one device to another Wired or wireless Flavors-versions Frame same in all versions to allow compatibility Speeds: 10BaseT- 10 Mbps 100BaseT- 100 Mbps, desktops 1000BaseT- gigabit Ethernet, servers Star bus topology, UTP cable |
|
|
|
Star bus topology |
Host systems connected to box via cables Box (switch) handles network communication (sending frames correctly) Bus- internal wiring of switch Star- shape of box, cable, host system Hybrid topology Doesn't go down if one cable breaks |
|
|
|
Switch |
Central box of networking system Connects devices w ports (4/8 or 32+) Improvement on hub (stupid repeater: sends frames to all ports, makes devices share network bandwidth) Memorizes MAC addresses, sends repeated signals to correct host Faster Each port is its own separate network Segment (connection bt device & switch) <100 m, can't use splitters to make one connection, two
|
|
|
|
UTP |
Unshielded twisted pair cable used for Ethernet AWG22-26 wires, one for sending, other for receiving CAT level on cable, TIA/EIA 568 standard defines levels STP-shielded, protects from EMI, used rarely 10BT- CAT 3/5+ 100BT- CAT 5+ 1000BT- CAT 5e+ RJ-45 connector, has CAT levels to match cable RJ-11 for telephone lines Pin 1 starts on r side when tab on bottom TIA/EIA T568A & T568B standards to connect pins to color wire Use one standard on one cable, keep records Crimper tool used to attach rj45 to cable Rj45 outlet has CAT levels too Solid core or stranded core (flexible, but breaks with wear & tear) |

|
|
|
CAT 1&3 |
1- standard telephone line 3-10BT, version with 4 wires for 100BT |
|
|
|
CAT 5/5e |
100BT 5e- 1000BT |
|
|
|
CAT 6/6a/6e &7 |
6/e- 1000BT @100m, 10 Gbps @ 55m 6a/e- 10 Gbps @100 m 7-10 Gbps @100 m w extra shielding |
|
|
|
Plenum vs PVC cable |
Plenum space- ceiling/wall/floor where cable runs Needs fire proof jacket to protect cable, PVC doesn't have |
|
|
|
Crossover cable |
Hook two devices directly UTP cable w. one RJ-45 T568A & other RJ-45 T568B |
|
|
|
Fiber optic |
Cable uses light instead of electricity, no EMI problems, travels further (2000m+) Usually 62.5/125, multi mode Two cables w two connectors(ST/SC connectors) or in one(LC connector, newer) needed bc half duplex (data flows one way) Multi mode-LED, multiple signals at once, 600m Single mode- lasers, faster, longer distance, rare Need fiber optic switch and NIC to use cable |
|
|
|
Coax cable |
Cable modems, satellite Shield to protect cable+insulation RG rating marked on cable RG59- 75 ohm impedance(resistance), thinner, shorter distance RJ6- 75 ohm BNC(rare) or F connector(normal cable modem) Splitters lower speed & quality 100mpbs max
|
|
|
|
LAN |
local area network Connected devices with few hundred meters Usually broadcast domain (connected by switch allows all devices hear broadcast frames) Cable, wireless or Ethernet over power connection |
|
|
|
Ethernet over power |
Bridges connected to power outlet to transmit UTP signals 100BT max Good for places Wi-Fi or cable doesn't reach |
|
|
|
Structured cabling |
TIA/EIA standard create safe, reliable cabling infrastructure, flexible for new demands 3 components: telecommunications room (all cables concentrate in), horizontal cabling (contains runs of cables, always solid core), work area Run is CAT 5e cable or better |
|
|
|
Telecommunications room |
Contains equipment rack, 19" wide, varying heights Rack mounted network hardware height measured in U(=1.75", 7" =4U) |
|
|
|
Patch panel |
-Female ports with permanent horizontal cable connections in back -110 punchdown block connect to UTP cables w punchdown tool -TIA/EIA 606 standard or internal code to organize cables -variety in type & number of ports 8, 12, 24, 48... -CAT ratings, backwards compatibility, use highest avail
|
|
|
|
Patch cables |
2-5' utp cables, stranded for flexibility Reinforced connector so can plug in & out multiple times Connects ports to switch |
|
|
|
WAN |
wide area network (like internet) Widespread devices connected using long distance tech (router) provided network protocol that handles routing |
|
|
|
Routing |
Require router and protocol Destroys broadcast frames |
|
|
|
Internet tiers |
Tier 1- small number of companies own backbone (long distance, fiber optic network) w network access points (NAP) in major cities, don't charge each other to connect Tier 2- regional networks pay tier 1 provider, most ISP Tier 3-smaller regions, connect to tier 2 |
|
|
|
Backbone routers |
Connect to each other form backbone network access points Provide alternate routes if one broken Message send failure, routers update list of good routers, resend |
|
|
|
TCP/IP |
-Basic software structure for communication on internet -Addressing scheme (IP), internet frameworks & language -TCP/IP services use TCP/IP structure & features -use defined ports, require application to run, have app specific settings |
|
|
|
Connect to ISP |
Hardware: modem, cable, router (default gateway), dhcp server Software: protocol(configured in os), applications to use TCP/IP services |
|
|
|
Dial up |
Analog, slowest Need: -telephone line: speed measured in baud, 2400 baud max -modem: converts analog to digital, PCI, PCIe, USB(gets power through USB too) -ISDN terminal adapter -software: Microsoft dial up network, governs connection ISDN uses digital dial up, faster Point to point protocol(PPP) hardware streaming protocol Make sure phone jack good, modem's properties, turn volume up |
|
|
|
Modems |
Transform signals |
|
|
|
Configure dial up |
Network and sharing, set up new connection Use info given by ISP, make sure enter correctly |
|
|
|
ISDN |
Digital dial up, digital lines -Bearer B channel: carries voice & data, 64 kbps -Delta D channel: carries setup & config data, 16 kbps -basic rate interface BRI: two b& one d channels -primary rate interface PRI: 23 b & 1 d, aka T1 lines -within 18k ft of central office to use -RJ45 network jack -terminal adapter: looks like modem, interface for comp |
|
|
|
DSL |
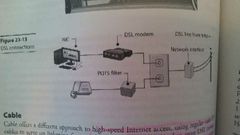
Digital subscriber line -telephone lines w receiver/modem at end to make faster -asynchronous DSL: ASDL, slow or fast -synchronous DSL: SDSL, faster, expensive -xDSL: variations -wireless router connections -config w info from ISP -be within hundreds or 18k' from phone service center
|
|
|
|
Cable |
-uses cable TV cables -faster than DSL -1-20 Mbps upload, 6-100+Mbps download -RG6/RG59 cable connect to cable modem then Ethernet to router/nic |
|
|
|
Fiber |
-fiber to node: FTTN, fiber connection to box in neighborhood, coaxial/Ethernet cable to location -fiber to premises: FTTP, fiber to location, then cable/wireless in location -1-75mbps download, 384kbps-8mbps |
|
|
|
Ethernet bridge devices |
Extend Wi-Fi range, line of sight wireless internet connection up to 8 miles+ |
|
|
|
Cell generations |
-read device info, gen not standards -4G/LTE: 300mbps download, 75mbps upload -1G was analog |
|
|
|
WWAN/WLAN |
wireless WAN(connect to other WAN)/LAN |
|
|
|
Satellite |
-dish to receiver, Ethernet, then nic -before had to connect to modem -latency from distance and weather, point dish to satellite |
|
|
|
Connect single vs multiple comp to internet |
-Single: config -multiple: router, bt main comp/LAN and ISP connection(WAN) |
|
|
|
Router |
-Ethernet ports and/or Wi-Fi radios -uses network address translation NAT technology: presents entire LAN to internet as single machine with public IP address (given by ISP), acts like firewall, LAN IP addresses private |
|
|
|
DNAT |
dynamic NAT Computers share pool of routable IP addresses to access Internet, private IP addresses on LAN each IP address costs $, limits access to internet too |
|
|
|
Basic router config |
-change default user name &pass -automatic/DHCP or static IP from ISP (manual entry) -ISP router can update automatically |
|
|
|
HTTP |
App protocol Web pages Port 80 |
|
|
|
HTTPS |
App protocol Secure web pages Port 443 |
|
|
|
FTP |
App protocol File transfer Port 20, 21 |
|
|
|
SFTP |
App protocol Secure file transfer Port 22 |
|
|
|
IMAP |
App protocol Incoming email Port 143 Search through emails w keyword & select messages to download to machine feature Less popular than POP |
|
|
|
POP3 |
App protocol Incoming email Port 110 |
|
|
|
SMTP |
App protocol Outgoing email Port 25 |
|
|
|
Telnet |
App protocol Terminal emulation Port 23 |
|
|
|
SSH |
App protocol Encrypted terminal emulation Port 22 |
|
|
|
RDP |
App protocol Remote desktop Port 3389 |
|
|
|
SIP |
App protocol Voice over IP Port 5060 |
|
|
|
DNS |
Utility protocol Allows use of DNS naming Port 53 UDP |
|
|
|
DHCP |
Utility protocol Automatic IP addressing Port 67,68 UDP |
|
|
|
LDAP |
Utility protocol Querying directories Port 389 TCP |
|
|
|
SNMP |
Utility protocol Remote management of network services Port 161 UDP |
|
|
|
SMB |
Utility protocol Windows naming/folder sharing Port 445 TCP CIFS, port 137-139, UDP |
|
|
|
AFP |
Utility protocol Mac file services Port 548, 427 TCP |
|
|
|
Internet troubleshooting |
-Network problem vs hardware (cable?) -disconnect nic -LAN connection -DNS? (Ping to check, 'ipconfig /flushdns' command to fix, use another DNS server 8.8.8.8 Google) -network & sharing, change adapter settings, r click network, diagnose -limited/LAN only connection: 'ipconfig' command, no APIPA address: DHCP down, restart router or manual entry network id & default gateway IP -'netstat' command to see hogging devices for slow connections |
|
|
|
Portable devices |
-desktop replacement: power first, portability second -Chromebook: cloud for data storage & software (SaaS) -netbooks: lightweight os -use to have trackpoints on keyboards -ultrabooks: thin, light, and powerful -tablet PC(convertibles or slates) not same as tablet -multi touch touchpad w gestures, disable touchpad w hardware switch or fn +key combo -16:9, 16:10 ratio -LCD/LED use twisted nematic, some IPS($$) -no plasma, OLED only for mobile |
|
|
|
Portable comp extensions |
-audio(3.5mm)/microphone port -add monitor: fn+key combo to cycle monitor setup selections or control panel, display, display settings, screen resolutions -smart card reader (built in or USB) to login w credit card/chip -Wi-Fi built in (802.11 b/g for older, n/ac for newer laptops) -wired Ethernet not in smaller portables (ultrabooks), turn off in BIOS or disable NIC in device manager, RJ45 port weak w overuse -hardware switches to turn off Wi-Fi/Bluetooth -express cards: 34/54 mm width, 75mm long, 5m thick. Connect to USB 2.0(parallel, 480mbps)/PCIe (serial, 2.5Gbps) bus -docking station w ports, proprietary connection, extra features (optical drive, express card slot) -USB adapter for everything (USB to rj45/Wi-Fi/Bluetooth/optical drive/Ethernet |
|
|
|
Portable computer power management |
-lithium ion, most efficient -lithium polymer for smaller electronics -store battery in cool (not freezing) dry place -clean contracts w alcohol & soft cloth -keep at 70-80% charged unless doing battery calibration -airplane mode to save battery -disable keyboard backlight -offline files: copy on comp syncs w copy in network. r click f/f, always available offline. --open f/f offline: control panel, sync center, tasks, manage offline files, view offline files
|
|
|
|
SMM, AMP, ACPI |

-system management mode, all CPUs have, puts CPU and peripherals to sleep -APM/ACPI: BIOS/OS specification to work w SMM, Intel --Need SMM CPU, APM compliant BIOS(works w CPU to shut off peripherals), energy Star devices (able to sleep), OS capable of request shutdown device --ACPI supports hot swappable devices --APM 4 power usage levels: full on, APM enabled, standby, suspend (shut down) --ACPI: G0, G1(sleep, 4 S sublevels), G2/S5(soft power, select devices can wake like keyboard, LAN, USB), G3(off) -config in CMOS/os(control panel, power), os settings override CMOS, enable APM, change time frames to sleep, determine wakeup events, ACPI settings -power plans: select or custom, hibernate takes RAM data into hard drive |
|
|
|
Maintain portable |
-screen cleaner, compresses air -careful of warm office, use hard flat surface, fan running really fast or silent (died) -if fixed input power supply, need transformer when travel to different volt outlet country |
|
|
|
Upgrade/repair laptop |
-Dis/reassembly: Document & label cable, screw locations Organize parts Refer to manual Use appropriate hand tools -manufacturers provide access to resources to authorized repair centers -upgrade RAM: get correct, works w existing RAM?, remove all electric power (removable and built in batteries) -upgrade mass storage: SATA 2.5" usually, PATA be careful with cables and jumpers & setting master/slave HDD or SSD(less storage, faster, less electricity) Prepare bootable repair disc/USB -can replace any component in laptop, depends if soldered on, need peel laptop bottom up, top down, or through keyboard |
|
|
|
Shared memory |
Video card takes part of RAM, not sharing CMOS setup to turn on/off, what portion Add RAM for overall performance Set shared memory to max for better video |
|
|
|
Laptop won't power on |
Verify ac power Bad ac adapter-no LEDS light up Faulty peripheral (USB, FireWire..) |
|
|
|
Laptop display problems |
Display on? LCD cutoff switch not stuck? Dim-lost inverter, loud him Flickering- turn up brightness/not power saving mode or replace, give headaches Control panel, display, to change screen auto rotation
|
|
|
|
GPS not working |
Control panel, locations Settings app, privacy |
|
|
|
Config touchpad |
Control panel, mouse or tablet PC settings Ghost cursor: aging display or config refresh rate Pointer drift: damaged touchpad |
|
|
|
Types of mobile devices |
-smartphone: multi touch surface, cellular data, standardized application programming interface (API), synch and distribution tools for apps and data, no FRU, service centers for repairs -tablets: no cell data -phablets: big smart phone -e reader: special display -wearable tech: light os, limited hardware, pair to host device. Smart watches, fitness monitors, glasses |
|
|
|
Mobile hardware |
-twisted nematic($) IPS($$) OLED($$$, no backlights, organic compounds used, less electricity, better image) screens -smart cameras, including add one os -digitizers: provides touch capability to screen, works with os, capacitive touchscreen, also convert analog to digital -uses GPS, cell, Wi-Fi connection to track location, geotracking w id or MAC address -accelerometer & gyroscope: maintain screen orientation -system on chip SoC: CPU, GPU+in one, ARM architecture chip usually -SSD -3.5 mm audio jack -microSD, micro HDMI(tablets) -near field communication NFC uses chips in device to exchange data within cm to few inches -micro/mini USB 3.0, newer type c 3.1 -lightning connector, 8 pin, apple only |
|
|
|
Mobile os |
-apple iOS: tight control development of hardware, os, developer tools, app deployment Line of business apps made for organization need apple license approval -Google android: based on open platform Linux, Google play and amazon app store&+ -Microsoft windows phone: one os, one experience, not restrictive as Apple -GUI, no command line Android& windows have launchers: GUI versions -Wi-Fi calling -virtual assistants: siri, windows cortana, Google now -software development kit (SDK): write application development, Apple Xcode. Android application package used post code compilation to install -emergency notification: can't silence, E911 system -mobile payment services: has bank info, can use NFC, ex. apple pay -airplane mode: no signal -safari, chrome, edge (win) browsers -cellular, 802.11, Bluetooth radios -PRL&PRI baseband/over the air updates: automatically, CDMA network, during firmware/os updates, controls which tower access and data rates |
|
|
|
Mobile device identifiers |
-international mobile equipment identity IMEI: 15 digit, for GSM(4G LTE, LTE advanced...) devices, on battery compartment, cell networks can use to block device from access, authenticate device -integrated circuit card identifier ICCID: id for SIM to authenticate subscriber -international mobile subscriber identity: user's account on SIM, can be used to unlock phone |
|

