![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
no serosa layer in GI has what indication |
tumors metastasize very easily |
|
|
polyhydramnios coughing when feeding |
TE fistula |
|
|
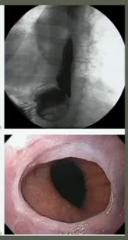
esophageal duplication cysts |
up to 30% don't present until adulthood for incidental finding
may cause dysphagia. Rarely cancer. Tx surgically |
|
|
Schatki's ring thin membranous ring at squamo-columnar junction
possible GERD. Tx with dilation |
|
|
male 70 y/o aspiration issues halitosis cough up food a lot |
Zenker's diverticulum laxity in muscles from age for pouch |
|
|
Lacerations |
Mallory-Weiss tears: syndrome. Longitudinal tear in GE junction. Often alcoholics, episodes of vomiting. Often spontaneously resolves
Boeerhaave syndrome: transmural. Emergency. |
|
|
esophagitis causes |
reflux esophagitis** eosinophilic esophagitis infectious: candida, herpes, CMV pill esophagitis irritants: hot tea, alkali or acid systemic: bullous pemphigoid, Crohn, GVHD |
|
|
difference GER and GERD |
GERD there is sx or tissue damage. 70% have normal endoscopy. Reflux esophagitis: inflam or objective evidence of injury (so from GERD) |
|
|
cough wheezing sore throat ear pain chest pain hematemesis |
reflux esophagitis!
a lot of these are common innervation for distal eso and other foregut structures. That and microaspiration |
|
|
what are the hardest things to eat? |
bread meat |
|
|
how does reflux esophagitis compare |
taller pillae with hyperplasia and inflammation |
|
|
when do you scope a pt with suspected GERD? |
men > 50 to check for cancer (never scope woman for fun for cancer)
weight loss dysphagia failure to respond to PPI after 1-2 months |
|
|
ways to monitor acid in GERD |
pH monitoring have thing inserted to measure pH |
|
|
tx GERD |
ppi funduplication |
|
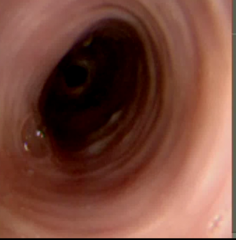
child feeding intolerance failure to thrive food impaction dysphagia failure to respond to PPI |
eosinophilic esophagitis |
|
|
eosinophilic esophagitis
tx |
increasing incidence from dx more common in children
PPI steroids allergen ID or eliminate: egg milk soy nut seafood gluten |
|
|
what woudl cause intraepithelial eosinophils |
reflux esophagitis eosinophilic esophagitis or gastroenteritis drug/pill induced esophagitis infxns achalasia |
|
|
infectious esophagitis |
immunocompromised: HIV, DM most common: candida, only surface with NO inflammation herpes CMV: giant cells |
|
|
pill induced esophageal injury |
doxycycline emepronium bromide: vasospasm KCl quinidine Fe Sulphate NSAID lye |
|
|
bullous pemphigoid |
usually demonstrate immunoglobulin G (IgG) and complement C3 deposition in a linear band at the dermal-epidermal junction, with IgG in salt-split skin found on the blister roof (epidermal side of split skin).
may be happening for years
|
|
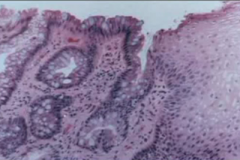
distal eso long term GERD |
barrett esophagus metaplastic columnar epithelium- intestinal metaplasia/goblet cells replace squamous epithelium in distal esophagus
increased risk of adenocarcinoma- have to watch, depending on dysplasia level |
|
|
how do you tx high grade dysplastic Barrett Esophagus? |
ablation therapy: radiofrequency ablation RFA, photodynamic therapty PDT, or cryotherapy
endoscopic mucosal resection
esophagectomy
continued surveillance |
|
|
what carcinomas happen in eso |
squamous cell carcinoma: m/c in world
adenocarcinoma most from Barrett eso, m/c in USA now (obesity related cancer) |
|
|
esophageal adenocarcinoma related factors |
obesity-related GERD and Barrett eso tobacco use lower H. pylori infxn?? |
|
|
dysphagia gradual obstruction aspiration pneumonia- TE fistula |
squamous cell carcinoma
usually middle 1/3 survival very poor |
|
|
squamous carcinoma risk factors |
China Iran (hot tea) south africa male>female balck>white drinking and smoking dietary: contamination of carcinogens genetic: SOX2 lye stricture, achalasia HPV |
|
|
different versions of squamous Ca |
keratin swirls fungating |
|
|
innervation of eso |
motor: vagus parasymp: vagus symp: all sorts ENS |
|
|
achalasia what happens causes |
motor disorder fromfailure of LES to relax decreased or absent peristalsis primary: degeneration of nerves secondary: inflam destruction of myenteric plexus Chagas dz: infxn |
|
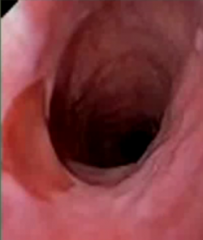
|
gastric inlet patch ectopic gastric mucosa: may cause bleeding has parietal cells in it so esophagitis or meckels diverticulum |
|
|
pyloric stenosis |
failure to thrive contraction alkalosis bilious emesis dx with US, tx with surgery |
|
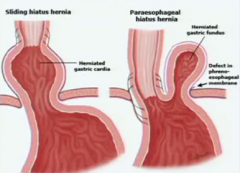
hiatal hernia |
very common sliding type 1 can contribute to reflux paraesophageal usually referred for surgical repair |
|
|
where are chief cells and pareital cells located endocrine |
chief in body and fundus parietal: body and fundus antrum: G cells D cells ECL, |
|
|
where does serotonin come from histamine |
enterchromaffin cells ECL cells |
|
|
why are NSAID's so bad |
lowers prostaglandins and causes epithelial injury also |
|
|
what is Zollinger-Ellison |
have tumor putting out gastrin so super high acid secretion |
|
|
why is H pylori so bad describe |
is under the mucus layer makes urease for inflam and ammonia which dmgs some have Cag A- changes inflam response, Cag A positive more likely to cause cancers (all cancers have H pylori)
curved or s shpaed, urease +, gram- |
|
|
how to dx h pylori |
serologic for antibodies- but could be prior dz urea breath test: carbon isotope labeled urea (can't be on PPI) stool antigen test- doesn't work if GI bleed
endoscopy: rapid urease test, histo, culture, DNA detection by PCR |
|
|
what does h pylori tx |
clarithroymycin, amoxicillin, PPI |
|
|
deep ulceration into muscularis propria exudative with PMN's necrosis granulation tissue scars |
peptic ulcer dz |
|
|
why would peptic ulcer become emergency |
perforation |
|
|
how to tx PUD |
suppress acid with PPI, heal ulcer eradicate H pylori** avoid NSAIDs
if refractory, can do surgery |
|
|
shalllow focal necrosis in otherwise normal stomach no inflam
|
acute gastric erosion |
|
|
what would cause acute gastric erosion |
NSAIDs aspirin excessive alcohol or smoking severe stress: trauma burn surgyer uremia systemic infxn cancer chemo or radiation
these all have hypoperfusion for shock, sepsis, impaired local defense, hypersecretion of gastric acid |
|
|
chronic gastritis |
histological rather than clinical entity
H pylori MCC atrophic gastritis: AI gastritis chemical: NSAID, bile reflux misc |
|
|
autoimmune gastritis |
type A, diffuse corporal, PA-associated in the body atrophy, intestinal metaplasia: ab's to parietal cells and intrinsic factor
means achlorhydria, hypergastrinemia the loss of IF means pernicious anemia increased cancer risk |
|
|
multifocal atrophic gastritis |
type B, type AB, environmental atrophy intestinal metaplasia in the antrum h. pylori, diet, environm. MCC precursor of adenoCa active -> atrophic -> IM -> dysplasia
gastrin is normal, no pernicious anemia |
|
|
differences AI gastritis and multifocal atrophic gastritis |
both atrophic
AI: in body, parietal cells, IF, pernicious anemia, hypergastrinemia
MFAG: antrum, h pylori, MC adenoCa precursor |
|
|
gastric Ca |
2nd mcc common east asia intestinal or diffuse type refrigerators help, less salt/smoke curing which cause intestinal kind
genetics |
|
|
high risk factors for gastric Ca |
no refrigeration lack fresh fruit or veg (antiox) preserved smoked salted foods water contaminated with nitrates H. pylori
AI gastritis gastrectomy for bile reflux adenomas polpys Menetrier's dz |
|
|
stepping stones from normal to carcinoma |
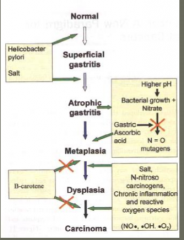
|
|
|
Menetrier's dz |
hypertrophic gastropathy |
|
|
most common place for gastric cancer |
antrum/pylorus
then cardia |
|
|
diffuse Ca characteristics |
ulcerative or infiltrative poorly differentiated, signet ring cells less frequent metaplasia equal for genders unknown or genetic cause |
|
|
intestinal Ca charactersitics |
polypoid, fungating well differentiated with gland formation universal metaplasia M>F known risk factors |
|
|
weight loss abdominal pain anorexia GI bleed anemia
|
gastric cancer |
|
|
where do gastric Ca met to |
duodenum pancreas liver lung ovary = Krukenberg tumor |

