![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
59 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why was Newland's work criticised? |
1) His groups contained elements that didn't have similar properties. 2) He mixed metals with non-metals. 3) He did not leave gaps for undiscovered elements. |
|
|
What were elements ordered by prior to the modern periodic table. |
Atomic mass |
|
|
Why was Mendeleev's periodic table more accepted than Newland's? |
1) He left gaps for undiscovered elements to keep elements with similar properties in the same group. 2) He was able to quite accurately predict the properties of undiscovered elements. |
|
|
Describe the trends of Group 1 |
As you increase the period: Increased reactivity Lower melting and boiling points General low density |
|
|
What is the common name for the Group 1 Metals? |
The alkali metals |
|
|
Describe the reaction of a Group 1 metal and water. |
G1 Metal + Water ----> G1 Metal Hyrdroxide + Hyrdogen |
|
|
Describe the trends of Group 7 element |
As you increase the period: Less reactive Higher melting and boiling point |
|
|
What colour are Group 1 metal's compounds and solutions? |
White compounds Colourless solutions |
|
|
What type of vapours do the Halogens have? |
Coloured vapours |
|
|
What are the Group 7 elements commonly called? |
The Halogens |
|
|
Why will Br not displace Cl in an aqueous solution of its salt? |
Because Br is less reactive than Cl |
|
|
Describe the properties of the Transition metals |
Good conductor of heat and electricity. Very dense, strong and shiny. Much less reactive than G1 metals Higher melting points than G1 metals |
|
|
What is special about the ions of transition metals? |
Often have more than one ion for each element. i.e Fe^2+ and Fe^3+ |
|
|
Are the compounds of transition metals white or colourful? |
Colourful |
|
|
State the common use of transition metals in chemical reactions. |
As a catalyst |
|
|
What does Manganese (IV) oxide commonly catalyse? |
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. |
|
|
What does Nickel commonly catalyse? |
The hydrogenation reaction of oils into fats. |
|
|
What causes permanent hardness? |
Calcium and magnesium ions (dissolved calcium and magnesium sulphate) |
|
|
What causes temporary hardness? |
Hyrdocarbonate ions (in calcium hyrdocarbonate) |
|
|
How can you remove temporary hardness? |
Boiling - to thermally decompose the calcium hydrocarbonate Add sodium carbonate (washing soda) Pass through an ion exchange column |
|
|
How can you remove permanent hardness? |
Add sodium carbonate (washing soda) Pass through an ion exchange column |
|
|
How does adding sodium carbonate remove hardness? |
Carbonate ions react with the Ca and Mg ions to form an insoluble precipitate. Ca and Mg are no longer dissolved in solution and so can't make it hard. |
|
|
How does an ion exchange column remove hardness? |
The columns exchange sodium ions or hydrogen ions (in the resin) for the Ca and Mg ions. |
|
|
Describe the stages of water treatment. |
1) Pass through a mesh screen to remove larger solids (i.e twigs) 2) Coarse filter 3) Sedimentation tank 4)Fine filter 5) Chlorine added |
|
|
Describe what occurs in a sedimentation tank |
Aluminium sulphate is added to clump particles together so they settle at the base of the tank. |
|
|
What is an aquifer? |
A naturally occurring store of water. |
|
|
Why is chlorine added to drinking water? |
To sterilise it as Cl kills microbes. |
|
|
Why is (activated) carbon added to water filters? |
To remove carbon-based impurities ('organic' chemicals), as well as things like Cl. This removed the 'chlorine taste'. |
|
|
Why is silver added to water filters? |
To prevent the growth of microbes. |
|
|
Why is fluoride added to drinking water? |
To reduce tooth decay. |
|
|
What is equilibrium? |
In a closed system, the amount of reactants and products will reach a certain balance and remain there. |
|
|
What is dynamic equilibrium? |
The reactions are still taking place in both directions but there is no overall chance in amount of product/reactant as the reactions are taking place at exactly the same rate in both direction.s |
|
|
What temperatures do endothermic and exothermic reactions favour? |
Endothermic : High temperature Exothermic : Low temperature |
|
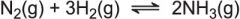
What pressure will favour the forward reaction? |
A high pressure as there are more gaseous moles on the right hand side. |
|
|
How will a catalyst affect the equilibrium position and rate of reaction? |
WILL NOT ALTER THE EQUILIBRIUM POSITION Will speed up the forward and backwards reaction by the same amount. Reaches equilibrium quicker. |
|
|
Where is nitrogen obtained from for the Haber process?? |
Dry air |
|
|
Where is hydrogen obtained from for the Haber process?? |
Methane |
|
|
What are the conditions used for the Haber process? |
450°C 200 atmospheres Iron catalyst |
|
|
What is the functional group in alcohols? |
-OH The hydroxyl group |
|
|
State the general formula of alcohol. |
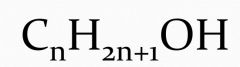
|
|
|
Describe the combustion reaction of alcohol. |
Alcohol+Oxygen ----> Carbon dioxide+Water |
|
|
What pH is the solution of alcohol dissolved in water? |
The first 3 alcohols dissolve completely to form a NEUTRAL solution. The OH- is bonded covalently and so doesn't ionise. |
|
|
What is the main alcohol used in alcoholic drinks? |
Ethanol |
|
|
Describe the reaction of an alcohol with sodium. |
Alcohol + Na ----> Alkoxide + Hydrogen |
|
|
State a method of making ethanol |
Fermentation of sugar cane |
|
|
What can alcohol be used for? |
Mixed with petrol and used as a fuel for cars. Pure ethanol is clean burning. |
|
|
What is the functional group in carboxylic acids? |
-COOH |
|
|
What pH is the solution of a carboxylic acid dissolved in water? And why? |
A weak acidic solution (higher pH) as they do not completely ionise. |
|
|
How can alcohols be turned into carboxylic acids? |
Oxidising them by: Adding an oxidising agent, Adding microbes that aerobically respire (fermentation) |
|
|
Why aren't carboxylic acids often used as solvents? |
As they turn the solution acidic but alcohols don't. |
|
|
State the general formula of carboxylic acids |

|
|
|
State the general formula of esters |

|
|
|
What must you react together to form an ester? |
An alcohol and a carboxylic acid |
|
|
How do you name an ester? |
The alcohol forms the first part; the -yl The carboxylic acid forms the second part; the -oate |
|
|
What is usually used to catalyse the formation of an ester? |
An acid catalyst (i.e concentrated sulphuric acid) |
|
|
Why are esters ideal for perfumes? |
Have pleasant smells Are volatile |
|
|
What do and don't esters mix well with? |
NOT VERY WELL WITH WATER Mix well with alcohols and other organic solvents. |
|
|
Why is inhaling the fumes from some esters bad? |
They irritate mucous membranes in the nose and the mouth. |
|
|
Flammable vapour + naked flame =? |
Flash fire |

