![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Science vs Engineering |
Understanding phenomena through observation and experimentation vs design under constraint |
|
|
What is Systems Engineering? |
Design and engineer/manage complex systems over their life cycle |
|
|
What is a system? |
Group of interrelated components functioning together towards a common goal or outcome |
|
|
App vs Information system |
App is software that performs some desired functions
Info System is a group of related components that receives, processes, transmits, stores, etc info(Software, Hardware, Data, Processes, Organization) |
|
|
What is a project? |
System development project Planned undertaking w/ beginning and end Produces desired results and product |
|
|
Scope vs. Time vs. Cost |
Scope-Control functions included in system and scope of team Time-Detailed schedule of all tasks Cost-Obvious Project management triangle: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/management_concepts/project_management_triangle.htm |
|
|
canonical system model (input, process, output) |
input -> process -> output that has systems and automation boundaries |
|
|
system boundary |
Outer boundary on canonical model, contains automation boundary |
|
|
automation boundary |
Inner boundary, Border between computerized portion of application and the people operating the application
|
|
|
subsystem |
component that makes up larger systems |
|
|
stakeholders (internal/external) |
People who have decision making power and sometime of command and ownership |
|
|
business process |
Situation Analysis -> Strategy Formulation -> Strategy Implementation -> Evaluation and Control |
|
|
oversight committee |
clients and key managers who review the progressand direct the project |
|
|
PERT/CPM |
Program Evaluation Review Technique/Critical Path Method Critical Path is sequence of events that cant be delayed http://www.math.csusb.edu/faculty/prakash/611/Project_Management.ppt.pdf |
|
|
WBS (Work breakdown structure) |
-Make list of all activities -Estimate size of each activity and way to measure -Analyze Dependencies |
|
|
Gantt chart |
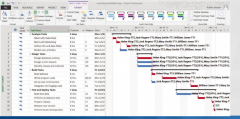
-Bar chart that portrays the schedule by the length of horizontal barssuperimposed on a calendar |
|
|
Critical path (longest path) |
a sequence of tasks that can’t be delayed withoutcausing the entire project to be delayed |
|
|
slack / float |
Flexibility in scheduling |
|
|
business benefits |
-The benefits that accrue to the organization -Tangible (in dollars) and intangible benefits |
|
|
Feasibility asks, fundamentally: Will this project fail, due to xxxxx? |
What is this asking? |
|
|
4 areas of feasibility (Technical, Organizational, Cost, Schedule) and Feasibility Questions |
Technical- Can the system be built by the team using technologyneeded? Training available? Organizational-How well does the new system fit the organizationalculture? Risk of negative impacts? Cost-Are the needed resources available? Skilled people Schedule-Can the system be built in the amount of time available?Fixed Deadline? |
|
|
What is in a system vision document? How is it used? Why create one? |
-Description of problem -Outline of Basic Solution -Business benefits derived |
|
|
Risk modeling (Assessment/Management) (Pay attention to assessment questions) |
Assessment: What can go wrong? Likelihood? Consequences? Management: What can be done? Tradeoffs? How does it affect future options |
|
|
"Risk" definition |
Probability and severity of adverse affects |
|
|
xWhat is pareto-optimality? |
Increase in one objective comes at the expense of another |
|
|
What is safety? |
Subjective assessment of the acceptability of risk(qualitative and risk)
|
|
|
Failure/Risk: Tools for examining root causes and effect (5 Why's and Ishikawa or fishbone diagram) |
-5 Why's is easy...keep asking why till you get there..should take 5 of them -Ishikawa: http://www.vertex42.com/ExcelTemplates/fishbone-diagram.html -People, Equipment, Process, Materials, Environment, Management |
|
|
tangible vs intangible benefits |
-Tangible is measured in dollars and such -Intangible is stuff like customer satisfaction, ease of use, survival and cant be measured |
|
|
What is an ERP system? |
Enterprise Resource Planning
Basic sales, accounting, reporting, HR, etc systems |
|
|
ERP systems major sources of failure. High risk or low risk? |
High risk of failure 1. Never get started 2. No clear destination 3. Planning 4. Part time project management 5. Underestimating resources 6. Over reliance on consultants 7. Customization 8. On the job training(new to implementing systems) 9. Lack of proper testing 10. Not enough user training |
|
|
top-down vs. bottom-up approach (as it relates to risk, and as it relates to ambiguity) |
Bottom Up Detailed -> General
Top Down(Ambigius) General -> Detailed |

