![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Recombination frequency is _________ but not _______ correlated with the _______ distance or ________ distance between two genes
|
Positively
Linearly Genetic Physical |
|
|
What is the name of the mathematical relationship between recombination frequency and genetic distance called?
|
Mapping Function
|
|
|
What are the 4 factors that effect the intensity of crossovers?
|
Sex
Individual Chromosome Position of chromosome |
|
|
What is Recombination Frequency?
|
its where a cross over in one region reduces the probability of a second crossover in the nearby region
|
|
|
Interference________ with _________ distance between two genes
|
Decreases
Increases |
|
|
When the Genetic Distance is more than ______ apart then the recombination frequency is ____ and will Display a _________ segeration
|
200
.5 Independent |
|
|
The relationship between _____________ _________ and gentici distance is _______ only within ___cM or recombination frequency lower than .5
|
Recombination Frequency
Linearly 10 |
|
|
What is the genetic distance between a double cross over?
|
5cM or smaller
|
|
|
The degree of interference can be defined as what?
|
1 - coefficient of coincidence, (is the observed number of double-recombinant ) divided by the number of expected DC
|
|
|
What is a haplotype?
|
is a group of alleles of continuously and tightly linked genes on the same chromosome
|
|
|
The alleles of a __________ are usually _________ _________ becasue they are closely linked.
|
Haplotypes
Inherited Together |
|
|
Genes that a hen carries in her ___ chromosome will not be transferred to its ______ offspring, but only to its ____ chicks
|
Z
Female Male |
|
|
Traits that are controlled by genes located in sex chromosomes are called ___-______ ______
|
sex-linked traits
|
|
|
__________ ________ is a science of studying the _______ _________ of a population, such as allele frequence and inbreeding.
|
Population Genetics
Genetic Constitution |
|
|
Population Genetics integrates _______ evolution with _________ genetics
|
Darwin's
Menedelian |
|
|
What are Darwin's 3 Theories of evolution?
|
1) Principal of Viaration
2) Principal of Heredity 3) Principal of Natural Selection |
|
|
What is the Principal of Viaration?
|
there are variations in morphology, physiology, behavior among individuals within any population.
|
|
|
What is the Principal of Heredity?
|
Relatives resemble each other more than they resemble unrealted individuals.
|
|
|
What is the Principal of Natural Selection?
|
Some forms or individuals are more successful at survival and reproduction than others in a given environment.
|
|
|
What are the 4 important parameters associated with populations?
|
1. Population Size
2. Mating System 3. Selection Pressure(the higher the pressure the fewer alleles will move on to next generation and vice-a-versa) 4. Environmental Factors |
|
|
What are breeding individuals?
|
They are the individuals of a population that actually contribute to the reproduction of the next generation.
|
|
|
What is the difference between Fixation and Polymorphism?
|
Fixation- is the stage of no alleles at a locus in a population
Polymorphism- is if there is more than one allele at a specific locus in a population |
|
|
The polymorphism or genetic diversity is the potential for genetic improvement.
|
The polymorphism or genetic diversity is the potential for genetic improvement.
|
|
|
What are the differences between Allele and Genotype Frequencies?
|
Allele Frequences are the porportion of an allele in a population.
Genotype Frequency are the porportion of a genotype at a locus in a population |
|
|
What is Heterozygosity?
|
It is the Proportion of heterozygotus individuals at a locus in a population.
|
|
|
What is the Hardy-Weinberg Law?
|
It is the allele frequencies in a population will not change generation after generation.
|
|
|
What are the 5 Assumptions that all have to be met to have a Hardy-Weinberg situation?
|
1) no selection
2) no mutation 3) no migrations 4) infantily large 5) random selection of mates |
|
|
1) there is NO SELECTION : all individuals of the population survive at equal rates and contribute equal numbersto the gene pool
2) There is NO MUTATION : no new alleles are creates 3) There is NO MIGRATIONS: no one moves into or out of the population 4) The population is INFANTILY LARGE: there can be no genetic drift by chance 5) Individuals choose their mates AT RANDOM |
:)
|
|
|
if selection is occuring in a population then some phenotypes are more fit than others and they will have more offspring
|
:)
|
|
|
What is the difference bewteen Inbred and outbred populations.
|
Inbred is when mating between individuals with common ancestors is much more frequent than by chance.
Outbred is when mating between relatives is by chance or less common |
|
|
What is inbreeding Coefficient?
|
Is the Probability of two alleles at any gene/locus in an individual are identical by descent.
|
|
|
What is it called when TWO alleles of a locus in an individual are both descended from an identical DNA molecule?
|
It is called :
Homozygosity by Descent or Identity by Descent |
|
|
What are some causes of inbreeding?
|
1)If there is a "loop" in a pedigree drawing, there is possibility of inbreeding
2)If the alleles are passed down in both pathways of a loop are the alleles that cause inbreeding |
|
|
The inbreeding coefficient in a closed population will always increase
|
The inbreeding cofficient in a closed population will always increase
|
|
|
Inbreeding coefficient depends on the __________ size.__________ the population size can reduce the increment of inbreeding in the the population, but it cannot ____ the previous inbreeding.
|
Population
Increasing Undo |
|
|
Inbreeding ___________ in each generation and it ______ be reduced in a _____ population
|
Accumulates
Cannot Closed |
|
|
Why is inbreeding harmful?
|
it is due to rare recessive alleles that become homozygous.
|
|
|
Does intensive selection increase inbreeding coefficient even though mating among sibs and close relatives is avoided?
|
yes, selection reduces the effective population size in each generation. Therefore the possibility of mating between relatived individuals increases
|
|
|
How can breeders reduce the incrememnt of inbreeding in their breeding stocks?
|
1) Maintain a large population
2) Avoid mating among close relatives 3) Lower selection intensity 4) Line crosses |
|
|
Why is inbreeding bad for breeding?
|
1) Health problems due to recessive alleles: disease susceptibility low reproduction and genetics defects
2) Reduces genetic diversity |
|
|
What is the difference between Simple and Complex traits?
|
Simple traits - are changed by alternative genotypes simple one gene will cause a change this is not affected by the enviornment
Complex traits - are controlled by mulit genes which are influenced by environmental factors |
|
|
What is the difference between Discontinuous and Continuous traits?
|
Discontinuous - are the traita which phenotypes are distributed into a range of classes (when talking about eggs you can have 1or 50 but not 23.4 (whole numbers only))
Continuous- are the traits which phenotypes are measured in a continuous scals (When talking about weight numbers like 23.5 or 66.9 NOT whole numbers) |
|
|
What are the 4 things that describe Simple Traits?
|
1) Rare
2) One or Two Genes 3) No environmantal Effects 4) Characteristic Phenotypes |
|
|
What are the 4 things that describe Complex Traits?
|
1) Common
2) Mulit Genes 3) Environmantal Effects 4) Discontinuous or Continuous Phentypes |
|
|
What is Quantitative Genetics?
|
It is a science that studies the modes of inheritance of complex or quantitative traits.
|
|
|
Why are Quantitative Traits refered to as quantitative traits?
|
It is becuase most of the complex traits are often measured and given a quantitative value.
|
|
|
What are the economic traits of poultry? and what types of traits are they?
|
Weight gain and Fat content of meat
They are quantitative traits |
|
|
What are the two measurements of poultry economic traits?
|
Invasive and Non-invasive
|
|
|
What is the difference between Invasive and non-invasive measurements?
|
Invasive- are methods that CAN cause physical harm to the birds
Non-invasive- are methods that CANNOT cause physical harm to the birds. |
|
|
What are some examples of
invasive and non-invasive measurements? |
Invasive: measure for disease resistance, measure for meat quality
Non-invasive: measuring for body weight, measuring for egg production. |
|
|
What kinds of test do the Progeny and Sibling test show?
|
they are ways to measure an invasive trait WITHOUT doing physical harm to bird being tested.
|
|
|
Accuracy of indirect measurements is positively associated with relatedness.
|
Accuracy of indirect measurements is positively associated with relatedness.
|
|
|
What are the Genetic effects on quantitative traits?
|
The phenotyipc variations due to different alleles in genes controlling the expression of a trait.
|
|
|
What are the Environmantal effects on quantitative traits?
|
The phenotypic variations due to different environmental conditions that individuals experence.
|
|
|
When refering to Genetic effects within a gene what does complete dominance mean?
|
it is when one allele completly masks another allele
it also is when the average of A1A1 = A1A2 |
|
|
When talking about Genetic effects what does incomplete dominance mean?
|
it is when on allele masks another
it is also when A1A2 does not equal 0 or A1A1 orA2A2 |
|
|
when refering to genetic effects within a gene what does Over-dominant mean?
|
it is when the Phenotypic expression of a heterozygote is higher or lower than its corresponding heterozygote
it also means that A1A2 is greater than A1A1 or thant A1A2 is less than A2A2 |
|
|
when refering to the genetic effects within a gene what does Additive effect mean?
|
it is when two alleles at a locus are contributing to the phenotypic expression without interfering with each other
it also means that A1A2 = 0 |
|
|
d=0 (additive)
d dont equal 0; a>d>-a (incomplete) d=a or d=-a (complete) d>a ; d<-a (over dominance) d>0, A1 over A2 if d>0, A2 overA1 |
d=0 (additive)
d dont equal 0; a>d>-a (incomplete) d=a or d=-a (complete) d>a ; d<-a (over dominance) d>0, A1 over A2 if d>0, A2 overA1 |
|
|
What is Epistasis?
|
It is the genetic interaction of non-allelic genes in which one gene interfers the expression of another
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of interaction in Epistasis?
|
Additive by Additive
Additive by Dominant Dominant by Dominant |
|
|
Additive by Additive is what type of interaction?
|
it is 2 genes of the same genetic effect
|
|
|
Additive by Dominate is what type of interaction?
|
there are 2 genes one is A that has an additive effect and gene B has a dominate effect
|
|
|
what is the interaction bewteen Dominant by Dominant?
|
It is when the 2 genes both have Dominant effect
|
|
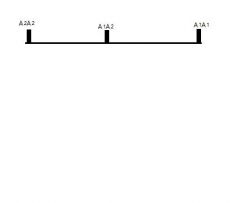
What type of effect is shown in image
|
Addative effect
|
|
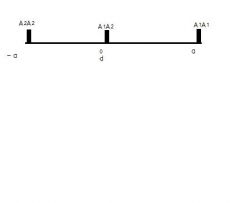
What type of effect is shown in the pitcture
|
Addative Effect
|
|
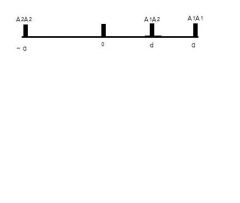
What type of Effect is shown in the picture
|
Incomplete Dominance
|
|
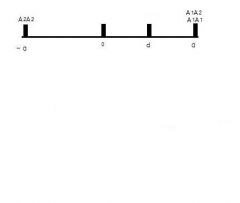
What type of effect is shown in the picture
|
Complete Dominace
|
|
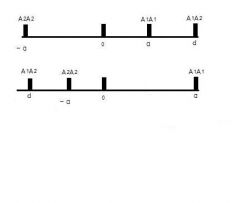
What type of effect is shown in the two Pictures?
|
Over Dominance
|

