![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Polulation ecology |
The study of populations in relation to their enviornment, including enviornmenyal influences on density and distribution, age structure, and population size |
|
|
Population |
Group of individuals of a single species living in the same area. Described by boundries and size |
|
|
Density |
Number of individuals per unit area or volume |
|
|
Dispersion |
Pattern of spacing among individuals within the boundaries of the population |
|
|
Can be used to estimate densities and total population size |
Sampling techniques |
|
|
Popualation size can be estimated by either (3) |
Extrapolarion from smaller samples, an index of population size, or the mark recapture method |
|
|
Mark recapture method formula |
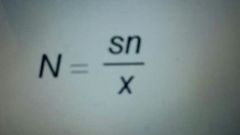
N is population, s is original marked sample, n is new sample, x is marked in new sample |
|
|
What decides density |
Interplay between processes that add individuals to a population and those that remove individual |
|
|
Immigration |
Influx of new individuals from other areas |
|
|
Emigration |
Movement of individuals out of a population |
|
|
Demographic events chamge |
density |
|
|
Spacing of individuals in a population is |
Influenced vy enviornemental and social factors |
|
|
In clumped dispersion individuals aggregate in |
Patches |
|
|
In uniform dispersion individuals are |
Evenly distributed |
|
|
Territoriality |
The defense of a bounded space against other individuals |
|
|
Random distribution |
Occurs in absent of strong attractions or repulsions |
|
|
Demography |
Is the study of the vital statistics of a population and how they change ocer time |
|
|
Death rates and birth rates are particularly important to |
Demographics |
|
|
It is useful to study population growth in an |
Idealized situation |
|
|
Idealized situations help us understand |
Capacity of species to increase and the conditions that facilitate that increase |
|
|
Exponential growth |
Population increase ynder idealized conditions |
|
|
The equation of exponential population growth is |
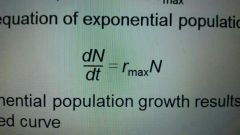
|
|
|
Realistic models don't have exponential growth and are limited by |
Carrying capacity |
|
|
Carrying capacity (K) |
The maximum population size the environment can support |
|
|
Carrying capacity varies with the abundance of |
Limiting resources |
|
|
Some populations overshoot _ before settling down to a relatively stable density |
Carrying capasity |
|
|
Some populations fluctuate greatly and make it difficult to define |
Carrying capacity |
|
|
Allee effect |
Populations which individuals have a more difficult time surviving and reproducing if the population size is too small |
|
|
Denisty independent |
birth rate and death rate do not change with population density |
|
|
Density dependent |
Birth rates fall and death rates rise with population density |
|
|
Equilibrium density |
Where density dependent and density independent populations have equal birth or death rate |
|
|
Crowded populations |
Have a lower birth rates due to increasing competition for resources |
|
|
Accumulation of toxic waste can |
Contribute to density-dependent regulation of population size |
|
|
The global population of humans is more than |
7.4 billion |
|
|
Human exponential growth started in |
1650 |
|
|
The global population is still growing but the rate of human growth begin to slow during |
1960s |
|
|
For Regional Human populations to maintain population stability or zero population growth they must exist in two configurations |
High birth rate and high death rate or low birth rate and low death rate |
|
|
Demographic transition |
Move from high birth and high death to low birth and love death |
|
|
Most of the current global population growth of humans is concentrated in |
Developing countries |
|
|
While uncertain the average carrying capacity estimate for humans on earth is |
10 - 15 billion |
|
|
Ecological footprint |
Concept that summarizes the aggregate Land and Water Area needed to sustain the people of a Nation |
|
|
Technosphere |
The 30 trillion ton congregate comprised of all the structures that keep human alive on the planet |

