![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
5 kingdoms |
1. Monera 2. Protista 3. Fungi 4. Plantae 5. Animalia * The criteria for a kingdom is cell structure, nutritional requirements, and developmental patters |
|
|
Monera |
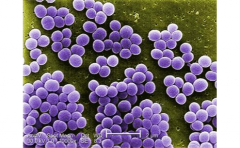
Organisms in the Monera kingdom prokaryotic, unicellular organisms. They can be either heterotrophic ( consumes food) or autotrophic (produces food). All members of the Monera kingdom reproduce asexually usually by asexual budding or fission. A member of the Monera kingdom is coccus bacteria. |
|
|
Protista |
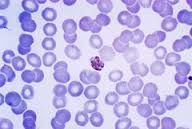
This kingdom consists of eukaryotic, unicellular ( some multi-cellular) organisms. Organisms found in this kingdom can also be heterotrophic or autotrophic. Most protist reproduce assexually by binary fission, but some do reproduce sexually using gametes. An example of a protist is plasmodium malariae. |
|
|
Fungi |

This kingdom contains organisms that are eukaryotic and multicellular; although some are unicellular. These organisms are the prime examples of autotrophic organisms. Most fungi reproduce assexually using spores. Mushrooms are an excellent example of fungi |
|
|
Plantae |

The Plantae kingdom consists of eukaryotic, multicellular organisms. All of the members of the Plantae kingdom are autotrophic. Members of this kingdom also reproduce sexually by pollination. An example of a member of the Plantae kingdom is a cactus. |
|
|
Animalia |

The Animalia kingdom contains eukaryotic, multicellular organisms. They are also the main examples of heterotrophic organisms. Members of this kingdom, called animals, can reproduce either sexually or asexually. An example of an animal is a lion. |

