![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the range for Left Axis Deviation?
Causes? |
LAD: -31 to -90
Causes: LVH LBBB (conduction abnormality) |
|
|
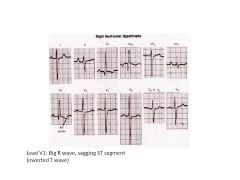
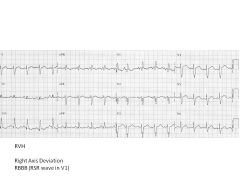
What is the range for Right Axis Deviation?
Causes? |
RVH
Lateral MI COPD, PE (Pulmonary Disease) -1 to -90 +91 to 180 |
|
|
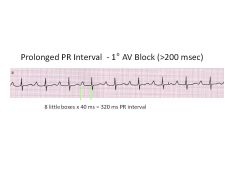
Long PR interval suggests ______.
Cutoff? |
>3 boxes
Delay in AV conduction |
|
|
Prolonged QRS suggests _______.
Cutoff? |
>3 boxes:
BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCK |
|
|
Prolonged QT suggests _______.
Cutoff? |
>1/2 RR:
Low Ca2+ OR predisposition for ventricular arrhythmia |
|
|
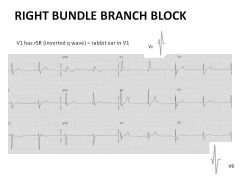
Causes of RBBB?
|
Anything that strains the right heart (pulmonary embolus, Pulm HTN, Pulm stenosis)
ASD with L-to-R shunt Aging can lead to this! Does not require treatment Not necessarily abnormal. |
|
|
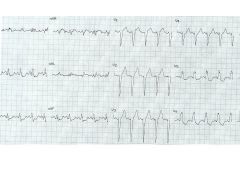
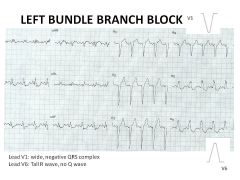
Causes of LBBB?
|
Organic heart disease:
Valvular Heart Dz CM Coronary Dz, esp prior MI HTN SEVERE!!! |
|
|
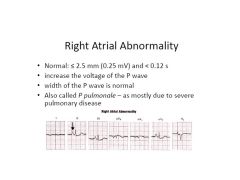
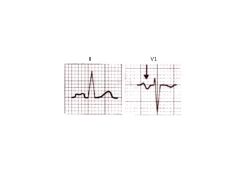
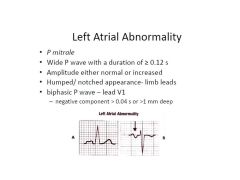
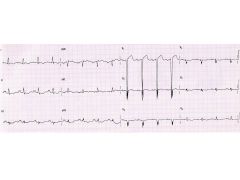
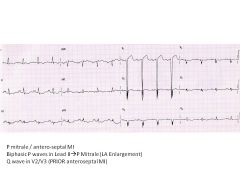
P Pulmonale vs P Mitrale
|
P Pulmonale: RA enlargement
P Mitrale: LA enlargement (looks like an M--for Mitrale) |
|
|
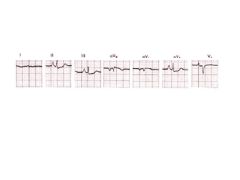
Pointed Q waves in these leads are indicative of an INFERIOR infarction.
|
II, III, AVF
|
|
|
Pointed Q waves in these leads are indicative of an ANTERIOR infarction.
|
V1, V2, V3, V4
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
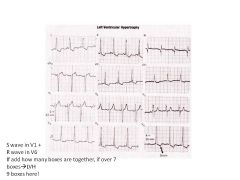
|
|
|
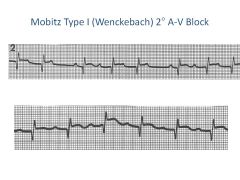
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
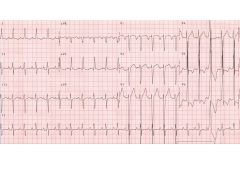
|
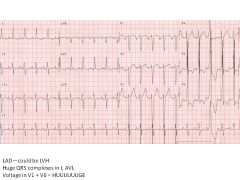
|
|
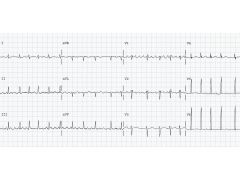
|
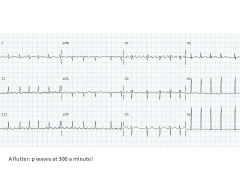
|
|
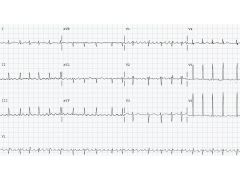
|
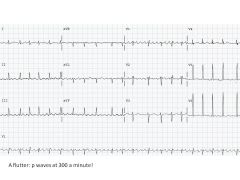
|

