![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Macrocytic anemia
|
Regenerative
|
|
|
Microcytic anemia
|
Fe deficiency
|
|
|
Where do we examine RBC & WBC morphology?
|
Counting area
|
|
|
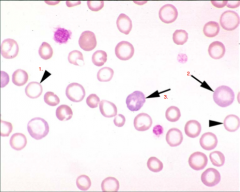
1. Hypochromasia (Less color)
2. Polychromasia (Blue color in young platelets) 3. Macro platelet |
|
|
1. What is hypochromasia associated with?
2. When we see polychromasia, it means...? 3. What do we call an erythrocyte stained with NMB (New Methylene Blue) stain? 4. What do we call an erythrocyte stained with Wright's stain? |
1. Iron deficiency
2. BM is responding 3. Reticulocyte 4. Polychromatic cell |
|
|
What are the 2 main options for a REGENERATIVE anemia?
|
Blood loss
Blood destruction (Recovering BM) |
|
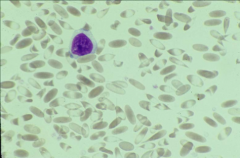
1. What type of anemia does this llama have?
2. In what animals do we not see an ↑central pallor with iron deficiency? |
1. Fe deficiency anemia
Spiculated points (keratocytes) & hypochromasia (↑central pallor) are the clues 2. CATS |
|
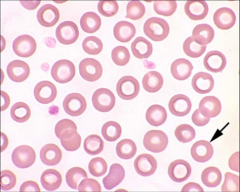
Is this true hypochromasia?
|
No, it is an incidental finding.
|
|
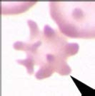
What spiculated RBC shape is this?
|
Acanthocytes
|
|
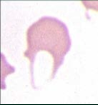
1. What spiculated RBC shape is this?
2. The fragments of the RBC released are called? |
1. Keratocyte (karate kick)
2. Schistocytes |
|

What RBC shape is this?
|
Spherocytes
|
|
|
What are in-vitro & in-vivo causes of ECHINOCYTES?
|
IN-VITRO:
Crenation (dries on slide) IN-VIVO: Rattlesnake envenomation (reversible shape change) |
|
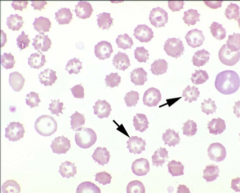
1. What spiculated RBC shape are these?
2. What is this shape diagnostic for? 3. Are polychromatic cells affected by rattlesnake envenomation? |
1. Echinocytes (numerous short spicules of similar size)
2. Rattlesnake envenomation 3. Middle right shows they are not. |
|
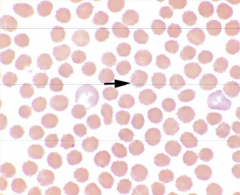
After a rattlesnake bite, is this RBC shape change seen in horses/cattle?
|
Because of the size, normally echinocytes (starfish) are not seen.
|
|
|
1. What are ACANTHOCYTES diagnostic for in CATS?
2. What are ACANTHOCYTES diagnostic for in DOGS? 3. How can we differentiate acanthocytes from echinocytes? |
1. Hepatic lipidosis
2. HSA 3. Acanthocytes are usually UNEVENLY distributed due to △'s in [LIPID] in RBC membrane. |
|
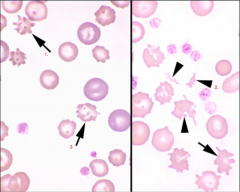
Identify structures:
1. 2. 3. |
1. Acanthocytes
2. Schistocytes 3. Acanthocytes |
|
|
When do schistocytes become evident?
|
IV trauma (DIC (will see ↓platelets), HSA)
Fe Deficiency Anemia |
|
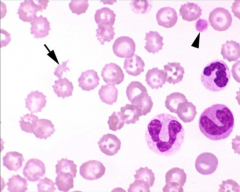
What is your diagnosis?
|
Presence of schistocytes and few platelets suggest DIC.
|
|
|
1. Keratocytes are pathognomonic for...
2. Acanthocytes are pathognomonic for... 3. Spherocytes are pathognomonic for... |
1. Fe deficiency anemia (Iron kick)
2. Hemangiosarcoma (Dogs) & Hepatic lipidosis (Cats) 3. IMHA |
|
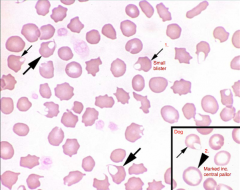
Identify the cells/structures & what is your diagnosis?
1. 2. Dx: |
1. Keratocyte
2. Hypochromatic cell Dx: Fe deficiency in the cat and dog (REMEMBER: no ↑in central pallor in the cat) |
|
|
What is a spherocyte?
|
An erythrocyte that appears small & lacks central pallor.
Volume = normal & pathognomonic for IMHA |
|
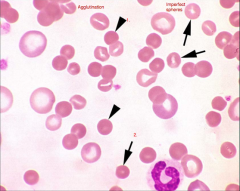
Identify the cells/structures & what is your diagnosis?
1. 2. Dx: |
1. Spherocyte
2. Imperfect sphere (incidental finding) Dx: IMHA based on spherocytes and AGGLUTINATION |
|
|
What antibody is required for agglutination of RBC to occur?
|
IgM (if IgG, then agglutination will not occur)
|
|
|
In IMHA, does IV hemolysis or extravascular hemolysis occur?
|
Both occur. IV hemolysis leads to ↑hemoglobin in the blood.
|
|
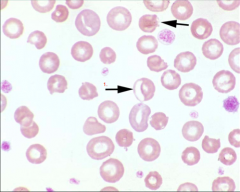
Identify the cell & what causes this polarization?
1. Cause: |
1. Eccentrocytes
Cause: Oxidative damage (onion, drugs) causes shifting of Hgb to one side of cell. |
|
|
Eccentrocytes are often seen in conjunction with ___ formation.
|
Heinz body formation
|
|
|
What are two indications of oxidative damage to cells caused by ingestion of onions or other substances that oxidatively denature hemoglobin?
|
Eccentrocytes (RBC membrane selectively affected)
Heinz body formation (Hgb denatured) |
|
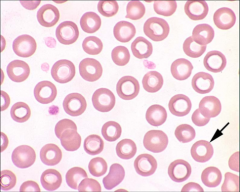
Identify the cells/structures & what is its significance?
Arrow: Significance: |
Arrow: Target cell
Significance: NONE |
|
|
What cells/structures have little/no diagnostic significance?
|
1. "Target" cells
2. "Bowl" shaped cells (due to force; aka torocytes) 3. Folded cells |
|
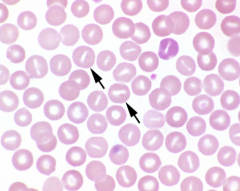
Identify the cells/structures, in what breeds is this hereditary, & what is its clinical significance?
Arrow: Breeds: Clinical significance: |
Arrow: Stomatocytes
Breeds (hereditary stomatocytosis): Alaskan malamutes, Miniature schnauzer, Drentse partrijshond Clinical significance: chondrodysplasia (dwarfism) in malamutes |
|
|
1. How can we confirm Heinz bodies?
2. In what animal may Heinz bodies be an INCIDENTAL FINDING? 3. What are their significance? |
1. Staining with NMB (New Methylene Blue)
2. Heinz bodies in CATS can be an incidental finding in contrast to dogs. 3. Precipitates of DENATURED & OXIDIZED hemoglobin |
|
|
What are potential erythrocyte oxidants associated with Heinz body hemolytic anemia in CATS?
|
Acetaminophen toxicosis
Zn toxicosis Onions Propylene glycol in cat food Illness (Diabetes mellitus, HyperTHYROIDism, Lymphosarcoma) Garfield saying: "O"- PIZA |
|
|
What are potential erythrocyte oxidants associated with Heinz body hemolytic anemia in DOGS?
|
Onions
Cephalosporins Zn toxicosis Odie being "CO-Z" |
|
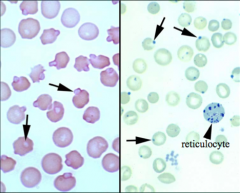
Identify the cells/structures pointed by the arrows, what stain was used to confirm their presence & what are their clinical significance?
Arrow: Stain: Significance: |
Arrow: Heinz bodies
Stain: New Methylene Blue [R] Significance: Denatured, oxidized, precipitated hemoglobin. |
|
|
1. What are potential erythrocyte oxidants associated with Heinz bodies in HORSES?
2. ...CATTLE? 3. ...SHEEP? |
1. WILTED red maple leaves (FATAL) & Phenothiazine
2. Onions & Kale 3. Cu toxicosis |
|
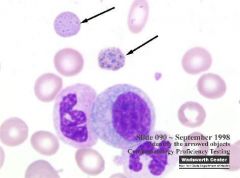
Identify the cells/structures indicated by the arrows, how do the form & what are their clinical significance?
Arrow: Formation: Significance: |
Arrow: Basophilic stippling
Formation: Abnormal aggregation of ribosomes Significance: Lead poisoning in small animals (ABSENCE of anemia) |
|
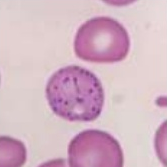
In what species are these cells normally found and what are they called?
Species: Name: |
Species: Ruminants
Name: Basophilic stippling |
|
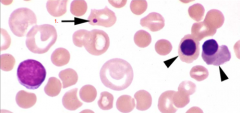
Identify the cells/structure & what are their clinical significance?
1. Significance: |
1. Howell-Jolly body
Significance: Splenic disease/splenectomy (normally removed by spleen) Regenerative anemia (normal) ↑Corticosteroids (mO not able to work) **Lead poisoning (ABSENCE of anemia)** |
|
|
What 2 findings may suggest LEAD POISONING?
|
Basophilic stippling (abnormal in SA)
Howell-Jolly bodies (ABSENCE of anemia) |
|
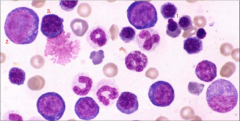
Identify the cells/structure:
1. 2. 3. |
1. Metarubricyte
2. Rubriblast (Can see nucleolus within nucleus) 3. Prorubricyte |
|
|
What is the most common bacterial parasite by far?
|
Mycoplasma haemofelis
|
|
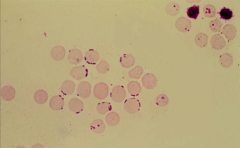
1. Identify the parasitic organism.
2. What does it cause? |
1. Mycoplasma haemofelis (small blue cocci/rings/rods on the edges/surface of the RBC)
2. Hemolytic anemia |
|
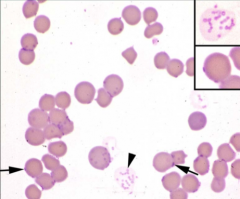
1. Identify the parasitic organism.
2. What does it cause? |
1. Mycoplasma haemofelis
2. Hemolytic anemia |
|
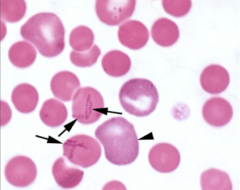
1. Identify the parasitic organism.
2. When are we more likely to see these organisms? 3. What is the cause of the anemia with RBC parasites? |
1. Mycoplasma haemocanis (chains of cocci across the face of the RBC)
2. Splenic disease/splenectomy (normally removed by spleen) 3. Ab-Ag complexes with parasite (by mO/complement) |
|
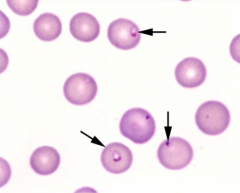
Identify the parasitic organism.
|
Cytauxzoon felis (FATAL, protozoan; "SITE-SUMIDO")
|
|
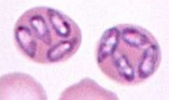
Identify the protozoal parasite that appears single or multiple pear shaped within the RBC.
|
Babesia canis (I miss you Babe = teardrop)
|
|
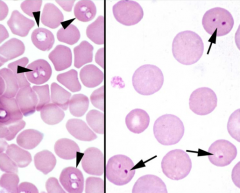
Identify the protozoal parasites indicated by the arrows.
|
[L] Babesia canis (I miss you Babe = teardrop)
[R] Babesia gibsoni (I miss you Babe = teardrop) |
|
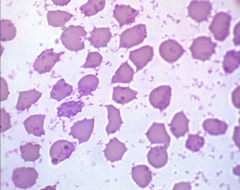
Blood drawn from a cow.
Identify the protozoal parasites. |
Mycoplasma wenyoni
|
|
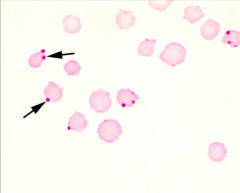
Identify the protozoal parasites indicated by the arrows.
|
Anaplasma marginale
|
|
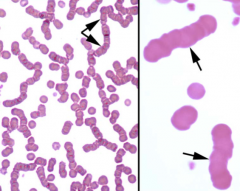
1. What is significant of this arrangement in horses?
2. ...in small animals? 3. How can we differentiate agglutination from rouleaux? |
1. Normal
2. ↑globulin 3. Add isotonic saline |
|
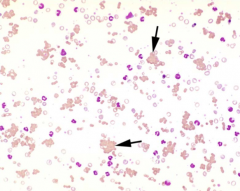
What is significant of this arrangement in small animals?
|
IMHA = Ab attachment (IgM)
|

