![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Osmosis |
The movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration. |
|
|
Partially permeable membrane |
Only smaller molecules (i.e water) can pass through and bigger molecules (i.e sucrose) cannot. |
|
|
How are exchange surfaces adapted? |
Short diffusion pathway Large surface area Ventilated |
|
|
Thorax |
Top part of your body |
|
|
Breathing in |
1) Intercostal muscles and diaphragm contract 2) Rib and sternum is pulled up and out. 3) Thorax volume increases 4) Decrease in pressure so air is drawn in. |
|
|
Breathing out |
1) Intercostal muscles and diaphragm relax. 2) Rib and sternum drop in and down. 3) Thorax volume decreases. 4) Increase in pressure so air is forced out. |
|
|
Ventilation |
Breathing in and breathing out |
|
|
What is the job of the lungs? |
To transfer oxygen to the blood. To remove waste carbon dioxide. |
|
|
How are alveoli specialised? |
An enormous surface area Moist lining for gas exchange Short diffusion pathway (thin walls) Good blood supply |
|
|
How are the villi specialised? |
Increased surface area so digested food is absorbed more quickly Single layer of surface cells Good blood supply to maintain concentration gradient |
|
|
How are root hair cells specialised? |
Long hairs give big surface area so most of the water and mineral ions are absorbed by root hair cells. |
|
|
Active transport |
The process by which dissolved molecules move across a cell membrane from a lower to a higher concentration. This requires an input of energy. |
|
|
Carrier proteins |
They pick up specific molecules and take them through the cell membrane against the concentration gradient. |
|
|
What picks up specific molecules to take them through a cell membrane against a concentration gradient? |
Carrie proteins |
|
|
Describe an example of active transport in plants. |
In root hairs to take in minerals as concentration of minerals is usually higher in root hair than in soil. |
|
|
Describe an example of active transport in plants. |
In the gut when there is a low concentration of nutrients in the gut but a high concentration in blood. |
|
|
Phloem |
Transports food substances (mainly dissolved sugars) to growing regions and storage organs. Transport goes in both directions. |
|
|
Describe the structure of phloem |
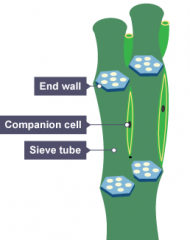
Columns of living cells. Small holes at ends of cells (sieve plates). |
|
|
Xylem + Phloem |
Vascular bundle |
|
|
Vascular bundle |
Xylem + Phloem |
|
|
Describe the transpiration cycle |
1) Water absorbed from soil through RHCs
2) Water moves by osmosis from to xylem 3) Transported through xylem up stem to leaves 4) Evaporates from leaves (transpiration) |
|
|
Xylem |
Involved in movement of water through a plant - from its roots to its leaves via the stem. |
|
|
Describe the structure of xylem |
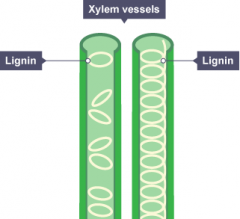
Tubes made from dead xylem cells which have cell walls removed at one end. Walls lignified (strengthened with lignin) to withstand pressure changes of water.
|
|
|
Describe the double circulatory system. |
First : pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs to take in oxygen. Blood returns to the heart. Second : Pumps oxygenated blood around the body. Returns to the heart deoxygenated. |
|
|
Arteries |
Carry blood away from heart Thick walls Contain thick layer of muscles and elastic fibres to help withstand pressure |
|
|
Capillaries |
Arteries branch into these. Involved in exchange of materials at the tissues. Very small Permeable walls Walls are 1 cell thick |
|
|
Veins |
Carry blood to the heart Capillaries join up to form veins Thinner walls Bigger lumen Have valves |
|
|
Red blood cells |
Big surface area No nucleus Contains haemoglobin which combines with oxygen to become oxyhaemoglobin in lungs. Releases oxygen to cells. |
|
|
White blood cells |
Engulf pathogens, produce antibodies and antitoxins to defend against disease. |
|
|
Platelets |
Help to clot blood at a wound. |
|
|
Plasma |
Liquid that carries most things in blood : WBCS and RBCs Soluble products of digestion Carbon dioxide Urea Hormones Antibodies and antitoxins |
|
|
Stents |
Tubes inserted inside arteries to keep them open so blood can pass through.` |
|
|
Homeostasis |
The maintenance of a constant internal environment. |
|
|
Name four things your body needs at just the right level |
Body temperature Water content Ion content Blood sugar level |
|
|
Name two things that your body needs to get rid of |
Carbon dioxide Urea |
|
|
What happens when you're too hot? |
Hairs lie flat Swear produced and evaporated Blood vessels dilate |
|
|
What happens when you're too cold? |
Hair stand up to trap air No sweat produced Blood vessels constrict Shiver |
|
|
Three main roles of the kidneys |
Removal of urea in blood Adjustment of ions in blood Adjustment of water content in blood. |
|
|
Urea |
1) Any excess amino acids are converted into fats and carbs by liver (cah't be stored). 2) Waste product from reaction is urea. 3) Urea released into bloodstream. 4) Kidneys filter it out of the blood. 5) Temporarily stored in bladder in urine before excreted from the body. |
|
|
Adjustment of ion content |
1) Ions taken in by food then absorbed into blood. 2) Excess ions removed by kidneys. 3) Some ions lost in sweat |
|
|
Adjustment of water |
In = food and drink Out = Urine, sweat, ventilation Controlled by : Liquids consumed Amount sweated out Amount excrete by the kidneys in the urine |
|
|
Sport drinks |
Contain water, sugar and ions to replace water and ions lost in sweat and sugar used in respiration. |
|
|
Nephrons |
Filtration units in the kidneys |
|
|
Main stages in a nephron |
1) Ultra-filtration 2) Re-absorption 3) Release of wastes |
|
|
Gas exchange in fish |
More difficult because concentration of oxygen in water is <1% vs 20% in air. Water in through mouth and passes through gills. Countercurrent exchange maintains concentration gradient |
|
|
Why can't fish survive out of water? |
The folds are kept supported and moist by the water that is continually pumped through the mouth and over the gills. Without water, the gills collapse and dry out to reduce surface area and gas exchange. |
|
|
Gas exchange in insects |
Need to respire quickly as very active. Waterproof exoskeleton - prevents too much evaporation. Improved rate of gas exchange due to network of tubes that carry air directly to the cells. |
|
|
Gas exchange in small organisms |
Don't usually have a specialised gas exchange system. Instead, exchange gas through surface of body. |
|
|
How do stomata control water concentration? |
Closed at night - no photosynthesis occurs so conserves water ---> slower transpiration Open during day - -transpiration speeds up |
|
|
What can be used to measure the rate of transpiration in a plant? |
A potometer |
|
|
What does a reservoir do in a potometer? |
Used to reset the air bubble |
|
|
Curled leaves |
Adaption for dry environment Increase humidity trapped in leaf Less evaporation due to less concentration gradient. |
|
|
Which ventricle is thicker and why? |
Left ventricle - has to pump the blood much further |
|
|
Which side of the body carries oxygenated blood? |
Left side |
|
|
State two positives of the double circulatory system. |
Blood can be pumped further so can sustain bigger animals. Enables a higher pressure - more rapid blood flow |
|
|
How do platelets help to clot blood. |
1) When blood is exposed to air, platelets and factor x stimulates fibrinogen to turn into fibrin. 2) Fibrin is long and thin compared to fibrinogen. 3) Fibrin will create a mesh over the wound. 4) Mesh will trap blood leaking out. 5) Blood will dry and form a scab. |
|
|
Advantages of artificial blood |
No religious objections Has no type, compatible with everybody Can manufacture large quantities Can store for a longer period of time easier Will not pass on disease |
|
|
Disadvantages of artificial blood |
More expensive More difficult to produce Not as efficient as haemoglobin (carries less oxygen) |
|
|
Pros of dialysis |
No complication with rejection Do not have to wait for donor Cam be done indefinitely No surgery needed - less chance of infection |
|
|
Cons of dialysis |
Very time consuming Patient is reliant on dialysis |
|
|
Pros of transplants (kidneys) |
Potential to last 10 years One major operation only Less expensive in the long run |
|
|
Cons of transplant (kidneys) |
May be rejected Reliant on finding a matching donor Implications with immuno-supressive drugs Major operation - high risk of death |
|
|
What is your body's response to high blood sugar? |
Changes detected by pancreas Insulin produced in the pancreas Converts glucose into glycogen |
|
|
What is your body's response to low blood sugar? |
Changes detected by the pancreas Glucagon produced in the pancreas Converts glycogen into glucose |
|
|
Where is glucose changed to or from glycogen? |
Muscles or the liver |
|
|
What are the cells in the pancreas called? |
Islets if Langerhans |
|
|
Describe the function of the atria |
To collect the blood |
|
|
Describe the functipn of the ventricle |
To pump the blood out of the heart |

