![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are reasons Organizations implement multi-domain forests?
|
#1.HIstorical domain structure- keeping an older domain structure in the forest, after adding a new 2012 DC to a separate and new domain.
#2.Organizational/Political Reasons- two seperate organizations or companies may share an administrative core, but require their own domains for separation of management and resources #3.Security Reasons- domains allows you to create security boundaries, and give one admin permission to manage computers/users in one domain, but not another. |
|
|
is a set of names that share a common root domain name
|
Domain Tree
Ex: spade.com dallas.spade.com west.dallas.spade.com A forest can have multiple domain trees, and each domain created in the forest is a child of the root domain. |
|
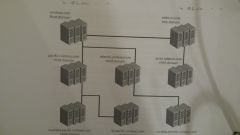
What is Intra-Forest authentication?
|
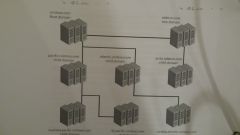
all domains within the same forest automatically trust one another, which means you can sign one user in the west.dallas.spade.com domain to a resource in the east.dallas.spade.com domain.
|
|
|
A single forest implementation isn't appropriate for separate organizations, and it makes its possible for a single Admin to have complete control which most organizations aren't comfortable with. When and if we need to allow users from a partner organization to have access to resources, what could we configure?
|
Trust Relationships or Fedaration
|
|
|
Domain Function Level determines the AD functionality and feature that are available. What can domain functional levels, can we use Server 2012 in ?
|
2k3
2008 2008 r2 2012 |
|
|
What is the limiting factor on a domain functional level, and what could be there reason for a Administrator not being able to raise the functional level
|
The Domain Controllers used to host Active Directory.
|
|
|
How can we alter the the DFL
|
#1. ADUC
#2.AD Domains and Trusts #3.Set-ADDomainMode *Must be a member of Domain or Enterprise Admins |
|
|
A forest can host domains running at different domain levels. What is the FFL dependent on?
|
The minimum domain functional level of any domain in your forest
|
|
|
What two strategies can we use to upgrade existing domains and forests?
|
#1. Upgrade the OS on each DC to Server 2012, DCs have to be x64 based and running Server 2008
#2. Introduce the Server 2012 DCs into an existing domain and then decomission existing DCs running earlier versions of Server. This is less complex that performing a direct upgrade |
|
|
When do you run adprep /and when is it not required?
|
#1.It isn't required to prepare AD for the introduction of Server 2012 DCs, because if you promote the first 2012 DC using the Schema Admin and Entreprise Admins group, it will automatically upgrade the schema
#2. You need to run adprep separately if your are performing an in-place upgrade of a 2008 x64 DC and if upgraded, it will be the very first 2012 DC in the domain. |
|
|
assist us in migrating from an existing AD environment rather than upgrading an existing environement.
|
ADMT
*3.2 isn't supported on 2012 |
|
|
For users logging on to domain computers, what is the easiest way for them to logon rather than having to use the "domain\user" method?
|
user@domain.com UPN suffix
*The UPN suffix is configured on the account tab of the user's properties sheet (ADUC/ADAC) |
|
|
is a database that tracks security principles, and these security principles are user accounts, group accounts, computer accounts.
|
directory service
|
|
|
What is the difference between “Physical and Logical”
|
#1. -*Physical: refers to hardware, things that we can touch
*DCS *Replication *Storage *Authentication *Sites/Subnets #2.these aspects can be changed relatively easily; and deals with concepts that can’t directly be touched -*AD Forest -*Domains -*Accounts (User/Computer) -*OU |
|
|
This means we have a nexus (connection point) over which, user logons can occur, and resource sharing occur very easily because we have ultimately, all (both) of the domains contained within a single ultimate boundary, called the forest
|
Two-Way Transitive Trusts
|
|
|
this means that a organization, will take their first domain (forest root) and not have any activity in it whatsoever, and we will use it to build out other domain trees or child domains, and populate these with users and computers and use these day-to-day and make use of the empty root domain, only for “Administration”
|
Empty Root
|
|
|
in our Forest-Root domain; We have two security group
|
#1. “Enterprise Administrators”
#2. “Schema Administrators” |
|
|
Purpose of the Empty Root Domain?
|
To allow Administration(EA & SA) to take special security precautions in the domain and use it only for forest wide tasks
|
|
|
What are the 4 Domain Boundaries?
|
#1.Administration ( Domain Admins)
#2.GPO Scopes & Auditing #3.Password and Account Policy #4.Replication for Domain DNS Zone Scope |
|
|
What are the 5 Forest Boundaries?
|
#1.Security Perimeter (AD FS)
#.2Replication for the Schema Partition -Replication for the Configuration Partition -Replication for the Global Catalog -Replication for Forest DNS Zones |
|
|
Why Would we want to deploy a multi-domains in a forests?
|
#1.If the physical topology (sites) have slow
WAN bandwidth #2.Mergers, Acquisition that involve multiple Namespaces. #3.Distributed Administration Politics #4.Empty Root to Protect #5. Separate User Accounts/ Shared Resources by Domain |
|
|
Why we would want to deploy multiple forest in an organization?
|
#1.Security Isolation
#2.Merger/Acquistion #3.Compliance Across Countries/Industries |

