![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
please define rheumatoid arthritis
|
a systemic autoimmune disease that attacks joints by producing a proliferative synovitis that leads to the destruction of the articular cartilage and underlying bone
|
|
|
|
disease process of rheumatoid arthritis
|
- basically an aberrant immune response that leads to synovial inflammtion and destruction of joint architecture
- genetic predisposition + immunologic trigger - CD4+ helper T cell activation - release of cytokines (e.g. TNF, IL-1), and antibodies - neutrophils, macrophages and lymphocytes attracted to the area - neutrophils and macrophages phagocytosethe immune complexes (like IgG + RF), releasing lyosomal enzymes capable of causing destructive changes to the joint - inflammatory response attracts more inflammatory cells to the area - inflammatory response also triggers angiogenesis, synovial proliferation and pannus invasion - effects of inflammation and structural changes include ---instability ---reduced motion ---muscle atrophy from disuse ---deformity ---redness, heat, swelling, pain, loss of function |
|
|
|
what is pannus?
|
- differentiates RA from other forms of inflammatory arthritis
- destructive vascular granulation tissue - it extends from the synoviom to the bare area of the bone at the junction of articular cartilage - inflammatory cells wihin pannus have a destructive effect of cartilage and bone - eventually develops between joint margins leading to reduced motion and ankylosis - picture overleaf |
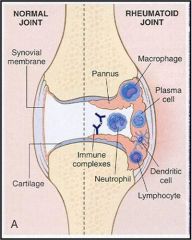
|
|
|
what is ankylosis?
|
stiffness and rigidity of a joint
|
|
|
|
what does aberrant mean?
|
'departing from the acceptable standard'
|
|
|
|
what are the clinical manifestations of RA?
|
- both joint and systemic
- RA is characterised by exaccerbations and remissions - variable - may involve a few joints for short periods or relentlessly progressive and debilitating - some recover completely |
|
|
|
what are the joint manifestations of RA?
|
- usually symmetrical and polyarticular
- joint pain and stiffness, 30 mins to several hrs - limitation of movement (initially due to pain, then to fibrosis) - most frequently affected joints are hands, fingers (MCP and PIP), wrists and feet, later may involve more - deformities due to forces applied from muscle and tendon imbalances secondary to swelling and thickening of the synovium -long term may casuse neurologic complications, occipital headaches, muscel weakness, numbness and tingling |
|
|
|
what are some extra-articular manifestations of RA?
|
-fatigue, weakness, anoerxia, weight loss, low grade fever
- vasculitis in small and medium sized arteries - haematologic abnormalites - pulmonary disease - cardiac complications - infection |
|

