![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Patterns Of Plates and Boundaries
|
Alfred Wegener - Theory that continents moved across earths surface
300 million years ago they were just one continent he named Pangea Made a theory called continental drift |
|
|
|
Continental Drift Theory
|
- Continents of Africa and South America seem to fit together
- 290 million year old glacial deposits can be found in South America, India and Antarctica - Geological sequences are found in Scotland and Canada - Fossils of reptiles, invertebrates and plants found on different continents - Coal reserves in Antarctica so must've been hot once |
|
|
|
Support for Theory of Plate Tetonics
|
Discovered the sea floor was spreading in Mid Atlantic.
Reserves in Earths polarity recorded in the new crust. To compensate for growth, earths crust at constructive plate margins are being destroyed. Ocean trenches where ocean floor subducted below the lighter less dense continental crust |
|
|
|
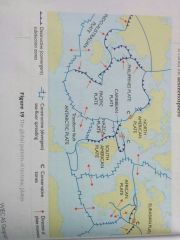
Seven Major Tectonic Plates
|
African
Antarctic Eurasian Indo-Australian North American South American Pacific Oceanic Plates are 50-100km thick Rock in them no older than 180 mil years Continental Plates 100 -250km thick Much older Rates of movement - 0.60cm - 10cm per year |
|
|
|
Earth Crust - Lithosphere + Aesthenosphere
|
Earths Crust and outer part of mantle is the lithosphere
Lower mantle - molten, semi molten is called Aesthenosphere |
|
|
|
Global Pattern Of Tectonics
|
|
|
|
|
Processes Associated With Margins
|
Movement of tectonic plates driven by thermal convection currents in the upper mantle.
The heat is from radioactive decay of minerals deep within the earth. Heat causes plumes of hot magma to rise. If crust is thinner of mid ocean floor magma pushes through and makes new crust as its cooled by water. |
|
|
|
Processes Associated With Margins pt.2
|
Actual driving mechanism not determined
In 1990s scientist thought it was called ridge push But now slab pull is the concept now Slab Pull - Dense ocean plate sinks into a subduction zone due to pull of gravity |
|
|
|
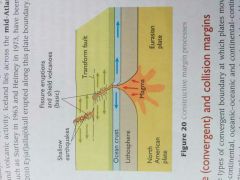
Constructive Margins
|
- Plates move AWAY from one another
- Magma rises, forms oceanic crust or continental crust - Characterised by: Shallow focused earthquakes and volcanic activity - Ex. Iceland lies across Mid Atlantic ridge and islands such as Surtsey 1963 and Heimy 1973 have been formed to volcanoes |
|
|
|
Destructive (Convergent) Margins
|
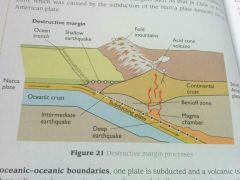
- Move TOWARDS each other
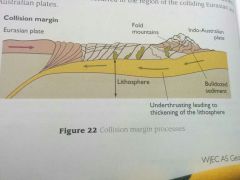
- 3 types 1. Oceanic-continental 2. Oceanic-oceanic 3. Continental-Continental - First two are destructive and one is subducted beneath the other -Collision Margins - where two plates both of continental crust move together - Oceanic-Continental - denser oceanic crust subducted beneath continental - Creates: Deep ocean trenches, volcanic mountain chains, batholiths beneath surface. - Shallow - intermediate earthquakes occur at these e.g Chile February 2010 LOOK AT HINT |
Oceanic-Oceanic - one plate subducted and volcanic island arc an adjacent deep sea trench may form.
|
|
|
Conservative (Transform) Margins
|

Plates slide past one another
No volcanic activity Shallow Focus Earthquakes common San Andreas Fault - West Coast North America is where Pacific and North American plates meet LA and San Fransisco at risk |
|

