![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
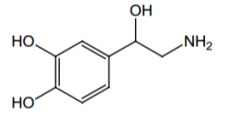
Name? |
norepinephrine |
|
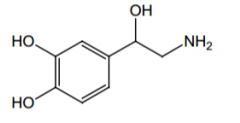
Agonist of what receptors? Direct or indirect acting? |
α and β1, direct |
|
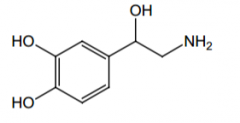
Orally effective? Why? |
No, because it is a substrate of both COMT and MAO. |
|
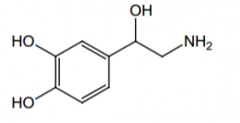
Indication? |
Hypotensive emergency |
|
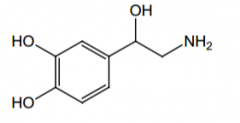
Stability concerns? |
It is air-oxidized to o-quinone. |
|
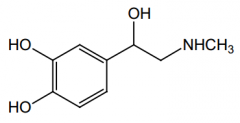
Name? |
epinephrine |
|
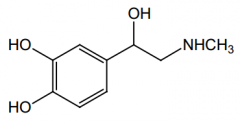
Stability concerns? |
Easily oxidized. |
|
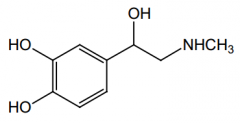
Agonist of what receptors? Direct or indirect acting? |
α, β1, and β2; direct |
|
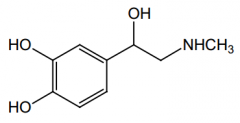
Orally effective? Why? |
No, it's a substrate for COMT and MAO |
|
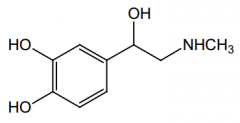
Indication? |
Nasal decongestant, local anesthetics, asthma, anaphylactic, open-angle glaucoma (as Epinephryl Borate) |
|
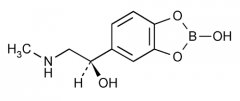
Name? |
Epinephryl Borate (epinephrine prodrug) |
|
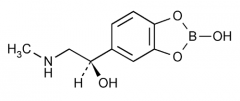
Indication? |
Open-angle glaucoma |
|
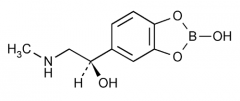
Why use this instead of epinephrine? |
It's less irritating to the eye. |
|
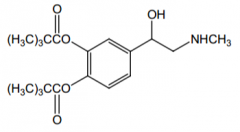
Name? |
Dipiveferin (epinephrine prodrug) |
|
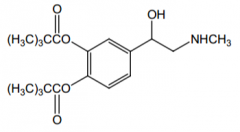
Indication? |
Glaucoma |
|
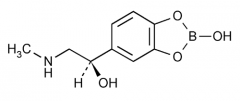
How is this prodrug converted to the active form? |
The lower pH of the lacrimal fluid releases epinephrine from its borate overlord. |
|
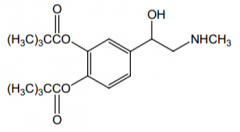
Why use this instead of epinephrine? |
It's lipophilic |
|
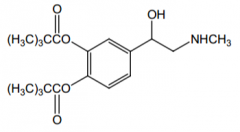
How is this prodrug converted to the active form? |
Esterases. |
|
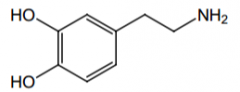
This drug is an agonist of what receptors? |
Renal D1 receptor, β1 (direct and indirect) |
|
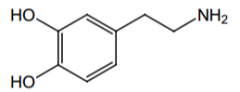
Direct or indirect agonist of β1? |
Both |
|
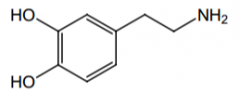
Indication? |
Treatment of shock |
|
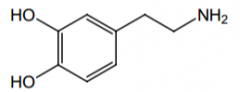
Orally effective? Why? |
No, it's a COMT and MAO substrate. |
|
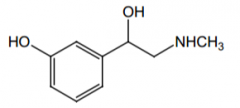
Agonist of what receptors? Direct or indirect acting? |
α1, direct |
|
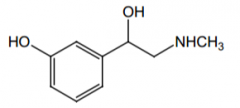
Indication? |
Hypotension shock (it's a vasoconstrictor), mydriasis and glaucoma |
|
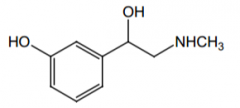
Orally effective? Why? |
Yes. It's not a COMT substrate. |
|
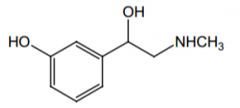
Does this drug cause CNS stimulation? |
No. |
|
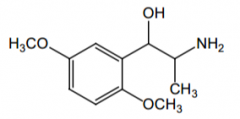
Agonist of what receptors? Direct or indirect acting? |
α1, direct |
|
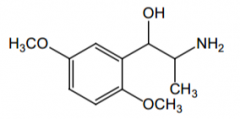
Indication? |
Maintain adequate arterial BP in surgery |
|
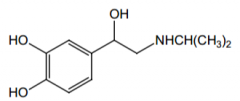
Name? |
Isoproterenol |
|
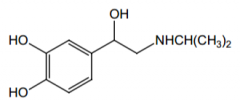
Agonist for what receptors? Direct or indirect acting? |
β1 and β2 (with equal potency), direct |
|
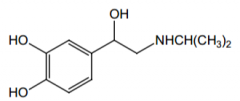
Indication? |
potent bronchodilator, cardiac stimulant |
|
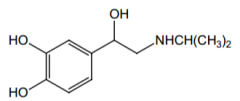
Route of administration? |
Inhalation, injection, sublingual |
|
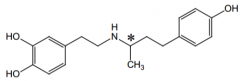
Name? |
Dobutamine |
|
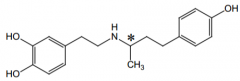
(+)-isomer is an agonist for what receptors? |
β1 and β2 |
|
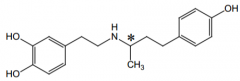
(-)-isomer is an agonist for what receptors? |
α1 |
|
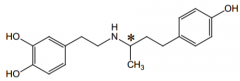
Do racemics have a stronger effect on the force of heartbeats or their rate? |
racemics exerts a much stronger inotropic (force) than chronotropic (rate) effect |
|
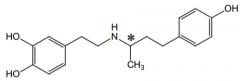
Indication? |
congestive heart failure or surgery |
|
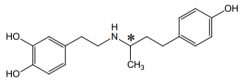
This is an analogue of which endogenous catecholamine? |
Dopamine. |
|
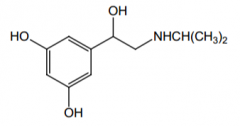
Name? |
Metaproterenol |
|
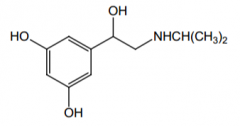
Agonist for what receptors? Direct or indirect? |
β2, direct |
|
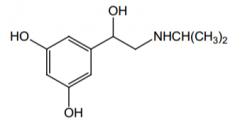
Indication? |
Bronchodilator for asthma |
|
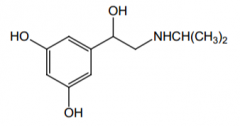
Orally effective? Why? |
Yes. Not a substrate for COMT, lowered affinity for MAO. |
|
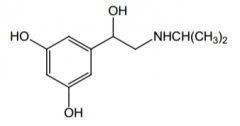
How does this drug compare to isoproterenol? |
Lower β2 affinity than isoproterenol, but longer duration |
|
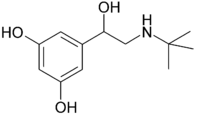
What am I? |
Terbutaline. A footnote under metaproterenol. I'm assuming they're pretty similar?? |
|
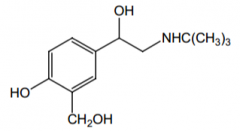
Name? |
Albuterol |
|
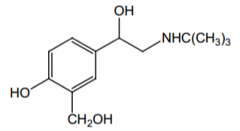
Agonist for what receptor? Direct or indirect acting? |
β2, direct |
|
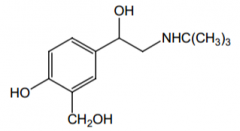
Indication? |
Bronchodilator for asthma |
|
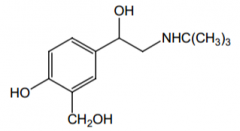
Orally effective? Why? |
Yes. Not a substrate for COMT or MAO. |
|
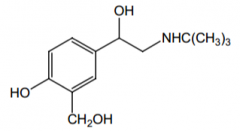
Duration compared to isoproterenol? |
much longer duration |
|
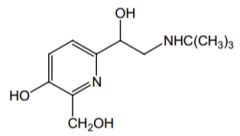
Tell me everything about this drug. |
Pirbuterol. Direct β2 selective agonist, bronchodilator used for asthma. Orally active (no COMT b/c no catechol, tertbutyl jutting off of amine means no MAO affinity) |
|
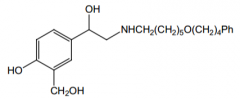
Tell me everything about this drug. |
Salmeterol. Direct β2 selective agonist, bronchodilator used for asthma. Orally active (no COMT b/c no catechol, hella big R group means no MAO affinity). Very long duration (12 hrs) |
|
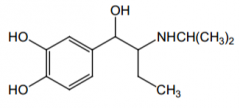
What does the ethyl group on this drug do? |
Makes it β2 selective. (this is isoetharine) |
|
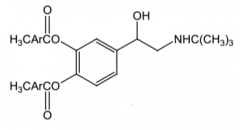
How is this prodrug converted to its active form? |
esterases. (this is bitelterol, an inhalation for bronchial asthma) |
|
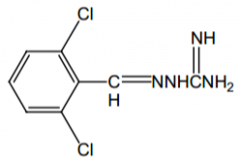
Name? |
Guanabenz |
|
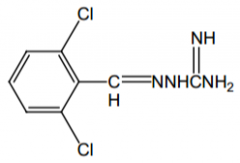
Agonist of what? Direct or indirect? |
α2, direct |
|
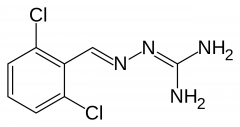
What is the name of the "open-ring" imidazolidine on this drug? |
Guanidine (This is guanabenz, with the guanidine drawn out) |
|
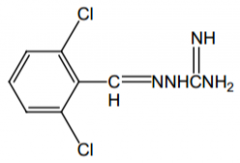
Indication? |
Antihypertensive |
|
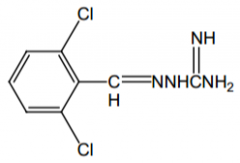
Active centrally? |
Yes |
|
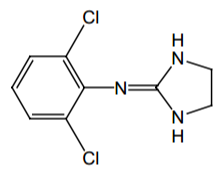
Name? |
Clonidine |
|
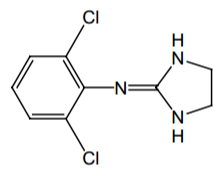
Agonist of what? Direct or indirect? |
α2, direct |

