![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How much can the marrow compensate for increased hemolysis?
|
5-8 times
|
|
|
3 signs of increased RBC production?
|
Increased reticulocyte count
Polychromasia Erythroid hyperplasia in the marrow |
|
|
3 signs of increased RBC destruction?
|
Increased LDH
Increased uncogugated bilirubin Decreased hepatoglobin |
|
|
How long does it take for the marrow to compensate for decreased RBCs?
|
4-7 days for retic count to go up
|
|
|
One intrinsic anemia that IS NOT inherited is?
|
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH)
|
|
|
Intravascular hemolysis can kill you by? (3)
|
Shock, DIC, renal failure
|
|
|
Cold agglutinin disease?
|
IgM attacks RBCs in cold tempuratures after an infection usually pneumonia.
|
|
|
Donath-Landerstieiner Antibodies?
|
IgG abs that bind RBCs in colder tempuratures and fix complement in warmer tempuratures. causes paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria (PCH)
|
|
|
4 signs or intravascular hemolysis?
|
Hemoglobinemia
hemoglobinuria hemosiderinuria decreased haptoglobin |
|
|
Direct antiglobulin (coomb's test) looks for?
|
immunoglobulin binding. autoimmuno hemolysis
|
|
|
Osmotic fragility test looks for?
|
hereditary spherocytosis
|
|
|
Sickle cell disease?
|
Sickle cell anemia with clinicl compliations
|
|
|
What is the main complication of sicklers?
|
Infarcts. lung, spleen brain and kidney
|
|
|
What are pts with no spleen more suseptable to?
|
encapulated organisms like Strep pneumoniae and hemophilius
|
|
|
What are the main crises of sicklers? (4)
|
Acute vasooccusive
sequestrian acute hemolytic acute aplasic |
|
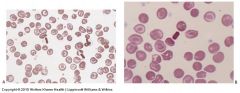
Diagnosis?
|
Hemoglobin CC disease
|
|

Diagnosis?
|
Hemoglobin SC disease
|
|
|
Most common RBC enzyme defect?
|
G6PD deficincy
|
|
|
Role of G6PD?
|
regenerates NADPH used to reduce back gluthathione after it detoxifies hydrogen peroixide
|
|
|
Inheretance pattern for G6PD?
|
X linked
|
|
|
Mechanism of anemia for G6PD deficincy?
|
increased sensitivity to oxidative stress
|
|
|
Heinz bodies?
|
aggregates of denatured hemoglobin seen with G6PD deficincy
|
|

What are these?
diagnosis? |
Bite and Blister cells
G6PD deficency |
|
|
Characterisitics of the african varient of G6PD?
|
mild activity G6PD activity decliens faster
|
|
|
charactersitics of mediteranian varient of G6PD?
|
reduced activity of G6PD even in retics. usually no helolysis at baseline and sensitivity of flava beans
|
|
|
Why might you get an normal value for G6PD during an attack?
|
The older cells that have the decreased activity are lyced leaving the normal younger cells
|
|
|
Spectrin?
|
Forms the skeleton of the RBC
|
|
|
Ankyrin?
|
Anchors the lipid bilayer to the spectrin sytoskeleton
|
|
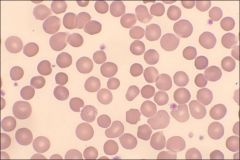
What are these?
|
Spherocytes
|
|
|
How can spherocytosis be treated? (3)
|
RBC transfusion
Cholecystectomy Splenectomy |
|
|
Elliptocytosis is inhereted how?
|
Autosomal dominant
|
|
|
elliptocytosis Is usually caused by?
|
defects in spectin
|
|

what are these?
diagnosis? |
elliptocytes
ellipocytosis |
|
|
Hereditary pyropokilocytosis is caused by?
|
Autosomal recessive inheritance of ellipotocysosis gene
|
|
|
which antibodies usually bind at colder tempuratures?
|
IgM
|
|
|
Cold reacting hemolysis is usually secondary to?
|
infection
|
|
|
Acrocyanosis?
|
When fringers, tips of ears and toes turn blue due to RBC agglutination that plugs up capillaries.
|
|
|
Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria? (PCN)
|
IgG Ab (Donath-Lansteriner) bind RBC at colder tempuratures and then lyce at warmer tempuratures
|
|
|
Most warm-reactive hemolysis occures?
|
extravasularly, most often the spleen
|
|
|
What is the antigen target usually assosiated with warm autoimmune hemolysis?
|
RH
|
|
|
Who usually gets idiopathic warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia?
|
women
|
|
|
treatment for idiopathic warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia?
|
Prednisone but problems with tappering. avoid transfusions
|
|
|
Mechanism of drug absorption type anemia?
|
usually penicillin, binds to RBCs. Ab binds to penicillin and is taken in by macrophages.
|
|
|
Neoantigen type anemia?
|
drug binds to the RBC and forms and antigen that is able to fix complement. intravascular
|

