![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Valvular Disease:
Causes Valves Commonly Affected |
Causes of Valvular Dz:
Malformations, deformations, stenosis, insufficiency (abnormal cusp/leaflet) 2/3 of all lesions are ACQUIRED lesions of MV or AV |
|
|
Where does calcification occur in the heart? Generally and specifically.
Is calcium all that's seen in calcifications? |
Calcium deposited in areas of wear and tear
Most frequently affects aortic valve and/or mitral annulus Bicuspid aortic valve especially prone Don't just see Ca2+, but also see lipid deposition and atherosclerosis |
|
|
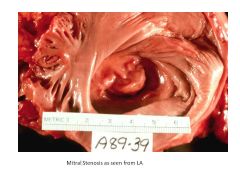
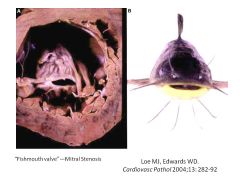
Rheumatic Heart Disease is a common cause of ___________.
|
Calcific Aortic Stenosis
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of calcific aortic stenosis?
|
Aging
(Stenosis = stiffening) |
|
|
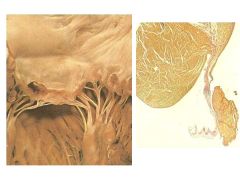
What is the mitral annulus?
Effect of calcification? |
Fibrous ring that surrounds the mitral
Calcification often does not impair valve function but can contribute to mitral insufficiency or mitral stenosis (Often continuous with calcium deposits in AV cusps) (Can extend into skeleton or conduction system) |
|
|
What causes mitral valve prolapse?
Effects? Complications? |
Myxomatous (weakening of CT) degeneration of mitral valve; manifestation of MARFAN SYNDROME (mutation in fibrillin gene)
Leaflets become large, hooded, floppy Can cause emboli, arrhythmia |
|
|
What valvular complication exhibits decreased expression of hyaluronan?
|
Mitral Valve Prolapse
|
|
|
Rheumatic Heart Disease:
Causes |
Hypersens Rxn induced by Group A Strep; Abs against M proteins of streptococci cross-react w/glycoprots in heart/other organs
|
|
|
What is an Aschoff body?
|
Area of fibrinoid necrosis/degeneration surrounded by macs, giant cells, lymphocytes.
Indicative of Rheumatic Heart Dz |
|
|
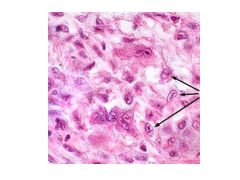
What is an Anitschkow cell?
|
Large mac with abundant amphophilic cytoplasm and nuclear chromatin which forms central irregular ribbon resembling a CATERPILLAR
Indicated of Rheumatic Heart Dz (NOT 100% OF THE TIME) |
|
|
Effects of Rheumatic Heart Disease on endocardium.
|
Endocarditis - necrosis in cusps/leaflets (usually AV or MV), may extend to chordae tendinae
Results in fibrosis with thick, stiff cusps and/or leaflets; chordae retract, thicken and fuse |
|
|
What is infective endocarditis?
Complications? |
Colonization with our without invasion of endocardium (not always on a valve)
Often destroys underlying tissue Can colonize prosthetic valves Complications: Valvular stenosis/insufficiency Abscess in annulus, paravalvular leak (prosthesis) |
|
|
Cause of Acute Bacterial Endocarditis?
|
Acute: due to highly virulent organisms such as staph aureus; can affect previously normal valves, risk of septic emboli
|
|
|
Cause Subacute Bacterial Endocarditis?
|
Organisms of lesser virulence at sides of enthelial injury (previously deformed valves or impact of high velocity flow)
Less destruction of underlying tissue than in acute bacterial endocarditis |
|
|
Causes of nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis?
Histologic difference from bacterial endocarditis? |
Debilitated patients (OLD)
Small noninfected, loosely attached masses of fibrin, platelets, othe rblood components on valves are deposited THROMBI WITH NO INFLAMMATION |
|
|
What form of endocarditis is associated with Lupus?
|
Libman-Sacks Endocarditis
|
|
|
What is carcinoid syndrome?
|
Fibrous plaque-like endocardial thickening on walls of chambers/valves
Secrete SEROTONIN If have high levels of serotonin, likely to have Carcinoid Syndrome Likely to be on Right Side of Heart |
|
|
Mechanical vs Tissue Prosthetic Heart Valves
|
Mechanical: non-physiological biomaterials
Tissue (bioprosthetic): chemically-treated animal tissue mounted on frame |
|
|
Complications of Prosthetic Valves
|
Embolism
Structural Deterioration |
|
|
Complications of Cardiac Transplant
|
Lymphocytic myocarditis (signs of rejection)
Long-term progressive intimal thickening of coronary arteries (graft arteriosclerosis) Lymphomas related to EBV in immunosuppressed pt |
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|

