![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
T/F: e-cigarettes are regulated by the FDA |
True
The FDA only has legal regulation over nicotine containing products that make therapeutic claims. |
|
|
T/F The nicotine in tobacco products contributes to the ill effects of smoking. |
False
The ill effects are due to other agents in the cigarettes, but harmful agents have been found in many unregulated nicotine products (i.e. e-cigarettes)
But remember: "All forms of tobacco are harmful" |
|
|
What are the strongest factors associated with smoking initiation in children and adolescents? |
Parents
Rebellion Peer pressure Teen-targeted candy flavored tobacco products |
|
|
What is a kretek? |
clove cigarettes
- have more tar and nicotine than std cigarettes |
|
|
Explain how the absorption of nicotine is pH dependent. |
Nicotine is a weak base (pH = 8)
- in acidic media, it is ionized and poorly absorbed across membranes - in alkaline media, it is unionized and readily crosses membranes - at physiologic pH, it is about 30% is unionized and readily crosses membranes
acidic beverages can lower the absorption of tobacco buccally |
|
|
Describe the prevalence of tobacco use across the United States.
By states...
|
Approximately 18% of US adults use tobacco - about 20% of those are ready to quit
lowest: Utah (10%), CA (12%)
WI: 20.4%
highest: Kentucky (28%) |
|
|
Describe health benefits associated with tobacco cessation. |
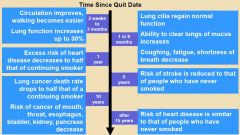
|
|
|
List five forms of tobacco and their potential harm. |
1. smoking tobacco 2. spit tobacco - peridontal effects, oral leukoplakia, cancer 3. waterpipe 4. dissolvable 5. electronic - propylene glycol → resp. irritation, asthma - glycerin → lipoid pneumonia
|
|
|
State the number of cigarettes in a pack and the average machine-yield of nicotine in U.S. cigarettes. |
content: 10 mg/cig intake: ~1 mg/cig (this is rising i.e. ultras)
Nicotine in "light" cigarettes may be higher
cigars: 10-400 mg 1 hr of hookah: 200 mg (like a pack of cigs) |
|
|
Describe the pharmacokinetic profile of nicotine (absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion). |
absorption: readily absorbed across membranes (pH dependent) and through skin; well absorbed in s.i. but 75% metabolized before reaching systemic; "distilled" into tar droplets for lung absoption
distribution: reaches brain within 10-20 seconds
metabolism: t1/2 = 2 hr 70-80% into cotinine (t1/2 = 16 hr)
excretion: 10-20% excreted unchanged |
|
|
Describe the pharmacodynamic effects of nicotine on the central nervous and cardiovascular systems. |
Nicotine binds to receptors in the brain and other sites in the body and has predominantly stimulatory effects.
CNS: pleasure, arousal, improved task performance, anxiety relief
CV: ↑ HR, ↑ cardiac output, ↑ BP, vasoconstriction
other: appetite suppression, ↑ metabolic rate, skeletal muscle relaxation |
|
|
Define nicotine addiction. |
compulsive nicotine use, without medical purpose in the face of negative consequences |
|
|
List symptoms of nicotine withdrawal and when they are likely to occur. |
- irritability / frustration / anger - anxiety - difficulty concentrating - restlessness / impatience - depressed mood / depression - insomnia - impaired performance - increased appetite / weight gain - cravings (months to years after quitting)
Most symptoms manifest in first 1-2 days, peak in the first week, and subside within 2-4 weeks |
|
|
Describe the most common drug interactions between medications and tobacco smoke.
Note: it is not an interaction with nicotine, it is an interaction with the smoke |
PAH's (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons) interact with CYP1A2, increasing drug metabolism, reducing pharmacologic response of other drugs, esp. caffeine
- bendamustine - olanzapine - caffeine - ropinirole - clozapine - tacrine - eriotinib - theophylline - fluvoxamine - irinotecan
Clopidogrel (Plavix) may have increased effect due to CYP1A2 induction |
|
|
Identify the two risk factors that must be present to increase the likelihood of stroke, MI, and thromboembolism in smokers who use combined oral contraceptives (or hormone patch). |
1. age 35 or older 2. smoke at least 15 or more cig/day
puts them at 30 times the risk of CV events vs. a non-smoker |
|
|
List nonpharmacologic aids for cessation and describe their place in treatment. |
- lower nicotine cigs, special filters (less effective) - QuitKey (assisted tapering) - pregnant, teens, chew - formal cessation programs - Quit Lines
not proven: acupuncture, hypnotherapy, lasers, massage (massage may help ease withdrawal symptoms or serve as a reward)
|
|
|
Identify patient populations for whom nicotine replacement therapies are not appropriate. |
adolescents pregnant/nursing chew/spit tobacco light smokers (<10/day)
precaution: - pt with CV disease (MI w/in past 2 weeks) |
|
|
What are the three classes of FDA-approved drugs for smoking cessation? |
1. NRT - nicotine replacement therapy 2. psychotropics - buproprion 3. partial nicotinic receptor agonist - varenicline (some success using varenicline for smokeless) |
|
|
Counsel a tobacco user on the proper use of Nicotine polacrilex gum, lozenge, patch, nasal spray, inhaler, buproprion varenicline (including dosing, instructions on use, potential side effects, and precautions) |
see hand out |
|
|
Describe the prevalence of tobacco use across the United States.
By ethnicity...
|
Multiple Race: 26% Amer. Indian: 22% White: 20% Black: 18% Hispanic: 12.5% Asian: 10.7% |
|
|
Describe the prevalence of tobacco use across the United States.
By education... |
GED: 41.9% less than high school diploma: 24.7% High School: 23% Some college: 21% Assoc. degree: 18% Undergrad degree: 9% Graduate degree: 6% |
|
|
What is the Fagerstrom test?
- primary question? |
a test for assessing nicotine dependence
How soon after waking up do you smoke your first cigarette? |
|
|
What is the difference between a Marlboro Red and a Light? |
light has an extra row of ventilation holes
- smoking method changes to cover these holes |
|
|
What serious CV risks are there for smokers who use oral contraceptives (3)?
What is the increased risk to smoking women over non-smokers? |
1. stroke 2. myocardial infarction 3. thromboembolism
- not a drug-drug interaction, it is a pharmacodynamic effect
- most serious for women 35 and older who smoke 15 or more cigarettes/ day -------30 times the risk of a non-smoker------- |
|
|
Which NRT has the fastest onset of action?
What percentage of patients become addicted to it? |
nasal spray
~ 10% become addicted to it |

