![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
How do we define AIDS?
|
+ HIV test AND
|
one of the following: <200 CD4 T cells/microL, AIDS-defining opportunistic infection, AIDS associated malignancies, HIV complicating infections
|
|
|
What does the bleeding time test?
|
PLATELET function
|
|
|
|
What does PT (prothrombin time) test?
|
EXTRINSIC & COMMON PTHWY
|
Factors: 7, 5, 2, 1
|
|
|
What does PTT (partial thromboplastin time) test?
|
INTRINSIC & COMMON PTHWY
|
all factors except 7 and 13
|
|
|
What does TT (thrombin time) test?
|
COMMON PTHWY
|
factors 2 and 1
|
|
|
Which factors does Vitamin K mature?
|
2, 7, 9, 10
|
|
|
|
Which diseases are related to factor 8 deficiency or absence?
|
deficiency--Von Willebrand Dz, absence--Hemophilia A
|
**increased PTT
|
|
|
What is DIC?
|
spontaneous activation of coagulation cascade (w/ intravascular coagulation).
|
initiated by--bacterial endotoxins, presence of dead tissue, AML. Labs: prolonged PT, PTT
|
|
|
Why do we give Heparin with Warfarin?
|
Because warfarin has a procoagulation effect during the first days. Heparin is given to act against it. It works faster, too.
|
|
|
|
What are the causes of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura?
|
Children: viral infection Adults: autoimmune
|
|
|
|
What are the causes of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura?
|
primary: autoimmune secondary: drugs-->clopidogrel, quinine, interferon alpha
|
spontaneous platelet aggregation w/ systemic platelet clot formation and consumption of platelets
|
|
|
What are shistocytes (helmet or bite cells) indicative of?
|
damage, may see in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
|
|
|
|
What is spherocytosis?
|
chronic dz characterized by hemolysis of spheroidal RBCs, anemia, splenomegaly.
Due to deficient spectrin. |
RBCs were sphere like, look 2-D
|
|
|
What marker is used for ischemia?
|
Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH)
|
oxygen can't enter the kreb cycle. Thus, after glycolysis-->pyruvate--(LDH)-->lactate (lactic acid)
|
|
|
What is G6PD?
|
x-linked recessive disorder, only way to make NADPH, RBC is very sensitive to oxidative damage.
|
RBC lysis occurs due to exposure to excess radicals (fava beans, sulfa drugs, quinine derivatives)
|
|
|
What is the defect in sickle cell anemia?
|
autosomal recessive-->HbS. Single amino acid substitution (valine-->glutamate) in beta globin chain (at the 6th amino acid pxn)
|
|
|
|
What kind of anemia results with hemogloblin pathology?
|
MICROCYTIC ANEMIA
|
|
|
|
What is thalassemia (alpha and beta)?
|
ALPHA--decreased synthesis of alpha globin chains, BETA--decreased synthesis of beta globin chains
|
Major beta--no alleles, SEVERE microcytic anemia. Minor beta--missing allele
**need alpha globins to survive |
|
|
What type of anemia results from immune mediated hemolysis?
|
normocytic, normochromic (normal platelets just not enough)
|
antibodies against one's own RBCs
|
|
|
What are the causes for warm agglutinin disease (immune mediated hemolysis)?
|
Drugs (methyldopa, dopa, high dose penicillin, cephalosporin), malignancies (leukemia, lymphoma), SLE
|
|
|
|
What are the causes for cold agglutinin disease (immune mediated hemolysis)?
|
Mycoplasma pneumonia, mononucleosis, lymphoma, 50% idiopathic
|
|
|
|
What is the Coombs test used for?
|
detect autoantibodies to rbcs
|
Direct: RBCs coated with antibodies (gold standard for immune mediated hemolysis) Indirect: free floating (isoimmunization in Rh- females)
|
|
|
How do you know if the patient has a B12 or folate deficiency?
|
B12- neurotoxic "be crazy", folate-no neuro. both will have megaloblastic anemia
|
|
|
|
What are the clinical findings of megaloblastic anemia?
|
defective DNA synthesis-->leukopenia, hypersegmented neutrophils, thrombocytopenia
|
|
|
|
What are the causes of Vit B12 deficiency?
|
malabsorption, diphyllobothrium latum (fish worm), lack of intrinsic factor (pernicious anemia, gastric bypass surgery), absence of terminal ileum (Crohns)
|
|
|
|
Where do you see a folic acid deficiency?
|
alcoholic and pregnant women
|
|
|
|
What are the signs and symptoms of Plummer Vinson Syndrome?
|
low grade, long term iron deficiency, esophageal webs, dysphagia for SOLIDS ONLY
|
|
|
|
What is Fanconi anemia?
|
recessive, inability to remove oxygen radicals from bone marrow
|
clincal findings: microcephaly, cafe au lait spots, small or absent thumbs, deformed or absent radius bones, recurrent aplastic anemia (bm failure), HIGH risk of leukemia or lymphoma
|
|
|
What are bite cells and heinz bodies (denatured hemoglobin) indicative of?
|
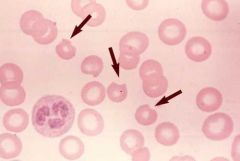
G6PD deficiency
|
|
|
|
What is indicative of basophilic stippling?
|
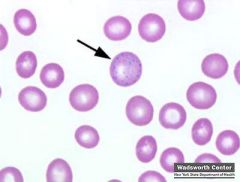
lead poisioning
|
|
|
|
What is Howell-Joly bodies indicative of?
|
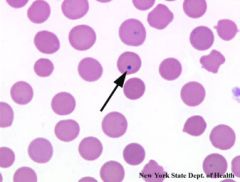
immature RBCs leaving the bone marrow, hyposplenia or asplenia
|
|
|
|
What are siderocytes?
|
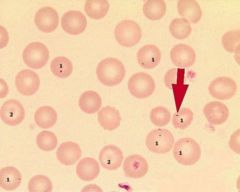
extra iron in RBC, due BM problems
|
|
|
|
What are reticulocytes
|
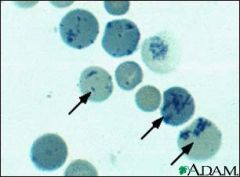
immature RBCS,
|
|
|
|
What is a cause of increased destruction of neutrophils?
|
Felty's syndrome--variant of rheumatoid arthritis, immune mediated destruction of neutrophils (anti-neutrophil antibodies)
|
|
|
|
What are some causes of a high number of wbcs (leukocytosis)?
|
"Neutrophils Like Making Everything Better" Neutrophils, Lymphocytes, Monocytes, Eosinophils, Basophils
|
|
|
|
What is a sign of acute myelogenous leukemia?
|
Auer rods, evidence of myeloid proliferation
|
|
|
|
What is the genetic abnormality assoc with chronic myelogenous leukemia?
|
Philadelphia Chromosome (9:22), translocation, bcr-abl fusion gene is created
|
low Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase
|
|
|
What are the markers for Hairy Cell Leukemia?
|
+ TRAP (tartrate-R-acid-phosphatase), CD25 markers present
|
"Harry was a 25 yo TRAP", B cell only, splenomegaly
|
|
|
What is indicative of Hodgkin's Disease (lymphoma, solid tumor)?
|
+ Reed Sternberg Cells
|
|
|
|
What are the 4 subtypes of Hodgkins Lymphoma?
|
BEST-->WORST prognosis. lymphocyte predominance-->nodular sclerosis-->mixed cellularity-->lymphocyte depletion (increased RS cells)
|
|
|
|
What is non-hodgkins lymphoma associated with?
|
bcl-2
|
|

