![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
81 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 4 general properties of matter?
|
Volume, weight, density, and mass.
|
|
|
What is the difference between mass and weight?
|
Mass: the amount of matter in an object, the measure of inertia of an object.
Weight: a measure of the force of attraction between objects due to gravity (depends on the size and distance of objects). |
|
|
What is density?
|
Mass per unit volume of an object.
(D=M/V) |
|
|
What do you need in a conclusion?
|
1. Restate the problem.
2. Restate your hypotheses. 3. Summarize the results. 4. Was the hypothesis right? YES: state a follow-up experiment. NO: state a new hypothesis with data). 5. Did you make a boo-boo? Tell HOW it effected your results. |
|
|
What is volume?
|
The amount of space that a substance or object occupies
For liquids: graduated cylinder For solids: either water displacement or calculations. |
|
|
What are the 4 states/phases of matter (plus a bonus)?
|
1. Solid
2. Liquid 3. Gas 4. Plasma 5. Bose-Einstein condensates |
|
|
How does the arrangement of atoms look in the 4 (plus a bonus) states/phases of matter?
|
Solid: molecules lightly packed.
Liquid: molecules are close together with some contact with each other. Gas: molecules very energetic, will separate from each other. Plasma: molecules high energy, will violently collide with each other. B-E Con: atoms "clump" when temp. nears 0 on Kelvin scale. |
|
|
How do molecules move in each of the 4 (plus a bonus) states/phases of matter?
|
Solid: doesn't move, just vibrates.
Liquid: moves easily, still but maintains contact. Gas: high energy and will separate. Plasma: high energy and will violently collide. Bose-Einstein Condensates: clump. |
|
|
Boyle's Law
|
The change in volume that occurs when the pressure of a gas is changed. Gas: in closed container, Temp: constant - NO change. (product of pressure and volume.)
P is the starting pressure (mL or L) P is the final pressure(mL or L) V is the starting volume (atm) V is the final volume (atm) To solve: 3 of the 4 values. |
|
|
Charle's Law
|
Describes the effect of temp. changes on the volume of a gas. (pressure remains constant.)
Temp increases, Volume increases. V = starting volume (mL or L) V = final volume (mL or L) T = starting temp. (convert to K) T = final temp. (convert to K) To solve: 3 of the 4 values, then convert to Celsius (-273). |
|
|
What are physical properties?
|
Characteristics of a substance that are observed w/out changing it into another substance with a different chemical composition. May alter its appearance, observed with senses.
|
|
|
What are physical changes?
|
Require energy to be lost or gained, change in form, shape, state.
|
|
|
What are chemical properties?
|
Characteristics of a substance that describes its ability to change into another substance, a substance must change into another to observe (chemical reaction).
|
|
|
What are chemical changes?
|
Changes in which substances either combine or react to form a new substance with new properties that are different from the starting material's.
|
|
|
What are the 5 ways that one can see that a chemical change has occurred?
|
1. a color change (very easy to see)
2. a gas is formed (bubbles or gas line forms) 3. a solid is forms (2 liquids are mixed), can look cloudy or the precipitate may fall downwards fast 4. a change in temp. is found w/out adding or removing heat (some reactions may absorb heat from outside (vessel=cold), some will release heat (vessel=warm) 5. water is formed (hard to detect) |
|
|
What are the 5 different types of chemical changes?
|
1. combination reactions
2. decomposition reactions (rotting) 3. combustion reaction (burning) 4. single replace meant reactions 5. double replacement reactions |
|
|
What is the equation for the combination reaction?
|
A+B=AB
|
|
|
What is the equation for the decomposition reaction (rotting)?
|
AB=A+B
|
|
|
What is the equation for the Combustion reaction (burning)?
|
C H +O =CO +H +heat
|
|
|
What is the equation for the single replacement reaction?
|
AB+C=AC+B
|
|
|
What is the equation for the double replacement reaction?
|
AB+CD=AC+BD
|
|
|
What are the properties of mixtures?
|
2 or more substances physically blended so they keep their own identities and properties. They can be separated by physical means.
|
|
|
How can mixtures be separated?
|
Filtration, flotation, mechanical, magnetism, and evaporation.
|
|
|
What is a heterogeneous mixture?
|
Doesn't look the same throughout, is the least mixed, substances are large enough to be seen.
|
|
|
What is a homogeneous mixture?
|
Appears the same throughout, best mixed mixture, each sample is identical.
|
|
|
What is a colloid?
|
Homogeneous mixture in which particles are mixed together but don't dissolve. (non-Newtonian fluids [Gook, Glop, Jello])
|
|
|
What is an alloy?
|
Solution of 2 or more metals, often mixed in liquid form then solidified, homogeneous mixture (used to harden other mixtures/metals).
|
|
|
What is a solution?
|
Mixture in which one substance is dissolved in another, not easily separated by physical means, particles evenly spread throughout mixture.
|
|
|
What is an example of a solution?
|
Salt + water = saltwater.
|
|
|
What is a solvent?
|
Substance that does the dissolving.
|
|
|
What is a solute?
|
Substance that is dissolved.
|
|
|
What is usually called the universal solvent?
|
Water.
|
|
|
What are subscripts?
|
They tell you how many atoms of a given element are in a substance.
|
|
|
What are coefficients?
|
They tell how many molecules of the substance you have.
|
|
|
What is an atom?
|
The smallest particle of an element that retains all of the chemical and physical properties of the element.
|
|
|
What are the subatomic particles that make up an atom?
|
Protons, neutrons, and electrons.
|
|
|
What is inside of the nucleus in an atom?
|
* Protons (charge: +1, mass: 1amu)
* Neutrons (charge: 0, mass: 1amu) * Takes up 99.98% of an atom's mass |
|
|
What is an atomic number?
|
Indicates the # of protons in each atom of a given element. Since atoms have a charge of 0, that's also the # of electrons.
|
|
|
What are isotopes?
|
Forms of an element that have the same # of protons but a different # of neutrons then the elemental form.
|
|
|
What is the mass number?
|
The number that tells you how many neutrons are in an atom. Subtract the atomic # from the mass # to get the number of neutrons.
|
|
|
How do you find the number of protons?
|
The atomic # tells you the number of protons in an atom.
|
|
|
How do you find the # of electrons in an atom?
|
The atomic # tells you the number of electrons, therefor the number of protons.
|
|
|
How do you find the # of neutrons in the atom?
|
Neutrons = mass # - atomic #
|
|
|
Where are protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom?
|
Protons and neutrons are in the nucleus, and electrons orbit the nucleus.
|
|
|
How many neutrons would there be if the atomic # was 11 and the mass # was 23?
|
12
|
|
|
How many electrons can the K shell hold?
|
2
|
|
|
How many electrons can the L shell hold?
|
8
|
|
|
How many electrons can the M shell hold?
|
18
|
|
|
What are the steps of the scientific method?
|
1. state the question
2. collect information 3. form a hypothesis (If, Then) 4. test the hypothesis 5. observe 6. record and study data 7. draw a conclusion |
|
|
What is a quantitative observation?
|
All about numbers, means a measurement has been made.
|
|
|
What is a qualitative observation?
|
Use senses to gather data. If vision is used, it is a direct observation. If other senses used, it is an indirect observation.
|
|
|
What are inferences?
|
An explanation of something based on observation and past experiences.
|
|
|
How do you write a good hypothesis?
|
Write an "If, then" statement.
|
|
|
How do you measure motion?
|
Distance divided by time.
d/t = motion |
|
|
What is motion?
|
The state in which on object's distance from another is changing, or a change in position in a certain amount of space.
|
|
|
What is the Archimedes's principal?
|
The buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid the object displaces.
|
|
|
What is a DNA strand made of?
|
Side-rails: alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate residues.
Nucleotide bases: A (adenine) T (thymine) C (cytosine) G (guanine). |
|
|
Who is Mendel?
|
Austrian monk known as the Father of Modern Genetics, trained as a mathmatician and scientist, worked in the gardens of a monastery, discovered that traits are passed from one generation to the next.
|
|
|
What are alleles?
|
Alternate form of a given gene for a given trait.
Ex: allele for height T (tall) t (short). |
|
|
What are traits?
|
Physical characteristics of an organism.
|
|
|
What is heredity?
|
Passing of the traits from parents to offspring.
|
|
|
What is a heterozygous allele?
|
When an organism has 2 different alleles [hybrid] (Tt).
|
|
|
What does hybrid mean?
|
Heterozygous.
|
|
|
What is a homozygous allele?
|
When an organism has 2 identical alleles (purebred) (TT).
|
|
|
What does purebred mean?
|
Homozygous.
|
|
|
What is a dominant allele?
|
Always expressed if present in an organism.
|
|
|
What is a recessive allele?
|
Is only present if there is not a dominant allele to cover it up.
|
|
|
What is a genotype?
|
A combination of alleles an organism has for a given trait.
|
|
|
What is a phenotype?
|
The physical appearance of an organism.
|
|
|
What is a Punnett Square?
|
Allows us to predict both the genotype and the phenotype of progeny from a given cross.
|
|
|
What would a Punnett Square look like for TT and Tt?
|
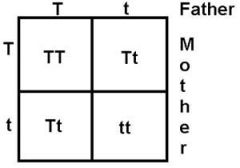
|
|
|
What are the four blood types?
|
A, B, AB, O.
|
|
|
What are the genotypes of the 4 blood types?
|
A: AA, AO
B: BB, BO AB: AB OO: OO |
|
|
What type of blood can donate any type of blood?
|
O (universal donor).
|
|
|
What type of blood can receive any type of blood?
|
AB (universal recipient).
|
|
|
What types of blood can donate or receive from others?
|
Type Donate Receive
A A, AB A, O B B, AB B, O AB AB A, B, AB, O O A, B, AB, O O |
|
|
What does sex-linked mean?
|
Any allele that is located on a sex chromosome.
|
|
|
What is Co-Dominance?
|
When you see both of the alleles since neither one is completely dominant over the other.
|
|
|
What is incomplete dominance?
|
The 2 alleles for a given trait blend together to make a third allele since neither allele is completely dominant over the other.
|
|
|
In blood types, is + or - dominant?
|
+ is dominant.
|
|
|
What pairs of DNA go together?
|
A and T
G and C |

