![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a 3rd generation type geometry for modern CT scanners?
|
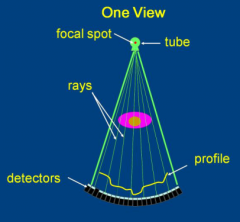
Tube and opposing detector array are fixed with relative to the detector array and both components rotate around patient.
|
|
|
What allows the gantry to rotate continuously with disrupting the electronics?
|
Slip rings allow continuous transmission of electrical energy for power or data
|
|
|
what defines a ray?
|
each detector the with focal spot of the xray tube
|
|
|
What is the main issue with CT xray tubes that require high output and extended operation?
|
Heat dissipation with water or oil
2 types of cooling designs: 1) Rotating anode, stationary tube envelope 2) Rotating envelope tubes |
|
|
What tube voltages are CT's designed to operate at?
|
80-140 kV
20-100 kW Focal spot of 0.6-1.2 mm |
|
|
Describe how bow-tie filters work
|
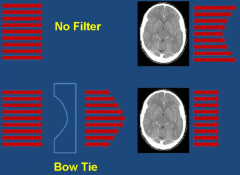
more beam attenuation near edges than at its center. The edge of patients do not require as much radiation as the center to form the image. this reduces scatter and makes the radiation dose more uniform throughout the patient. Limits range of intensities seen by the detector and makes the noise more uniform.
|
|
|
What are the 2 types of CT detectors?
|
1) Scintillator
2) Gas detector |
|
|
how does a scintillator detector work?
|
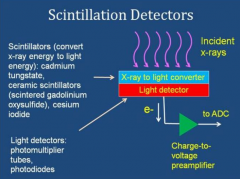
incident photons emit light which can be amplified by a photomultiplier tube or solid state device (photodiode)
|
|
|
How does a gas detector work?
|
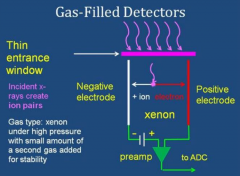
Photons interact with Xenon in a gas chamber accross which a voltage is applied. Each interaction results in ionization which can be quantified
|
|
|
Multislice vs. Single slice
|
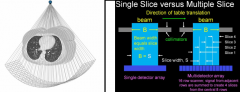
|
|
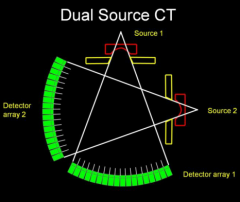
What are the benefits of a dual source CT design?
|
1) Speed
2) Can obtain attenuation maps using different energies which allow for material specific reconstructions and post processing (ie. contrast can be removed thereby generating pre- and post contrast equivalents on a single scan.... lower patient dose. |
|
|
When referring to CT, why do we use effective mAs instead of conventional definition of radiographic mAs
|
because a given point in the patient is only in the beam for a portion of the time that the tube is turned on.
|
|
|
How do kVp and mAs affect the number of photons and their energy distributions?
|
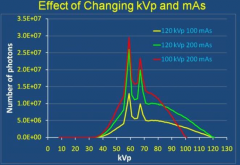
mAs= number of photons
kVp = energy |
|
|
How does mAs affect the image quality?
|
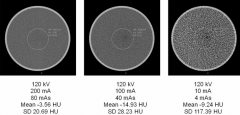
higher mAs = more photons to work with,= less noise = lower standard deviations
|
|
|
Define Pitch (aka beam pitch)
|
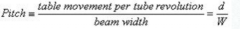
Table movement per tube revolution/beam width = d/W
|
|
|
Example: if the table moves 12 mm in one revolution and the beam width is 8mm, what is the pitch
|
table movement per tube revolution/beam width
12/8 = 1.5 |
|
|
What is slice pitch?
|
table movement per tube revoltion/ slice thickness = d/S
|
|
|
how do you convert slice width to beam width?
|
slice width x number of detectors
|
|
|
What is the effect of pitch on patient dose?
|
the smaller the pitch the more overlapping radiation = larger patient dose
|
|
|
What is the effect of slice thickness on image noise and spatial resolution
|
large slices = decreased spatial resolution (in z axis) and decreased noise
|
|
|
what is the effect of slice thickness on patient dose.
|
thin slices= larger patient dose.
|
|
|
what are the three factors upon which attenuation coefficient depends?
|
type of material, physical density and photon energy
|
|
|
What is the beer-Lambert law?
|
the number of photons reaching the detector is related to the sum of the linear attenuation coefficients of each voxel in the ray. Therefor referred to as raysum
|
|
|
The set of all CT projections at one slice positions placed side-by side is called a _____________
|
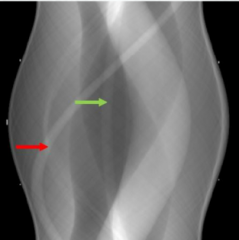
sinogram
|
|
|
What are the 2 methods of image reconstruction?
|
1) Analytical- Filtered backprojection (fast and noisy)
2) Iterative (slow and clean) |
|
|
How does iterative reconstruction work?
|
see chart
|
|
|
What is the convolution kernal?
|
Filter that is applied to the scan information before it is backprojected to form the 3D matrix
|
|
|
When we look at an axial slice what are we really looking at?
|
axial reconstruction of a 3D volume
|
|
|
Quesion: if the FOV is 40 cm x 40cm and the image matrix is 1024 x 1024, what is the size of a pixel?
|
p= FOV/m
p= 40 cm (400 mm)/1024 p=0.4 mm |
|
|
what are the x,y and z dimensions of a voxel?
|
x and y = pixel size (determined by FOV and matrix size)
z= slice thickness. |
|
|
True or false: A kernel will change the actual CT number
Windowing and leveling will change the actual CT number |
True
False |
|
|
Since the CT scan is aquired helically, only a single projection is taken of an axial section. However, multiple views are needed to generate the axial section. How is this overcome?
|
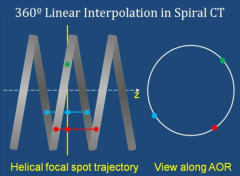
For a 360 information, linear interpolation assumes that the change between 2 points is linear and fills in the gap.
|
|
|
How does 180 degree linear interpolation work?
|
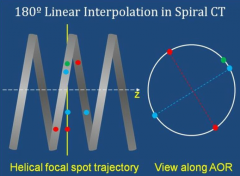
raysums measured from any angular position are approximately the same as those measured from a position exactly 180 degrees away. However, in a 180 degree interpolation, the slices used for interpolation are closer together resulting in better spatial resolution.
|
|
|
Which is better 180 degree or 360 degree linear interpolation?
|
180 degree
|
|
|
Which scan mode has better z resolution? (axial or helical)
|
axial
helical us prone to volume averaging due to linear interpolation. |
|
|
what is the benefit of helical acquisition?
|
speed-especially for time sensitive imaging (ie. PE studies) and when imaging moving anatomy (cardiac work)
|
|
|
how do variable kv and mAs systems work
|
acquire frontal and lateral scouts from which attenuation tables are generated which drive the tube current and mas during scan.
new systems can do this on the fly based on information obtained from the leading detector row |
|
|
In CT fluorsocopy what moves and what stays still?
|
the table stays still, the tube moves continuously
|

