![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is nervous tissue? |
Tissue containing neurons that initiate and conduct nerve impulses to coordinate homeostasis, and neuroglia that provide support and nourishment to neurons. |
|
|
What are neurons? |
A nerve cell, consisting of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon. |
|
|
What are nerve action potentials? |
Electrical impulses conducted by neurons to other neurons, to muscular tissue, or to glands. Also called nerve impulses. |
|
|
What is a dendrite? |
A neuronal process that carries electrical signals, usually graded potentials, toward the cell body. |
|
|
What is an axon? |
The usually single, long process of a nerve cell that propagates a nerve impulse toward the axon terminals. |
|
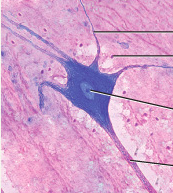
What type of tissue is this? |
nervous tissue |
|
|
Where would you find nervous tissue? |
Nervous system. |
|
|
What are the functions of nervous tissue? |
Exhibits sensitivity to various types of stimuli; converts stimuli into nerve impulses (action potentials); conducts nerve impulses to other neurons, muscle fibers, or glands. |
|
|
What are neuroglia? |
Cells of the nervous system that perform various supportive functions. The neuroglia of the central nervous system are the astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells; neuroglia of the peripheral nervous system include Schwann cells and satellite cells. Also called glial cells. |

