![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Otalgia
|
ear pain
|
|
|
Acute Otitis Media
|
any inflammation of the middle ear
|
|
|
Otitis media with effusion
|
collection of fluid in the middle ear
also known as serous otitis media Secretory otitis nonsuppurative otitis |
|
|
parotitis
|
inflammation of the parotid gland
|
|
|
swimmer's ear
|
otitis externa
|
|
|
malignant otitis externa
|
cellulitis involving the ear and surrounding tissue
|
|
|
pinna
|
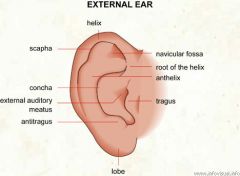
auricle
top part of the ear that projects like a wing |
|
|
lower part of the ear
|
lobule
|
|
|
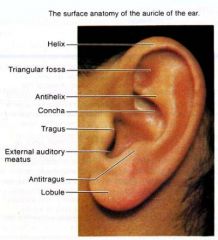
tragus
|
cartilaginous projection in front of the exterior meatus of the ear
|
|
|
battles sign
|
Hemorrhage over the mastoid bone
may occur with a basal skull fracture |
|
|
Cholesteatoma
|
cyst like mass behind the eardrum
|
|
|
myringitis
|
red inflamed eardrum without effusion
|
|
|
Amblyopia
|
Amblyopia, commonly known as lazy eye, is the eye condition noted by reduced vision not correctable by glasses or contact lensesIf not detected and treated early in life, amblyopia can cause loss of vision and depth perception.
|
|
|
Causes of amblyopia?
|
Anything that interferes with clear vision in either eye during the critical period (birth to 6 years of age) can cause amblyopia. The most common causes of amblyopia are constant strabismus (constant turn of one eye), anisometropia (different vision/prescriptions in each eye), and/or blockage of an eye due to cataract, trauma, lid droop, etc
|
|
|
Strabismus
|
cross-eyed or wall-eyed, is a vision condition in which a person can not align both eyes simultaneously under normal conditions. One or both of the eyes may turn in, out, up or down. An eye turn may be constant/ intermittent (turning only some of the time, such as, under stressful conditions or when ill). Children do not outgrow strabismus!
|
|
|
otorrhea
|
inflammation of ear with purulent discharge
|
|
|
oulorrhagia
|
hemorrhage from the gums
|
|
|
otodynia
|
otalgia
pain in the ear |
|
|
tenesmus
|
urge to defecate but without needing to pass stool
|
|
|
colic
|
tenision pain caused by forceful peristaltic contractions
can be caused by a irritative substance, infection or a body's attempt to pass contents through an obstruction |
|
|
obstipation
|
absence of stools
|
|
|
Dysmenorrhea
|
painful periods
|
|
|
Menorrhagia
|
is an abnormally heavy and prolonged menstrual period (lasting longer then 7 days) at regular intervals. Causes may be due to abnormal blood clotting, disruption of normal hormonal regulation of periods or disorders of the endometrial lining of the uterus. Depending upon the cause, it may be associated with abnormally painful periods (dysmenorrhea).
|
|
|
Menometrorrhagia
|
Menometrorrhagia is a condition in which prolonged or excessive uterine bleeding during and between menstrual periods
|
|
|
Stress incontinence
|
inct associated with activities that increase the intraabdominal pressure such as coughing, sneezing, running or laughing
small amt of urine lost Post void is normal |
|
|
Urge incontinence
|
uncontrolled urge to void, secondary to detrusor muscle irritability or hyperactivity or a hypersensitive bladder
volume lost is large Post void is normal |
|
|
Overflow inct
|
presence of an obstruction or interruption in the nervous system
results from overdistension of the bladder |
|
|
dyssynergia
|
loss of synergistic urinary sphincter relaxation that normally occurs with bladder detrusor muscle contraction
happens with overflow inct PVR.100 ml |
|
|
dysuria
|
painful urination
|
|
|
pyuria
|
> 5 WBCs /HPF
|
|
|
polyuria
|
volume greater than 3 L/day
depends on the fluid intake and pt's state of hydration |
|
|
balanits
|
inflammation of the glans penis
|
|
|
balanoposthitis
|
Balanitis involving the foreskin and prepuce is termed balanoposthitis.
|
|
|
phimosis
|
inability to retract foreskin
|
|
|
paraphimosis
|
inability to replace retracted foreskin
|
|
|
Onycholysis
|
Onycholysis: Loosening of the nail from the nail bed, usually starting at the border of the nail. The nail tends to turn whitish or yellowish, reflecting the presence of air under it.
|
|
|
Psoriasis
|
A reddish, scaly rash often located over the surfaces of the elbows, knees, scalp, and around or in the ears, navel, genitals or buttocks. Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that is mediated by T lymphocytes
|
|
|
Beau's lines or ridges in the nail plate.
|
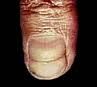
Beau's lines are deep grooved lines that run from side to side on the fingernail. They may look like indentations or ridges in the nail plate.
|
|
|
slinkys
|
KUB is helpful to demonstrate loops of distended bowel (“slinkys”).
|
|
|
Hypokinesia
|
Hypokinesia refers to decreased bodily movement
|
|
|
kinesia (ki·nēˑ·zh)
|
kinesia (ki·nēˑ·zh),
n condition resulting from regular or irregular motions while moving in any combination of directions, such as riding in a car, boat, or an airplane. General discomfort or headaches are characteristic of mild cases, whereas severe cases are marked by nausea and dizzi-ness |
|
|
constitpation
|
What is pt's BASELINE? diverse interpretation; usually involves less frequent passage of stool than normal, or passage of hard stool.
|
|
|
Hemorrhoidal bleed
|
= BRBPR
|
|
|
Papilledema
|
Papilledema findings may lag 24-48 hours behind alterations in ICP. A change in ICP will be reflected in the retinal veins within seconds to minutes, by decline. The disc appears elevated, erythematous, with blurred margins, vessels engorged. Flame hemorrhages appear close to disc on retina, and vessels appear engorged and tortuous.
In diabetic retinopathy, note hard exudates, neovascularization and microaneurisms. |
|
|
Exudates
|
Exudates
Hard exudates are lipoprotein leakage, sometimes appear shiny with sharp edges usually more yellow in color than soft exudates. Seen in HTN, DM, and renal disease. |
|
|
A detached retina appears as though ?
|
A detached retina = an emergency. It appears as though the retina is folded and bunched up on itself.
|
|
|
Torticollis
|
is a twisting of the neck secondary to spasm of muscular disease, often presenting on awakening and remitting spontaneously within several days.
|
|
|
Total chol =?
|
Total chol = LDL + HDL + VLDL
|
|
|
Lightheadedness
|
Lightheadedness is a feeling that you are about to faint or "pass out." Although you may feel dizzy, you do not feel as though you or your surroundings are moving. Lightheadedness often goes away or improves when you lie down.
|
|
|
Vertigo
|
Vertigo is a feeling that you or your surroundings are moving when there is no actual movement. You may feel as though you are spinning, whirling, falling, or tilting. When you have severe vertigo, you may feel very nauseated or vomit. You may have trouble walking or standing, and you may lose your balance and fall.
|
|
|
cardiomegaly
|
as cardiomegaly (heart contour exceeds
½ chest configuration) |
|
|
Kerley “B” lines
|
increased interstitial markings, upper zone flow redistribution, perihilar haziness.
|
|
|
ciliary flush
|
Ciliary flush is usually present in eyes with corneal inflammation, iridocyclitis or acute glaucoma, though not simple conjunctivitis. A ciliary flush is a ring of red or violet around the cornea of the eye.
|
|
|
esotropia?
|
(most common) when eyes are crossed
|
|
|
exotropia?
|
when eyes diverge
|
|
|
“hypertropia?
|
when eyes are up and “hypotropia” when eyes downturn
|
|
|
Glaucoma?
|
vision threatening disease secondary to increased intraocular pressure (IOP) from obstruction of aqueous humor flow in anterior chamber of the eye.
|
|
|
Acute angle-closure glaucoma (AACG) refers to?
|
sudden obstruction of flow of humor. Increased IOP may result in optic nerve atrophy, decreased peripheral vision and possible eventual blindness. Pts at risk who have anatomically narrow anterior chamber angle
|
|
|
Chronic open-angle glaucoma(COAG) results due to?
|
partial obstruction to the aqueous outflow at the trabecular meshwork
|
|
|
nystagmus
|
Nystagmus means involuntary eye movement. It may refer to either of these:
Physiologic nystagmus Pathologic nystagmus |
|
|
Keratitis
|
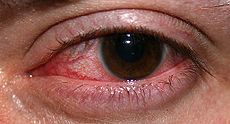
Keratitis = corneal inflammation or infection that may threaten vision; most often induced by contact lens use (sleeping with lens in eyes); on PE note ciliary injection, watery or purulent d/c, light sensitivity; possible cloudy cornea, decreased visual acuity, decreased papillary responses, extraocular herpetic rash
|
|
|
Dysequilibrium
|
Dysequilibrium is a sense of unsteadiness or loss of balance that involves the legs or trunk. Dysequilibrium may occur while a person is standing or walking.
|
|
|
People with vertigo may also have ?
|
People with vertigo may also have nausea, sometimes with vomiting, and abnormal jerky eye movements (nystagmus).
|
|
|
Light-headedness
|
Light-headedness is a feeling that fainting may occur in the next few moments. Light-headedness usually occurs when a person gets up quickly after sitting or lying down for a while.
|
|
|
Benign positional vertigo
|
Benign positional vertigo: Vertigo occurs when the head is moved—for example, when a person lies down, gets up, turns over in bed, or looks up. Benign positional vertigo develops when particles that are normally distributed evenly in the fluid-filled canals of the inner ear clump together.
|
|
|
Meniere's disease
|
Meniere's disease: Vertigo is usually accompanied by hearing loss and a low roaring or ringing in the ears (tinnitus). Meniere's disease is caused by excess fluid in the inner ear.
|
|
|
Hallpike maneuver
|
Hallpike maneuver. For this maneuver, the person sits on a table. The doctor rapidly lays the person down with the person's head hanging over the edge of the table. In the same movement, the doctor turns the person's head to the right or left. If the dizziness is caused by an inner ear disorder, the Hallpike maneuver may quickly produce nystagmus and dizziness
|
|
|
Tests for dizziness
|
The doctor uses a stethoscope to check the rate, rhythm, and sound of the heartbeat. Blood pressure is measured after the person has been lying down for about 5 minutes and immediately after the person stands up. Sometimes it is measured again after 3 minutes. These measurements help determine whether the cause of the dizziness is orthostatic hypotension.
|
|
|
Romberg test
|
1) Done to test clients equilibrium
2) Have client stand with arms at side and feet together 3) Have client perform initially with eyes open and then with eyes closed 4) Stand close to client to prevent falls Client should maintain position for 20 seconds with only minimal swaying |
|
|
What tests can be done to find out the origin of dizziness?
|
The doctor checks some aspects of brain and nerve function, particularly the senses of position and balance. For example, a person may be asked to stand still with the eyes open, then with the eyes closed. If the person sways more than expected, the dizziness may be caused by an inner ear disorder, a brain disorder, or a problem with the body's ability to send information from the large joints to the brain.
|
|
|
What blood tests can be done to find out the origin of dizziness?
|
Blood tests may be done. Typically, the number of red blood cells and levels of sugar, vitamin B12, and thyroid hormones are measured.
|

