![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
-Gases are the ___ dense phase of matter -Gases are fluids -Gases conform to the ___ of their containers -Gases are easily ___ |
-Gases are the least dense phase of matter -Gases are fluids -Gases conform to the shape of their containers -Gases are easily compressible |
|
|
equivalencies to 1 atm |
= 760 mmHg = 760 torr = 101.325kPa |
|
|
Temperature at STP Temperature at standard state |
STP = 273K or 0 C standard state 298K or 25 C |
|
|
1 mol of gas at STP will occuply: |
22.4L |
|
|
Equations for ideal gases assume negligible ___ and ___ of gas molecules. |
Equations for ideal gases assume negligible mass and volume of gas molecules. |
|
|
Ideal gas law |
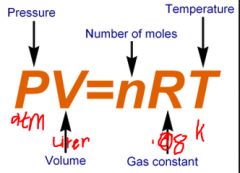
|
|
|
density of a gas equation |
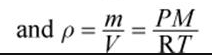
|
|
|
Dalton's law of partial pressure |
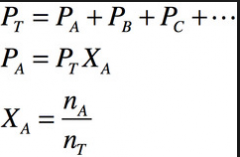
states that individual gas components of a mixure of gases will exert individual pressures in proportion to their mole fractions. The total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the component gases. |
|
|
Partial pressure |

mole fraction is (mol of gas)/(total mol of gases) |
|
|
Henry's law |
the amount of gas dissolved in solution is directly proportional to the partial pressure of that gas at the surface of a solution. |
|
|
Assumptions of Kinetic Molecular Theory -Gas particles have ___ volume -Gas particles don't have intermolecular ___ or ___ -Collisions between gas particles are ___ -Ave KE of gas is directly proportional to ___ -random motion |
-Gas particles have negligible volume -Gas particles don't have intermolecular attractions or repulsions -Collisions between gas particles are elastic -Ave KE of gas is directly proportional to temperature. -random motion |
|
|
Graham's Law |
Gases with lower molar masses will diffuse or effuse faster than gases with higher molar masses at the same temperature. |
|
|
Diffusion vs Effusion |
-Diffusion: spreading out of particles from high to low concentration. -Effusion: movement of gas from one compartment to another through a small opening under pressure. -Both are slower for larger molecules. |
|
|
Real gases deviate from ideal behavior under ___ pressure (___ volume) and ___ temperature conditions. |
Real gases deviate from ideal behavior under high pressure (low volume) and low temperature conditions. |
|
|
At moderately high pressures, low volumes, or low temperatures, real gases will occupy ___ volume than predicted by the ideal gas law because the particles have ___ attractions. |
At moderately high pressures, low volumes, or low temperatures, real gases will occupy less volume than predicted by the ideal gas law because the particles have intermolecular attractions. |
|
|
Gases are ___ fluids with rapid molecular motion, ___ intermolecular distances, and ___ intermolecular forces. |
Gases are compressible fluids with rapid molecular motion, large intermolecular distances, and weak intermolecular forces. |
|
|
If all gases have the same temperature, then the ___ molecules travel the fastest |
lightest |
|
|
Gases can deviate from ideal behavior at high pressure and low temperature because... |
molecules are closer together and can participate in intermolecular forces. |

