![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does having multiple (more than one) independent variable's allow: |
A determination of not only the effect of each Independent variable on the dependent variable, but how they interact aswell. E.g. How long it takes to fall asleep with lights on + whether or not there's loud music. Absent = different. loud music = equal. |
|
|
What is a fully crossed experimental design: |
When you have multiple Independent variables and you collect all combinations of levels data, this leads to a factorial design. |
|
|
What is a factorial design: |
When each level of one factor (independent variable) is combined with every level of other variable. E.g. with gender and meal size. we would get - Small meal: M & F - Large meal: M & F |
|
|
How do you figure out how many possible conditions are in a factorial design: E.g. with the meal size & Gender |
Times the number of levels by each other for each Independent variable. 2x2 factorial design. 2 outcomes for each times each other = 4 possible outcome. |
|
|
In a 2x2 factorial design (4 possible outcomes) where all IV's are between subjects, how would the 40 people be distributed: |
Small Large Male 10 10 Female 10 10 |
|
|
In a 2x2 factorial design where all IV's are within-subjects, how would the 40 people be distributed amongst the 4 outcomes: |
Large Small Male 40 40 Female 40 40 |
|
|
In a 2x2 factorial design where one IV is within subjects and one IV is between subjects (mixed design), what would distribution of the 40 look like and explain: |
Large Small Male 20 20 Female 20 20 As, each participants receives each level of the within-subjects IV and one level of the between subjects IV. |
|
|
With factorial designs you can get two types of effects, what are they: |
Main effects = The effects of one IV on the DV, ignoring the other IV's. Interaction effects = The effects of one IV on the DV taking into account the other IV's in the study. |
|
|
What are main effects and interaction effects: |
Main effects: The effects of one IV on the DV, ignoring other IV's. There's a main effect for every IV. Interaction effect: The effects of one IV on the DV, taking into account the other IV's in the study. There's an interaction for every combination of IV's. |
|
|
What should be interpreted first between main effects and interaction effects: |
Interaction effects before main effects. |
|
|
When looking at graphs showing data for an experiment like the gender with food and appearance, what 2 types of line styles would we expect to see for an interaction: |
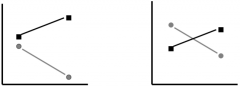
Converging and diverging: |
|
|
How would you know if there is no interaction: |
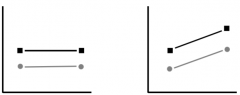
If the lines are parallel. |
|
|
How many sources of variability are there in a 2-factor experiment: |
3 sources of variability. 2 main effects (1 for each IV) 1 interaction effect. |
|
|
What is the relationship between between interaction and main effects: |
They arnt really dependent on each other in anyway. |
|
|
Can you determine if the observed effects are statistically significant, and why: |
No not really, you need to do statistical tests to just see if they are statistically different. |

