![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
D2 receptor antagonists exert their therapeutic benefit primarily by blocking DA transmission in the __________ tract. This decreases the ________ (positive or negative) symptoms of scz.
|
mesolimbic, positive (ex. hallucinations)
|
|
|
What receptor do typical antipsychotics block? (main effect)
|
dopamine 2
|
|
|
What receptors do typical antipsychotics block that lead to unwanted side effects? What are these side effects?
|
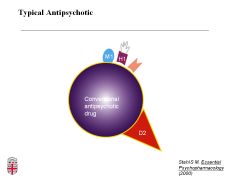
muscarinic (M1): blurry vision, dry mouth, conspitation, urinary retention
histaminic (H1): sedation, weight gain and alpha-1: orthostatic hypotension |
|
|
What is akasthesia?
|
subjective feeling of restless in the lower extremities
**can treat with beta blockers |
|
|
What side effects does a D2 receptor blockade have on the three dopamine pathways that it is not targeting? 1. nigrostriatal, mesocortical, tuberoinfundibular
|
1. nigrostriatal: extrapyramidal symptoms (dystonia, parkinsonism, akathsia)
2. mesocortical: worsening of negative symptoms (alogia, affective flattening, apathy) 3. tuberoinfundibular: hyperprolactinemia (infertility, decreased bone density) |
|
|
What are some symptoms of Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome? What is the appropriate treatment?
|
muscle rigidity, fever, autnomic instability, elevated WBC, elevated CPK
treatment: stop antipsychotic, supportive treatment |
|
|
What is tardive dyskinesia?
|
involuntary choreoathetoid moveents of the face, trunk, or extremities
|
|
|
_______ and ________ are high potency typical antipsychotics. ___________ is low potency.
terms: haloperidol, chlorpromazine, fluphenazine |
high potency: haloperidol, fluphenazine
low: chlorproazine |
|
|
What two receptors do atypical antipsychotics block?
|
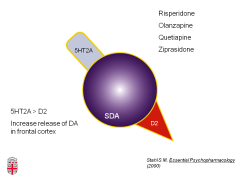
D2 and 5HT2A
|
|
|
Which neurotransmitter binds to a 5HT2A receptor?
|
serotonin
|
|
|
What is the normal effect of serotonin on dopamine release?
|
serotonin attenuates dopaine release
|
|
|
True or False: The effects of combined 5HT and DA antagonism (via an atypical antipsychotic) results in a smaller DA blockade in the mesocortical, nigrostriatal and tuberoinfundibular pathways.
|
True.
|
|
|
What is the major side effect of atypical antipsychotics?
|
metabolic syndrome
|
|
|
What is the most effective antipsychotic?
|
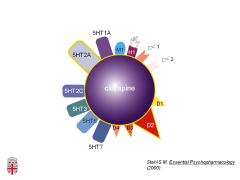
Clozapine
**dirty drug, hits a lot of receptors |
|
|
Approximately ______ percent of scz patients discontinued their medication due to ineffectiveness or side effects.
|
75
|
|
|
What are some psychosocial approaches to treatment?
|
family education/therapy, CBT, supported employent, assertive community treatment, social skills training
|
|
|
What effect does an atypical antipsychotic have on the mesocortical pathway?
|
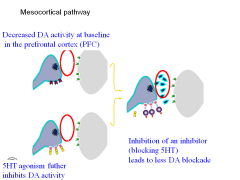
Normally, serotonin at the 5HT2A receptor decreases dopamine activity (which is already too low in scz patients).
An atypical antipsychotic would inhibit the inhibition of dopamine by serotonin--> Less DA blockade |

