![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are some mammary gland natural defense mechanisms?
|
・Mechanical barriers (teat orifice & canal)
・Bactericidal compounds on surface of teat canal ・Humoral factors in milk (lactoferrin, opsonins, Ig) ・Cellular factors (nO & mO) |
|
|
What is the most costly disease in dairy herds?
|
Mastitis (inflammation of the mammary gland)
|
|
|
Hematogenous and percutaneous routes _____ occur.
Usually infectious agents gain access through the _____. |
Rarely/ Teat canal
|
|
|
BACTERIUM that is SPECIFIC and causes CONTAGIOUS mastitis in ruminants and healing is characteristically by FIBROSIS (→ atrophy of quarters (usu. 1))
|
Streptococcus agalactiae
|
|
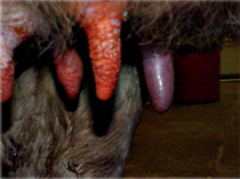
BACTERIUM that causes ACUTE inflammation due to ɑ-TOXIN and is characterized by ABSCESSES, NECROSIS (→vasoconstriction→ischemia), GANGRENE in cattle.
|
Staphylococcus aureus
|
|
BACTERIUM that is GALACTOGENIC (→sudden onset of agalactia) enters by hematogenous route, AFFECTS ALL 4 QUARTERS, responds POORLY to therapy with LACK of obvious signs of systemic illness.
|
MycoPLASMA bovis (Michael wants all the cheese and may cause Mycoplasma Otitis in calves due to contaminated milk)
|
|
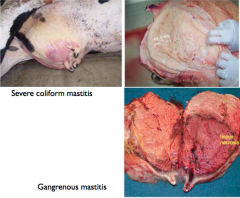
Organism that is ENVIRONMENTAL and infects cows through teat canal. May cause an ACUTE and often FATAL disease (most severe in NEWLY CALVED COWS (immunosuppressed))
|
E. coli (potent ENDOTOXIN → vascular damage → fluid exudate, hemorrhage, thrombosis & necrosis)
|
|
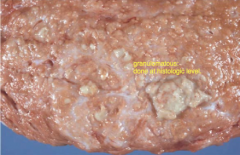
GRANULOMATOUS mastitis is often caused by...
|
・MycoBACTERIUM bovis (Hematogenous)
・Nocardia asteroides (Iatrogenic) ・Crytococcus neoformans (Iatrogenic) ・Candida spp. (Iatrogenic) |
|
|
MASTITIS in the EWE & GOAT is usually caused by...
|
Staphylococcus aureus
Mannheimia haemolytica |
|
|
A disease of goats primarily where lactating females/kids are SUSCEPTIBLE to infection and likely succumb in the SEPTICEMIC phase of the disease.
|
Contagious agalactia
|
|
|
Etiologic agent of CONTAGIOUS AGALACTIA which affects GOATS primarily (and sheep).
|
Mycoplasma agalactiae
|
|
|
Viral diseases not commonly associated with masitis but may predispose animals to secondary bacterial disease:
|
Ovine Progressive Pneumonia (Maedi-Visna)
Caprine Arthritis Encephalitis (CAE) Foot & Mouth Disease |
|
|
Mammary tumors are commonly seen in ____ and ____.
|
Bitches/Queens
|
|
|
What are the most commonly diagnosed mammary tumors in dogs?
|
Epithelial tumors (remainder are sarcomas & mixed)
|
|
|
______ at an EARLY AGE is well documented to SIGNIFICANTLY REDUCE the risk of MAMMARY TUMOR DEVELOPMENT in dogs.
|
Ovariohysterectomy
|
|
|
What neoplasm is locally invasive with a very aggressive clinical course and has the WORST PROGNOSIS?
an aggressive disease that |
Inflammatory carcinomas
|
|
|
What PROGNOSTIC FACTORS are taken into consideration when grading canine mammary tumors?
|
・Histological type (carcinoma/sarcoma/mix)
・DEGREE OF INVASION (in circulatio = poor prognosis) ・Degree of nuclear differentiation ・Lymphoid cellular reactivity ・Tumor size (>3cm) ・Ulceration ・Inflammation/inflammatory carcinoma ・Estrogen/progesterone receptor status |
|
|
YOUNGER DOGS are more likely to have ___ neoplasms than older dogs.
OLDER DOGS (>9.5 years) are more likely to have ___ neoplsms |
Benign/Malignant
|
|
|
1. Tumor >5cm in size MORE LIKELY to be ___ & MORE LIKELY to show LN ___.
2. ___ invasion & ___ metastasis are SIGNIFICANT prognostic factors |
1. Malignant/Metastasis
2. Lymphatic/LN |
|
1. How common are feline mammary neoplasms?
2. Most neoplasms in cats are ___. 3. What is the SINGLE MOST IMPORTANT PROGNOSTIC FACTOR in CATS? |
1. Not as common as in dogs.
2. Malignant 3. Tumor size (<2 cm = better prognosis) |

