![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
10 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
NICE guidelines for prescribing anti-hypertensives
|
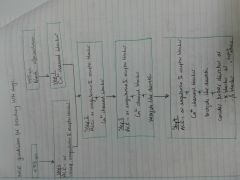
|
|
|
ideal blood pressure values to maintain
(and in diabetes/renal disease) |
<140/90
<130/80 |
|
|
lifestyle changes to manage HTN (5)
|
-lose weight if big fat fatty
-exercise -reduce salt intake -reduce alcohol intake -stop smoking(not realated to HTN but is also a major cardiovascular risk) |
|
|
6 main anti-hypertensives
|
-beta-blockers
-alpha-blockers -diuretics -ACE-i -angiotensin II receptor blockers -calcium channel blockers |
|
|
e.g., action, effect, adverse effects
-BETA-ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR BLOCKERS -alpha-blockers -diuretics -ACE-i -angiotensin II receptor blockers -calcium channel blockers |
-e.g.PROPANOLOL (BETA 1 AND 2), ATENOLOL (BETA 1 SPECIFIC)
-COMPETITIVE REVERSIBLE ANTAGONIST - bind to receptor sites but are silent - prevent access of norad to site -decrease HR -decrease contractility -to lesser extenet decrease RENIN release from kidney -adverse effects - exacerbate asthma, intolerance to exercise, hypoglycaemia, vivid dreams |
|
|
e.g., action, effect, adverse effects
-beta-blockers -ALPHA ADRENORECEPTOR BLOCKERS -diuretics -ACE-i -angiotensin II receptor blockers -calcium channel blockers |
-e.g. phentolamine (alpha 1 and 2), doxazocin (alpha 1 selective)
-COMPETITIVE REVERSIBLE ANTAGONIST -reduce sympathetic ton in arterioles -adverse effects - postural hypotension, reflax tachycardia |
|
|
e.g., action, effect, adverse effects
-beta-blockers -alpha-blockers -DIURETICS -ACE-i -angiotensin II receptor blockers -calcium channel blockers |
-eg BENDROFLUMATHIAZIDE
-reduces renal reabsorption of Na and water -small vasodilator action too -adverse effects - hypokalaemia |
|
|
e.g., action, effect, adverse effects
-beta-blockers -alpha-blockers -diuretics -ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITOR -angiotensin II receptor blockers -calcium channel blockers |
-eg. captorpil, enalapril, ramopril, perindopril
-reduced formation of angiotensin II vasoconstrictor -reduced release of aldosterone -adverse effects - sudden fall in BP with first dose, persistant cough due to reduction of bradykinin breakdown - an peptide that activates sensory nerves in the lungs) |
|
|
e.g., action, effect, adverse effects
-beta-blockers -alpha-blockers -diuretics -ACE-i -ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS -calcium channel blockers |
-eg LOSARTAN, CANDESARTAN (AT1 blockers)
-there are 2 receptor subtypes AT1 and AT2 -AT1 receptor mediates vasoconstricor action and aldosterone releasing action of angiotensin II -no cough as with ACE-i |
|
|
e.g., action, effect, adverse effects
-beta-blockers -alpha-blockers -diuretics -ACE-i -angiotensin II receptor blockers -CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS |
-e.g. - VERAPAMIL, DILTIAZEM, NIFEDIPINE
-act on L-type (long acting) voltage gated calcium channels, decresing Ca entry into smooth and cardiac muscle by 1 - open channel block (veramapril and diltiazem, block channel once opened) 2 - allosteric modulation (nifedipine, binds to allosteric site and reduce probability of it opening) -relax vascular smooth muscle - vasodialtion -decrease CO by action on cardiac muscle -adverse effects - headache, constipation, arrythmias |

