![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Things in a Circulatory system |
- blood vessels - heart (pump) - valves |
|
|
|
Double circulatory system |
- blood travels through the heart twice per circuit - this is for tissues like muscles that need oxygenated blood faster - in mammals |
|
|
|
Single circulatory system |
- blood travels through heart once every circuit - fishes |
|
|
|
Steps of double circulatory system |
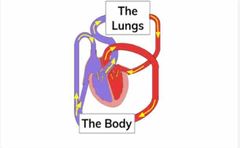
- DB enters the heart (right atrium) - DB pumped out of heart by right atrium towards the lungs - lungs oxygenate blood (diffusion, CO2 & O2) - blood returns to heart - OB pumped to the body by left ventricle - DB returns to heart |
DB - deoxygenated blood OB - oxygenated blood |
|
|
What happens when heart beats (pumps) ? |
- blood enters heart via RA - RA contracts forcing blood down to the ventricles - ventricles contract forcing blood out |
RA - right atrium LA - left atrium |
|
|
Structure of heart |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Hearts chambers |
- right atrium - left atrium - right ventricle - left ventricle (Opposite when viewing a diagram) |
|
|
|
Septum |
Thick wall that separates right and left ventricles |
|
|
|
Valves |
- all prevent back flow - atrioventricular valves stop back flow of blood from ventricles into atrium - semilunar valves stop back-flow of blood into the heart |
|
|
|
Thickness of the ventricles |
- Left ventricle wall is thicker than right as it has to force blood at higher pressure bc it has to travel longer distances (around whole body) - right ventricle only pumps to the lungs |
|
|
|
Ways to measure heart rate |
- stethoscope (hear valves) - pulse rate (flow of blood) - electrocardiogram (ECG) (detect electrical signals |
|
|
|
Effects of exercise |
- muscle cells need more energy from respiration - breathing rate increases to take in more O2 and rid of CO2 - heart pumps faster to circulate oxygenated blood - heart and breathing rate of fit ppl bc normal faster bc less lactic has been built up |
|
|
|
Testing recovery |
1) measure pulse & breathing rate (BR) 2) 4mins intense exercise 3) measure pulse & BR immediately 4) measure again after 2MINS 5) did they return to normal? |
|
|
|
Risk factors of CHD |
- smoking - lack of exercise - overweight - diet high in saturated fats - over 40 - genetic predisposition |
|
|
|
What happens in CHD |
- arteries narrow bc of plaque (fatty deposits) build up around the walls - limits blood flow leads to less O2 being supplied to heart muscles |
|
|
|
Surgeries to treat CHS |
- small tubes (stents) put into arteries to keep them open - Angioplasty when balloon is out into artery to break blockage - A by-pass divert blood flow away from blocked artery by taking blood vessel from somewhere else in body |
|
|
|
Drugs to treat CHS |
Aspirin - reduce inflammation and prevent blood clots forming |
|
|
|
Arterioles |
Connect arteries to capillaries |
|
|
|
Artery functions and adaptations |
Transport oxygenated blood away from heart to organs except pulmonary artery - thick muscle walls to cope with high pressure from heart - small luman for high pressure - elastic fibers letting them stretch and spring back |
|
|
|
Veins functions and adaptations |
Capillaries join veins after passing through body and they transport deoxygenated blood (except pulmonary vein) from organs to heart - thin walls as blood is at low pressure - bigger lumen as blood at low pressure - valves to prevent back flow |
|
|
|
Pulmonary vein (lungs) |
Transports oxygenated blood from lungs to heart |
|
|
|
Pulmonary artery (lungs) |
Transports deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs |
|
|
|
Capillaries functions and adaptations |
Arteries branch out into capillaries for efficient exchange of O2 and CO2 - food and oxygen moves out of capillaries and into cells - waste products (CO2) move out of cells into blood
|
|
|
|
Capillaries functions and adaptations |
Arteries branch out into capillaries for efficient exchange of O2 and CO2 - food and oxygen moves out of capillaries and into cells - waste products (CO2) move out of cells into blood - shunt vessels that connect arteries to veins allow controlled of blood flow (vasoconstriction & vasodilation)
|
|
|
|
Artery and vein comparison |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Acronym for arteries |
Arteries take blood Away from heart AA |
|
|
|
Renal vein aorta |
Filtered blood leaves the kidneys through the renal vein |
|
|
|
RBC functions and features |
- small size to pass through capillaries - no nucleus for more hemoglobin (carry more O2) - biconcave shape (larger surface area allows rapid diffusion) - hemoglobin (carries O2 for respiration) |
|
|
|
(WBC) Lymphocytes - functions and features |
- produce proteins, antibodies imp body’s immune response - change shape to squeeze through walls of blood vessels into tissue - have nucleus |
|
|
|
(WBC) Phagocytes - functions and features |
Engulf harmful microorganisms in process known as phagocytosis |
|
|
|
Aorta |
The heart pumps out oxygenated blood TK the body through the aorta |
|
|
|
Renal artery |
Blood arrived to be filtered through the renal artery |
|
|
|
Pulmonary artery |
Heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery |
|
|
|
Pulmonary vein |
Heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs through the pulmonary vein |
|
|
|
Vena cava |
Heart received oxygenated blood from the body through a vein called vena cava |
|
|
|
Lymphatic System function |
- lymph nodes are points that filter out harmful substances - high conc of WBC at lymph nodes (imp in immune response) |
|
|
|
Lymphatic system exchange |
- oxygen & glucose move out of blood into tissue fluid - urea & CO2 move out of body cells into blood via tissue fluid |
|
|
|
Lymphatic system structure |
- lymph vessels transport lymph fluid - lymp vessels collect lymph fluid leaked from body’s tissue and return to blood at lymph nodes |
|
|
|
Cells in blood |
- red blood cell (erythrocytes) - white blood cell (lymphocytes and phagocytes) - platelets |
|
|
|
Renal vein aorta |
Filtered blood leaves the kidneys through the renal vein |
|
|
|
RBC functions and features |
- small size to pass through capillaries - no nucleus for more hemoglobin (carry more O2) - biconcave shape (larger surface area allows rapid diffusion) - hemoglobin (carries O2 for respiration) |
|
|
|
(WBC) Lymphocytes - functions and features |
- produce proteins, antibodies imp body’s immune response - change shape to squeeze through walls of blood vessels into tissue - have nucleus |
|
|
|
(WBC) Phagocytes - functions and features |
Engulf harmful microorganisms in process known as phagocytosis |
|
|
|
Platelets |
- trigger blood clotting at sites of wounds - no nucleus (small cell fragments) |
|
|
|
Aorta |
The heart pumps out oxygenated blood to the body through the aorta |
|
|
|
Renal artery |
Blood arrived to be filtered through the renal artery |
|
|
|
Pulmonary artery |
Heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery |
|
|
|
Pulmonary vein |
Heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs through the pulmonary vein |
|
|
|
Vena cava |
Heart received oxygenated blood from the body through a vein called vena cava |
|
|
|
Lymphatic System function |
- lymph nodes are points that filter out harmful substances - high conc of WBC at lymph nodes (imp in immune response) |
|
|
|
Lymphatic system exchange |
- oxygen & glucose move out of blood into tissue fluid - urea & CO2 move out of body cells into blood via tissue fluid |
|
|
|
Lymphatic system structure |
- lymph vessels transport lymph fluid - lymp vessels collect lymph fluid leaked from body’s tissue and return to blood at lymph nodes |
|
|
|
Cells in blood |
- red blood cell (erythrocytes) - white blood cell (lymphocytes and phagocytes) - platelets |
|
|
|
Blood clotting |
- reduce blood loss & prevent pathogens going in body - platelets form clump around damaged part of blood vessel - a soluble substance in blood, fibrinogen is converted into insoluble substance fibrin - fibrin forms mesh around clump RBC also trapped forming clot |
|

