![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Streptococcus genus organism properties
|
gram +
cocci chains catalase - Various alpha, beta, gamma hemolytic |
|
|
Pertinent Species streptococcus
|
GAS (pyrogenes)
GBS (agalactlae) Pneumoniae Viridians No longer enterrococci |
|
|
How can streptococcus be differentiated?
|
Hemolysis when grown on blood agar
beta - pyrogenes or agalctiae alpha - pneumoniae or viridians Pneumoniae - have capsule with NO lancefield group ag Rapid strep test - looks for Anti A antibodies. If negative confirm the negative with culture test. |
|
|
Enterrococcus
|
This is simiilar to the streptococcus (gram + & Catalase - )
Group D ag Gamma hemolysis |
|
|
Why is a culture required in pharyngitis?
|
To much overlap from viral etiology and risk of post streptococcal sequelae.
|
|
|
GAS organism properties
|
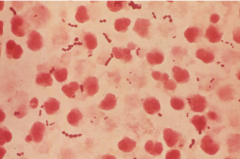
chains, cocci, gram positive
|
|
|
Describe Beta hemolysis, alpha hemolsys, gamma hemolysis.
|

Performed on 5% SBC
Beta - Complete hemolysis of RBC, result in "clear" yellowish zone. Alpha - partial hemolysis, greenish discoloration Gamma - lack of hemolysis |
|
|
Describe catalase positive and negative. What is the reaction? What is streptococci? what are the 3 staph species?
|

H2O2 --(catalse)--> H2O + O2
Strep - catalase (-) Staph (3 species) - catalase (+) |
|
|
Describe Coagulase slide test. When is coagulase test used? Which one is +, which one are - ?
|

Positive coagulase test shows clumping of suspension with in 10s.
Coagulase test is used to determine staph aureas from both the Staph epidermis & staph saprophyticus + coagulase = s. aureas - coagulase = s. epidermis or s. saprophyticus |
|
|
Describe coagulase tube test? When is tube used compared to slide? What is the reaction occuring?
|

When slide coagulase test has autoagglutination prior to adding plasma or on a negative slide test, it must be confirmed by the tube test. Reason is that s. aureas produces free coagulase that can dissociate away (opposed to bound coagulase)
Acts just like human thrombin Fibrinogen --(Clumping factor0----> Fibrin clot |
|
|
Cytochrome Oxidase
|
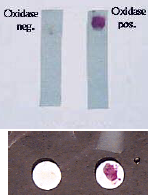
This enzyme is present as the bacterial ETC. The presence of enzyme will turn reagent purple in 5-10s
Oxidase + = Neisseria, P aeruginosa, Vibrio, Enterobacteriacae, Campylobacter or helicobacter |
|
|
How is pneumococci different from other streptococci?
|
Capsule that varies and is a virulence factor (90 different serotypes)
|
|
|
What is the crucial adherance structure for GAS? In nasopharynx? in Skin. What does it bind to on the epithelial cell? What adheres to langerhans cells?
|
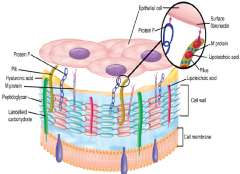
Fibronectin of the epithelial cells are bound differently in nasopharnyx (NP) & skin.
NP - M protein provides scaffold for LTA to bind Skin - M protein binds to subcorneal keratinocytes Protein F is important for binding langerhans cells Lancefield antigens are contained inside the cell wall. |
|
|
Functions of M protein?
|
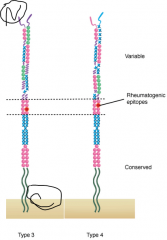
Binds Fibrinogen, Serum factor H, and Ig.
Site for binding Ig is the variable region accounting for the 80 serotypes. Suspect for etiology of Rheumatic fever induced Antibody. |
|
|
Extracellular Products of GAS?
|
Streptolyin O - forms pores in lipid bilayer. Is antigenic and basis of ASO titer
StrepSAg - in about 10% GAS. |
|
|
Symptoms of Scarlet fever? What is etiology?
|
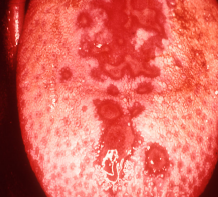
Red face with circum-oral pallor, strawberry tongue (red papillae + yellow/white exudate), sandpaper rash upper chest to trunk + extremities.
Associated with GAS Often these symptoms are superimposed on symptoms of STSS |
|
|
Describe pattern of rash in scarlet fever
|
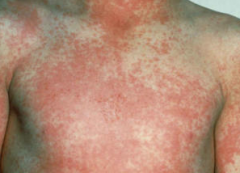
Sandpaper rash appears 2nd day of the fever and spreads from chest to the trunk & extremities.
|
|
|
Describe the components of shock induced by Superantigens SAg?
What are symptoms of shock in general? |
Cytokine storm - shock, renal impairment, & diarrhea
Low BP, tachycardia, poor end organ perfusion. |
|
|
What is azotemia?
|
This is renal failure. The name refers to the elevated Nitrogen. This results in an increase in BUN.
In the case of shock, prerenal azotemia is suspected and BUN:Cr should be >20. |
|
|
Progression of symptoms and lab findings of STSS?
|
1. Begins with infection
2. vague myalgia, chills, severe pain at infection site 3. This leads to necrotizing fascitis & myonecrosis (tabloid flesh eating bacteria) 4. Continues with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hypotension, & organ failure 5. Lab findings are lymphocytosis, azotemia, & often bacteremia |
|
|
What is etiology of TSS, STSS?
|
TSS - is staph aureas
STSS - is streptococcal (only GAS) |
|
|
Difference of Streptolysin O or S? and what test result they determine?
|
Streptolysin O is oxygen labile and only lysis in anaerobic conditions.
Streptolysin S is oxygen stable and will lyse in both anaerobic/aerobic conditions. Therefore it is important to incubate tests anaerobically. |
|
|
GAS transmission and what diseases is it associated with? What systemic effects can result?
|
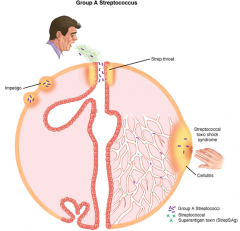
Group A streptococcal (GAS) disease overview. The primary sources of infection are respiratory droplets or direct contact with the skin. Impetigo results from minor trauma such as insect bites in skin transiently colonized with GAS. In streptococcal toxic shock, StrepSAgs producing GAS in a superficial lesion spread into the bloodstream. Note both toxin and bacteria are circulating
|
|
|
Describe Erysipleas
|
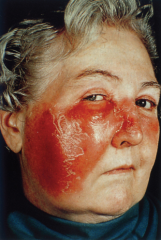
GAS of skin + subcutaneous tissues. Mostly the dermis is effected.
It has a rapidly spreading, well demarcated area of erythema & edema & pain. Systemic symptoms include fever & lymphadenopathy. |
|
|
Describe entry and invasion by GAS
|
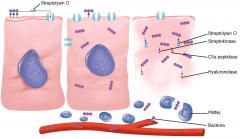
Group A streptococcal disease, cellular view. The cellular events are similar to Staphylococcus aureus (see Figure 24–4). Streptolysin O is a pore-forming toxin (like -toxin), and there are many extracellular products. A difference is that although S aureus tends to be localized, group A streptococci (GAS) tend to spread diffusely, as shown in the cell on the right. This may be due to hyaluronidase (spreading factor) or resistance to phagocytosis. Below the cells, factor H binding is mediating GAS escaping the polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs).
|
|
|
What are Aschoff bodies?
|
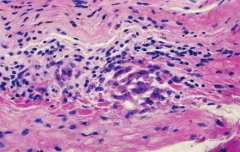
Aschoff nodule. Reacting lymphocytes and large mononuclear cells in myocardium demonstrate a cellular component to the immune reaction in rheumatic fever.
|
|
|
Routes of entry and disease of Pneumococcus & GBS?
|
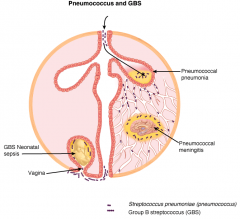
GBS and pneumococcal disease overview. S pneumoniae is aspirated from the normal orophyaryngeal flora to the lung were it produces pneumonia. Bacteremic spread can infect other sites particularly the brain where meningitis is produced. GBS vaginal colonization during pregnancy leads to infection of the fetus either in the uterus or during childbirth.
|
|
|
Risks of transmission GBS to neonate?
|
Present in mother's vaginal flora
Ruptured membranes (>18H prior) Premature birth Disease will present in first few days of life or months later. 50% of the time sx are apparent at birth. |
|
|
Organism Pattern Streptococcus Pneumoniae
|
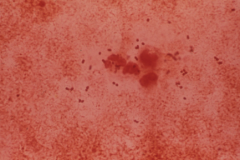
Streptococcus pneumoniae in sputum of patient with pneumonia.
oval diplococci |

