![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In what form is Iron absorbed by the small intestine?
|
FE2+ form or part of a heme ring
|
|
|
How are Iron levels adjusted physiologically?
|
By changing the rate of absorption
|
|
|
How do we lose iron?
|
we lose about 1mg a day or 2 if your are a woman. Otherwise you need to bleed it out somehow
|
|
|
Why is iron overload a bigger problem?
|
We have no physiological method of getting rid of it
|
|
|
Stores vs erythropoisis regulator?
|
erythropoesis regulator is more potent and overrides the stors regulator
|
|
|
Transferrin?
|
carries 2 iron in ferrus form in the blood
|
|
|
Describe how the transferrin receptor works?
|
Transferrin with 2 iron binds and is pinocytosed. iron is realeased and the receptor is returned to the surface and transferrin is also released
|
|
|
Ferritin? Is found where?
|
storage molecule of iron. found in macrophages, hepatocytes and reticuloendothelial system
|
|
|
Hemosiderin?
|
another storage molecule for iron. thought to be partially degraded ferritin
|
|
|
ferritin levels rise when?
|
states of inflammation
|
|
|
Hepsidin?
|
regulatory molecule that works to decrease plasma iron.
|
|
|
Max amount of iron that can be absorbed by the duodenum?
|
4 mg a day
|
|
|
conversion of ferric iron to ferrous iron requires?
|
An acidic envirnment
|
|
|
What is the channel that transpotts iron to the plasma?
|
Ferroportin
|
|
|
What form of iron binds transferrin?
|
Ferric iron Fe3+
|
|
|
2 things in the diet that increase iron absorption?
|
Ascorbic acid and breast milk
|
|
|
Why is cow's milk a bad idea for iron absorption?
|
iron is hard to absorb and it can cause bleeding
|
|
|
IRE and IRP?
|
Iron regulatory protiens and Iron responsive elemets can alter gene transcription
|
|
|
HAMP?
|
Another name for Hepcidin. decreases plasma iron
|
|
|
How does Hepcidin cause anemia?
|
It blocks the transfer of iron to RBCs
|
|
|
What 2 things stimulate HAMP transcription?
|
Inflammatory cytokines and iron excess
|
|
|
What happends to Serum iron, TIBC, Saturation % and ferritin during Iron deficency, inflammation and combined?
|
Iron Deficency: Serum is low TIBC is high, Sat is very low and ferritin is low
Inflammation: Serum is low, TIBC is low, Sat is low and ferritin is high. Combined: Serum is low, TIBC ?, Sat is low and Ferritin is ? |
|
|
some situations where there is increased plasma but hemoglobin is still normal?
|
Pregancy, congestive heart failure and splenomegaly
|
|
|
problems with the hemoglobin reference range?
|
Reference rage is wide but the idividual's range is narrow
|
|
|
symptoms of anemia?
|
fatige
shortness of breath paplitations syncope |
|
|
factors that effect severity of symptoms?
|
age, health, rate of onset
|
|
|
PE signs of anemia?
|
light Pallor, tachycardia, jaudise glossitis Angular cheilitis
|
|
|
Hypoproliferative?
|
Bone marrow is not stimulated. little cell turnover but they are normal
|
|
|
Hyperproliferative?
|
Bone marrow is making cells like crazy but the cells are getting destroyed
|
|
|
Maturation Defect anemia?
|
problem with production and are released early
|
|
|
2 main causes of hypoproliferative anemias?
|
1. decreased erythropoitin
2. decreased RBC precoursers in marrow |
|
|
3 main catagorie of maturation defect anemias and some examples?
|
Cytoplasmic: iron deficiency, thalassemia
Nuclear: DNA synthesis defects and Vit B12 deficincy combined:myelodyspasia |
|
|
2 types of hyperproliferative anemias?
|
Hemorrahagic
Hemolytic |
|
|
Cause of a Microcytic MCV?
|
defective cytoplasmic maturation
|
|
|
Cause of Macrocytic MCV?
|
reticulocytosis or defective nuclear maturation
|
|
|
Hypochromia?
|
widening of the normal central pallar
|
|
|
sideroblastic anemia?
|
disorder of porphyrin or heme synthesis
|
|
|
Normocytic anemia with an appropriate marrow responce think?
|
Hemhorrage and hylolysis
|
|
|
Normocytic anemia with an inappropriate marrow responce think?
|
marrow hypoplasia or infultration
|
|
|
what can cause decreases erythropoitin? (5)
|
Kidney disease, liver disease, endocrine disease, malnutrition, chronic inflammation
|
|
|
Some types of macrocytic animias?
|
Megaloblastic anemia, reticulocytosis, aplastic, myelodysplasia.
|
|
|
Hypoproliferative?
|
Bone marrow is not stimulated. little cell turnover but they are normal
|
|
|
Hyperproliferative?
|
Bone marrow is making cells like crazy but the cells are getting destroyed
|
|
|
Maturation Defect anemia?
|
problem with production and are released early
|
|
|
2 main causes of hypoproliferative anemias?
|
1. decreased erythropoitin
2. decreased RBC precoursers in marrow |
|
|
3 main catagorie of maturation defect anemias and some examples?
|
Cytoplasmic: iron deficiency, thalassemia
Nuclear: DNA synthesis defects and Vit B12 deficincy combined:myelodyspasia |
|
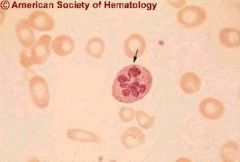
What would this suggest?
|
Megaloblastic anemia due to folate dicicency or b12
|
|
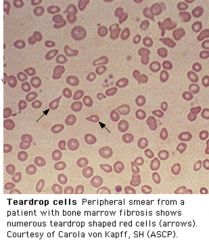
What is this?
|
teardrop RBCs
|
|
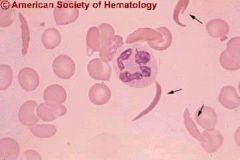
diagnosis?
|
Sickle cell anemia
|
|
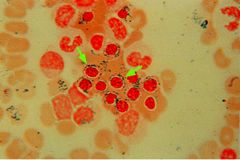
Diagnosis?
|
Sideroblastic anemia. iron has collected in the mitochondria around the cell. caused by defects in protopophorin synthesis
|
|
|
Hepatoglobin?
|
Bind to free hemoglobin in the plasma
|
|
|
Decrease in hepatoglobin means?
|
hemolysis because hepatoglobin is binging large amounts of free hemoglobin
|
|
|
How does iron end up in urine?
|
Intravascular hemolsis causes hemoglobin to be released into the plasma. it is filtered by the kidney and hemoglobin is released. iron is taken in and stored in the kidney cells untill they are sloughed off into the urine.
|
|
|
Myelophthisis?
|
means space occuping lesion in bone marrow
|
|
|
Most common cause of iron deficiency?
|
Blood loss specifically gastrointestinal bleeding
|
|
|
Plummer-Vinson syndrome?
|
combination of burning pain in the mouth due to glossitis and dysphagia due to esophageal webs seen often in iron deficincy
|
|
|
3 mechanisms of anemia caused by inflammation?
|
1. cytokines decrease erythropoitin and it effect on bone marrow
2. cytokines increas hepsidin levels 3. activation of macrophages increases hemolysis |

