![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does PET stand for? |
Positron emission tomography
Positron-electron annihilation with formation of two 511 keV photons in opposite directions. 11C, 13N, 15O, 18F, 68Ga, 82Rb |
|
|
What is LoR?
|
line of response. Opposing detectors of a PET scanner will detect photons if they occur on in 180 degree orientation (electronic collimation) and within a specified time window (5-12 ns)
|
|
|
What are benefits of physical collimation?
|
No need for physical collimation, more sensitive, better spatial resolution.
|
|
|
What are the 4 coincident events in PET?
|
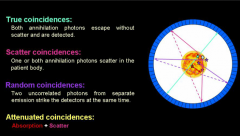
1) True: annihilation photons aren't scatted before reaching detector
2) Scatter: When 2 correlated photons (same event) undergo compton scatter before reaching oppsing detectors resulting in misregistered LoR = incorrect position, decreased contrast and overestimation of activity concentration of tracer 3) Random: When 2 uncorrelated photons strike apposing detectors within given window 4) Attenuated: 5) Multiples: When more than 1 annihilation events are detected by 2 detectors in a given coincidence window. Event is rejected |
|
|
How does TOF PET work?
|
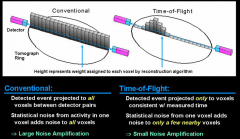
The time difference between arrival of opposed photons can be used to estimate relative position along the LoR.
|
|
|
Fusion between modalities requires accurate registration of anatomy.
|
This requires matched anatomic positioning
|
|
|
PET CT is supplimentary and complimentary
|
provides functional information to anatomic imaging to improve sensitivity. But also uses anatomic information from CT to generate attenuation maps to improve quality of emission information.
|
|
|
What standard is used to compare different commercial and research PET-CT/PET-MR systems
|
NEMA standard assesses sensitivity, spatial energy, temporal and contrast resolutions, counting rate, dead time, scatter fraction, and many other physical parameters.
|
|
|
Spatial resolution is described by what?
|
FWHM: full width half max
|
|
|
How is scanner sensitivity measured?
|
fraction of all conincident 511 keV photon pairs emitted from the object that are recorded by the system
|
|
|
What is energy resolution?
What is scatter fraction |
Precision with which one can measure the incoming photon energy. The better the resolution, the narrower the energy window that can be used which reduces scatter.
Sensitivity to scattered radiation (ratio of scattered/unscattered+scattered) |
|
|
What is time resolution?
|
how well one can detect whether two coincident photons truly arrive simultaneously
|
|
|
What parameters are responsible for the system contrast resolution?
|
Energy and temporal resolution.
|
|
|
What is the most popular data format for storing PET information?
|
Sinograms
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of image reconstruction?
|
Analytic: Filtered backprojection (faster but streakier)
Iterative: Slower but less noisy |
|
|
How is SUV calculated?
|
Concentration of activity measured by PET, divided by the injected dose normalized to patient weight multiplied by decay factor
correction to lean body mass is better |
|
|
What is the predominant interaction that occurs and PET energy levels?
|
Compton scatter
|
|
|
What is the average total dose of a PET/CT?
|
25 mSv
|

