![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is cardiac myopathy |
conditions of muscle of heart
(myopathy --> disease of muscle tissue in which muscle fibres do not function, for various reasons)
|
|
|
abnormalities of the heart can be divided into 2 categories, what are these and what are the possible complications that could occur under each category |
electrical: cardiac arrythmia structural: heart valves ventricular muscle coronary arteries |
|
|
what are the 4 main areas in which the imaging of the heart focuses? |
valves Chambers coronary arteries left ventricle |
|
|
in the heart valves, what is imaging useful for seeing |
stenosis regurtitation |
|
|
in the chambers of the heart, what is imaging useful for |
the general structure and function of the chambers |
|
|
in the coronary arteries of the heart, what is the imaging useful for and what imaging type is particularly useful for coronary problems? |
stenosis
Myocardial perfusion scan (also referred to as MPI) is a nuclear medicine procedure that illustrates the function of the heart muscle (myocardium). It evaluates many heart conditions such as coronary artery disease (CAD), hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and heart wall motion abnormalities. |
|
|
what potential problems can be seen in the heart left ventricle using cardiac imaging |
hypertrophy infarction (obstruction of the blood supply to an organ or region of tissue, typically by a thrombus or embolus, causing local death of the tissue). |
|
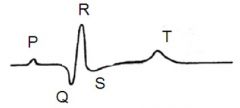
what is the P wave showing on an ECG |
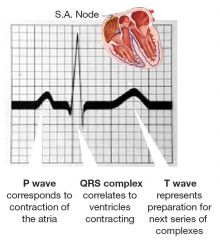
atrial contraction/ depolarisation |
|
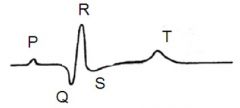
what does the flat line between the P and Q phase in an ECG correspond to |
the electrical conduction spreading between the SA node and the AV node |
|
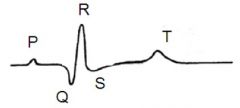
what does the QRS phase on an ECG correspond to |
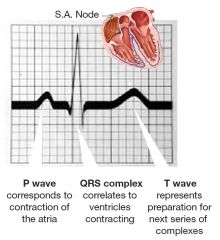
ventricular contraction/depolarisation |
|
|
where is the 12 lead ECG placed |
on the skin of the limbs and across chest |
|
|
what is the ECG a measure of |
the conducting system of the heart/ the electrical activity in the heart |
|
|
under what circumstances X-rays normally done, and what is the main benefit in terms of heart of doing an X-ray |
in emergencies it can give info on the size of the heart |
|
|
from where is the ultrasound submitted from in 2d-echocardiography |
an echo probe |
|
|
what is the first and second structures which the echo probe comes across in the echocardiography |
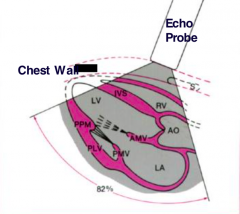
first right ventricle then left ventricle |
|
|
what different angle of echocardiography exist |
long axis short axis four chamber |
|
|
from what angle is long axis view taken in an echocardiography |
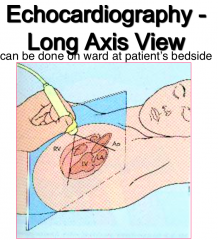
|
|
|
what does the heart image seen look like on the long axis view of echocardiography |
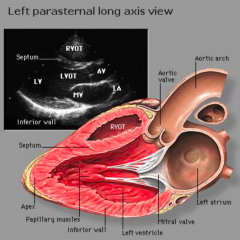
from the top |
|
|
from what angel is the short axis view taken in an echocardiography |
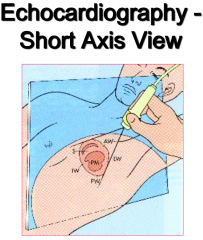
|
|
|
what does the heart image seen look like on the short axis view of echocardiography |
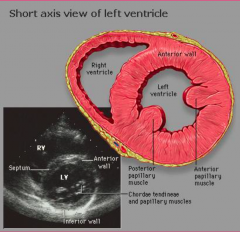
|
|
|
from what angel is the four chamber view taken in an echocardiography |
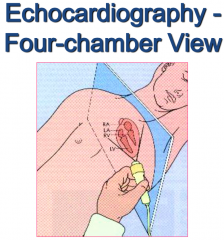
|
|
|
what does the heart image seen look like on the four chamber view of echocardiography |
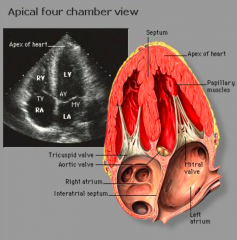
|
|
|
what is the echo doppler particularly useful for seeing clinically |
heart valve regurtitation |
|
|
what is MRI good for seeing in general |
•Tissues •Structures •Blood flow |
|
|
what are the main clinical uses of MRI in heart tissue |
it can be used to see regurgitation occurring "live"
(can be used to differentiate between normal and scar tissue) |
|
|
what is cardiac angiography |
radiography of blood or lymph vessels, carried out after introduction of a radiopaque substance. |
|
|
err yea....cardiac CT can also be used btw.... there are no questions to think about it haha |
err yea....cardiac CT can also be used btw.... there are no questions to think about it haha |
|
|
what different types of cardiac imaging are there |
-12 lead ECG -Chest X-Ray -2D echocardiography -Echo doppler -MRI -Coronary angiography -Cardiac CT |

