![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three name resolution systems?
|
DNS, Link Local Multicast Name Resolution (LLMNR), and NetBIOS.
|
|
|
What two name resolution services can resolve names without the use of DNS?
|
LLMNR and NetBIOS
|
|
|
What must be enabled in order for the Network Map and network browsing to work?
|
Network discovery must be enabled
|
|
|
What is the LLMNR process in resolving a name?
|
First it checks the LLMNR cache.
If no entry is found, the client who is requesting the look up send out two LLMNR quesry packets to the local network. The first one goes to the IPv6 address of FF02:0:0:0:0:0:1:3. The second to the IPv4 multicast address of 224.0.0.252. If the client is located on the same subnet, the client will hear the query and respond over IPv6 or IPv4 or both depending which protocols are enabled. |
|
|
What are two disadvantages of LLMNR?
|
It does not resolve names of computer running Server 03, XP, or any version of Windows earlier than Vista.
The second is that is can not be used to resolve names of computer beyond the local subnet. |
|
|
How do you disable LLMNR for many computers at a time by using Group Policy?
|
In a GPO, navigate to Computer Config>Policies>Administrative Templates>Network>DNS Client and then search for the policy "Turn Off Multicast Name Resolution".
|
|
|
In Windows Vista, 7, Server 08, and Server 08R2, what is used to resolve a computer name when DNS is not configured and LLMNR is either disabled or unable to resolve a computer name?
|
A NetBIOS broadcast query is used.
|
|
|
What are the three name resolution methods included in NetBIOS?
|
NetBIOS broadcasts.
WINS LMHOSTS file which is located in %systemroot%\System32\Drivers\Etc |
|
|
Where do you enable or disable NetBIOS?
|
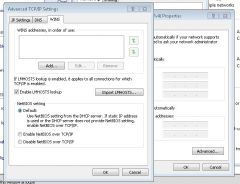
To change NetBIOS settings, open the properties of a local area connection. Then open up the properties of Internet Protocol Version 4 and click the Advanced button to open up the Advanced TCP/IP Settings dialog box.
|
|
|
What are the 4 node types that NetBIOS uses?
|
Broadcast (b-node)
This node type uses only broadcast NetBIOS name queries for name registration and resolution. Point-to-point (p-node) This node uses point to point communications with a WINS server to resolve names. Does not use broadcasts. Mixed (m-node) This node first uses broadcasts (b-node) and then uses WINS queries (p-node) if broadcasts are not successful. Hybrid (h-node) Uses WINS queries first (p-node) and then uses broadcasts (b-node) as a fallback mechanism if no WINS server is configured. If a WINS server is unavailable and the queried for name is not found, to reduce broadcasts, these computers will use the LMHOSTS file to search for name to IP mappings before using b-node. By default, Windows clients are configured as hybrid nodes. |
|
|
How do you determine the current NetBIOS node type?
|
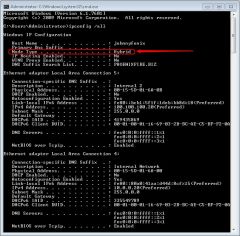
By viewing ipconfig /all in a prompt.
|
|
|
What are the three types of top-level domains?
|
Organizational domains.
Geographical domains. Reverse domains. |
|
|
When is a server authoritative for a domain?
|
When the server relies on locally hosted database data (as opposed to cached info from other servers) to answer queries about hosts in a given domain.
|
|
|
What is a DNS zone?
|
A contiguous portion of a namespace for which a server is authoritative. A server can be authoritative for one of more zones and a zone can contain one or more contiguous domains.
|
|
|
What is a DNS resolver?
|
A DNS resolver is a service that uses the DNS protocol to query for more info from other DNS servers.
The function of the DNS resolver is performed by the DNS Client service. |
|
|
What are resource records?
|
Resource records are DNS database entries that are used to answer DNS client queries.
|
|
|
If a computer needs to resolve a DNS name, what is the first method it attempts to use?
|
A computer first checks the resolver cache to answer a query.
|
|
|
When a DNS server receives a query, how does it first attempt to revolve the name?
If a DNS sever cannot resolve a query by using the first method, which method will it use next? |
1. A DNS server first attempts to resolve a query by using resource records stored in a locally configured zone.
2. If DNS can't resolve a query by using zone data, it attempts to answer the query by using cached information. |
|
|
TRUE OR FALSE?
In the default configuration for DNS Clients in Windows, DNS queries are recursive, which means that the client requests the DNS server to perform recursion if necessary. |
TRUE
|
|
|
TRUE or FALSE?
By default, Windows based DNS servers are configured to accept recursive queries and perform recursion to resolve names on behalf of clients. |
TRUE
|
|
|
What is the name and location of the root hints file?
|
cache.dns
windows\system32\dns |
|
|
When would a DNS server contact a root server?
If a DNS server contacts a root server to resolve the name www.contoso.com and the root server can't answer the query, how does the original server know which server to query next? |
1. A DNS server contacts a root server when it cannot answer a query with its own cached or authoritative data.
2. The root server responds to the DNS server with a referral for the address of the DNS server authoritative for the .com domain. The DNS server then contacts this server for which is has received a referral. |

