![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Regarding maxfac trauma, which is incorrect
1 >20% of head neck and facial injuries in women are due to domestic violence 2 mobility of midfacial maxillary fractures is assessed by grasping the anterior maxilla with thumb and index finger while stabilising the forehead at the nasal bridge 3 objective impairment in visual acuity is the most sensitive single predictor of eye injury 4 malocclusion, pain on biting, loss of bite strength and limitation of jaw movement are a good indicators of jaw fracture |
3 INCORRECT - SUBJECTIVE impairment (not objective)
|
|
|
What are the features of base of skull fracture?
|
Periorbital bruising
Postauricular bruising Haemotympanum CSF otorrhoea |
|
|
Which fracture site and nerve would produce
1 sensory changes in lower lip and lower alveolar margin? 2 sensory changes in upper lip, upper alveolar margin |
1 maxilla, alveolar nerve branches of infra orbital nerve
2 mandibular canal, inferior alveolar nerve injury (branch mandibular nerve) |
|
|
Regarding facial trauma which is incorrect
1 the association between facial injury and cervical spine injury is well established 2 the association between facial injuries and intracranial injuries is more frequent than facial and C-spine injury 3 the major cause of death from facial trauma is asphyxia from up airway obstruction 4 anterior traction on fractured mandible or mobile section of maxilla may relieve airway obstruction 5 significant mid facial injuries in a stable patient are an indication for considering surgical tracheostomy in OT |
1 incorrect, questionable association
|
|
|
Regarding facial trauma which is incorrect
1 traumatic facial haemorrhage is life threatening in 5% of mid facial fractures 2 the evidence for prophylactic antibiotics in most injuries is weak 3 fractures other than undisplaced nasal, maxilla or zygomatic arch fractures require acute maxfac review 4 most mandibular fractures do not require internal fixation 5 the most common orbital floor fracture is as part of a zygomaticomaxillary fracture, rather than an orbital blowout fracture |
4 INCORRECT - most do
|
|
|
Answer the following regarding orbital blowout fractures
1. Definition 2 mechanism 3 possible examination findings 4 radio graphic findings |
1 fracture of orbital floor without fracture of orbital margin
2 increased intraorbital pressure (eg via fist or ball) disrupting weak orbital floor 3 enopthalmos, differing pupil levels, diplopia and impairment upward gaze, intraorbital hypo, hyper or paraesthesia 4 emphysema orbit, maxillary sinus collection, teardrop sign of herniated contents 'hanging' into maxillary sinus ALL orbital floor or margin fractures require referral |
|
|
Describe the Le Fort classification
Which is most common Which require urgent reduction? Most midface fractures are combinations with different patterns on each side of the face T/F |
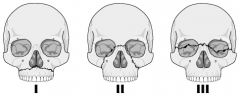
Midface fractures
I - only maxilla at level nasal fossa II - maxilla, nasal bones, medial aspect orbit. MOST COMMON III - separates midface from base of cranium, base of nose, ethmoids, across orbits, zygomatic arches II AND III - may require urgent reduction to improve airway and arrest haemorrhage. Midface mobility can occur, skull base fractures are associated, and CSF rhinorrhea can occur T |
|
|
Which is CORRECT? Regarding nasal fractures
1. Displaced nasal fractures should be reduced in 10-14 days 2. Imaging is usually required for nasal fractures 3 persistant epistaxis and CSF rhinorrhoea are common with simple nasal fractures 4 epistaxis and exclusion of nasal haematoma are immediate priorities |
1 incorrect 7-10
2 usually not required 3 common with nasoETHMOIDAL fractures 4 CORRECT |
|
|
Regarding TMJ dislocation which is INCORRECT
1 differential diagnosis includes extra pyramidal dystonia 2 post reduction x rays are required 3 manual reduction in ED under sedation is appropriate 4 avoiding wide opening of the mouth post reduction for 1-2 weeks, soft diet for several days is important |
2 incorrect - not always necessary
|
|
|
Regarding penetrating injuries to the face which is incorrect
1 maxillary entry sites are more likely to require a emergency airway than mandibular sites 2 shotgun and stab wounds typically produce less damage than gunshot wounds 3 central nervous system injuries are common and CT head and or cervical spine should be performed with CT facial bones 4 angiography is necessary 40% of the time and is indicated with proximity to major vessels or the skull base 5 ocular trauma is the most common complication of penetrating facial trauma |
1 INCORRECT - mandibular entry more likely to require emergency airway
|
|
|
Significant facial trauma and a compromised or deteriorating airway - options of management
|
Controversial. Consider immediate surgical airway
|

