![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Arteriography shows narrowing of radius by 50%. What is the expected change in blood flow?
|
Decrease radius by 1/2-->Increase resistance 1/16
Thus flow will decrease to 1/16 |
|
|
When a person moves from a supine position to a standing position, what compensatory changes occur?
Why? |
Standing will DECREASE venous return, DECREASE cardiac output, DECREASE arterial pressure
Need to INCREASE contractility to INCREASE HR |
|
|
What does an increased ejection fraction signify?
What is its effect on end-systolic volume? |
EF = SV/EDV
An increase in EF means a higher fraction of end-diastolic volume is ejected in stroke volume (could be due to administration of a positive inotropic agent). When this occurs, the volume remaining in the ventricle after systole DECREASES. |
|
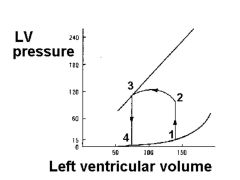
If HR is 70 bpm, calculate cardiac output.
|

SV = 140-60 = 80
Q = 80 * 70 = 5600 mL = 5.6 L |
|
|
The ventricles are completely depolarized in which isoelectric portions of the EKG?
|
Only isoelectric segments of EKG are PR and ST
Ventricular depol occurs during ST |
|
|
Patient develops orthostatic hypotension after sympathectomy.
This is due to a/n [exaggerated/suppressed] response of the baroreceptor mechanism. |
Suppressed bc no longer has sympathetic circuit to increase HR/contractility
|
|
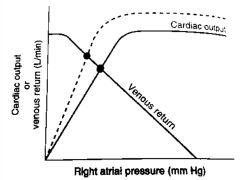
The dashed line in the figure illustrates the effect of __________.
|

Increased contractility
|
|
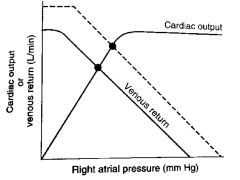
The dashed line in the figure illustrates __________.
|
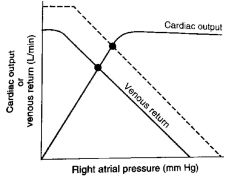
Increased blood volume, thus, increased mean systemic pressure
|
|
|
How can venous pressure be modified to increase tendency for edema to occur?
|
Increased venous pressure will increase tendency for edema.
|
|
|
The upstroke of the action potential in the SA node is due to the influx of ______.
|
Ca2+
|
|
|
The upstroke of the action potential in Purkinje Fibers is due to influx of ______.
|
Na+
|
|
|
In the SA node, phase 4 depolarization is attributable to ______.
|
Increase in Na+ conductance
|
|
|
alpha1 vs beta2 effects
|
alpha1: Vasoconstriction of arteriolar smooth muscle
beta2: VasoDILATION of arteriolar smooth muscle |
|
|
During which phase of the cardiac cycle is aortic pressure highest?
|
Reduced ventricular ejection (right after rapid ventricular ejection ends)
|
|
|
What is the effect of histamine on arterioles?
|
Dilation
|
|
|
During which phase of the cardiac cycle is ventricular volume lowest?
|
Isovolumetric ventricular relaxation; volume ;lowest when ventricle is relaxed (diastole)
|
|
|
During which phase of the ventricular action potential is the conductance to Ca2+ highest?
|
Phase 2 of plateau (right before repolarization)
|
|
|
Aldosterone vs ADH
|
ADH: increase arterial bp, increases water permeability of distal tubule and collecting ducts
Aldosterone: Indirectly increases water resorption via retention of Na+ |
|
|
EF 0.4
HR 95 bpm Q 3.5 L/min EDV? |
EF = SV/EDV
Q = HR x SV =92 mL |

