![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
heat capacity |
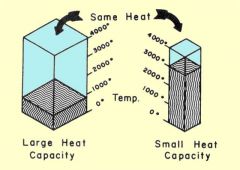
is the amount of heatrequired to raise the temperature of an object or substance one degree. The temperature change is the difference between the final temperature ( Tf ) and the initial temperature ( Ti ). |
|
|
energy |

a property of objects which can be transferred to other objects or converted into different forms, but cannot be created or destroyed |
|
|
carbon dioxide |

Carbon dioxide is a colorless and odorless gas vital to life on Earth. This naturally occurring chemical compound is composed of a carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. |
|
|
carbon footprint |

The GHG footprint, or greenhouse gas footprint, refers to the amount of GHG that are emitted during the creation of products or services. It is more comprehensive than the commonly used carbon footprint, which measures onlycarbon dioxide, one of many greenhouse gases. |
|
|
greenhouse effect |
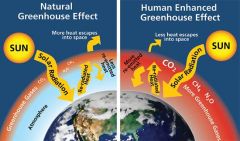
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be in the absence of its atmosphere. If a planet's atmosphere contains radiatively active gases (i.e. greenhouse gases) the atmosphere radiates energy in all directions. |
|
|
air pressure |
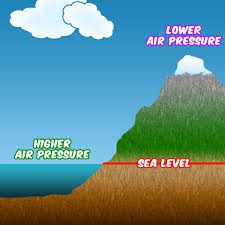
Atmospheric pressure, sometimes also called barometric pressure, is the pressure exerted by the weight of air in the atmosphere of Earth (or that of another planet). In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. |
|
|
solar radiation |
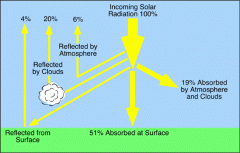
is radiant energy emitted by the sun, particularly electromagnetic energy. About half of the radiation is in the visible short-wave part of the electromagnetic spectrum. |
|
|
re-emitted heat |
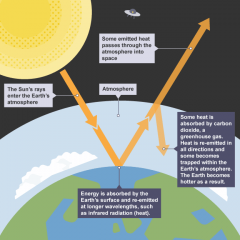
to send forth (liquid, light, heat, sound, particles, etc.); discharge. |
|
|
atmospheric temperature |
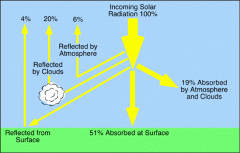
is a measure oftemperature at different levels of the Earth'satmosphere. It is governed by many factors, including incoming solar radiation, humidity and altitude. |
|
|
carbon emission |

Carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere, and the emissions of other GHGs, are often associated with the burning of fossil fuels, like natural gas, crude oil and coal. |
|
|
concentration |

In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: massconcentration, molar concentration, numberconcentration, and volume concentration. |

