![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Steps of the discovery of atomic structure |
- Thomson proposes plum pudding model of a positively charged nucleus with electrons scattered inside it - 1909 Rutherford scattering experiment disproves plum pudding model |
|
|
Describe rutherford’s scattering ecperimtn |
- alpha particles are fired at a film gold film - a circular detector screen is behind the film to detect where alpha particles have been deflected by gold nuclei - if plum pudding model was correct, it’d be expected the alpha particles would be deflected by small amounts - in fact, some particles were deflected by large angles, a few were even deflected back the way they came (repelled) |
|
|
What conclusions can be drawn from the scattering experiment? |
- atom is mostly empty space as many alpha particles passed straight through the foil - nucleus of the atom is positively charged as some atoms were deflected by large amounts - nucleus is very small as very few particles were fully repelled back the way they came - most of the mass of the atom is in the nucleus as high momentum alpha particles were deflected by it |
|
|
How to find an estimate of radius of a nucleus? |
- fire a +ve charged particle at the atom, it’ll be repelled - it is at its closest when its Electric potential = its initial kinetic energy - Ek = V = Qq/4πε0xr - r = Qq/(4πε0 x V) |
|
|
What equation do you use to find radius of a nucleus using electron diffraction? |
E=hc / λ Sinø = 1.22λ / 2R R = 1.22λ / 2xsinø |
|
|
How does intensity of maxima produced by electron diffraction change as ø of diffraction changes? |
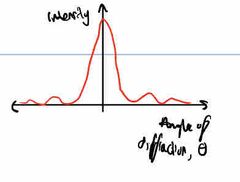
Intensity decreases as ø increases |
|
|
Why do alpha particles have short range? |
Strongly ionising, transfer energy when they ionise atoms So, they ionise lots of atoms rapidly and quickly lose all their energy |
|
|
What can beta particles be used for? |
Control of thickness of material |
|
|
What can gamma rays be used for |
- tracers, technetium has 6 hour half life, long enough for tests, short enough to not cause major damage - radiotherapy, from multiple angles to not damage surrounding tissue |
|
|
How is radiation in medicine made safer |
- radiotherapy beams rotate to limit damage to surrounding tissue - staff leave the room to be shielded from radiation |
|
|
Experiment to distinguish between alpha, beta, gamma radiation |
- Use Geiger Counter to record background radiation count - place radioactive source in front of Geiger muller tube, record cps - place paper between them, if count rate drops significantly, its alpha radiation - if not, place aluminium between them, if count rate drops significantly, its beta If not its gamma |
|
|
What are causes of background radiation? |
- radon in the air, releases alpha particles when it decays - rocks, buildings - cosmic background radiation, colliding with particles in the atmosphere - living things - carbon-14 - man-made - medicine, industrial |
|
|
What’s the relationship between distance from source and intensity of radiation |
I ∝ 1/x^2 I = k/x^2 |
|
|
How to minimise risk when handling radioactive material |
- hold source far from body - use long handling tongs - if not handling material , stay far away |
|
|
Experiment to show intensity compared to distance from radioactive source |
- record background radiation with Geiger muller tube, take each recording 3 times and use an average - set up a ruler and radioactive source in front of the Geiger muller tube - record new cps - move source a distance away from the Geiger muller tube, record new distance and cps - correct count rate for background radiation - plot graph of corrected cps against distance, x - you’ll find inverse square law |
|
|
How does intensity of maxima produced by electron diffraction change as ø of diffraction changes? |
Intensity decreases as ø increases |
|
|
Explain how isotopes decaying happens and the probabilities |
Decays happen in the nucleus of unstable isotopes The decay of a specific nucleus is random With a large sample size of a given isotope the time it takes for half the nuclei to decay is constant |
|
|
What’s the formula for activity |
A= λN |
|
|
Relationship between A and N? |
A ∝ N |
|
|
What is half life |
Time for N or A to half Or mass |
|
|
What would a graph of Ln(N) against t look like |
Straight line , negative gradient Y intercept = Ln(N0) |
|
|
What is equation for half life |
T1/2 = Ln2/ λ |
|
|
What is λ ? |
Decay constant |
|
|
What is the equation for N or A at a given time? |
N=N0 e^-(λt) |
|
|
What uses does half life have? |
- radioactive dating - carbon dating - medicine - tracers, 6 hour half life |
|
|
Why are long half lives dangerous |
Means an isotope will be radioactive for a long time, so must be stored and disposed of safely |
|
|
What is the rough radius of a nucleus |
5fm |
|
|
What’s a stability graph |
Shows number neutrons against number of nucleons Shows what kind of decay certain nuclei undergo |
|
|
What situations do nuclei decay in |
- too heavy - alpha - neutron rich - beta - proton rich - beta plus - excess energy - gamma |
|
|
What happens during electron capture |
Nucleus captures one of its own electrons Proton turns into a neutron Gamma ray is emitted |
|
|
What must be conserve in deccays |
Energy Momentum Nucleon number And more |
|
|
Give the main parts of a nuclear reactor |
- fuel rods - chain reactions - moderator - critical mass - control rods - coolant - shielding |
|
|
What is the purpose of fuel rods |
Contain uranium 235 , that fissions when a neutron is fired at it |
|
|
Explain the chain reaction in a nuclear reactor |
It happens when a neutron is fired at uranium and the decay of the uranium produces more neutrons that collide with more uranium nuclei and so on |
|
|
What’s a stability graph |
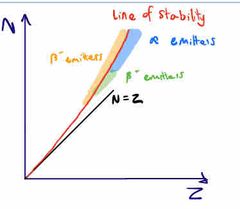
Shows number neutrons against number of nucleons Shows what kind of decay certain nuclei undergo |
|
|
What’s critical mass |
The minimum mass needed to keep a chain reaction going at a steady rate Nuclear reactors use a supercritical mass |
|
|
What are control rods for |
Contain boron that absorbs neutrons, this slows the chain reaction down In an emergency fuel rods are fully inserted into reactor to absorb as many neutrons as possible and stop the reaction as fast as possible |
|
|
What is the relationship between nucleon number, A and radius of a nucleus, R? |
R ∝ A^(1/3) |
|
|
What is coolant for |
Removes heat from the reactor and takes it away as steam to turn the turbines |
|
|
What is shielding for |
Keep staff safe from as much radiation as possible |
|
|
What is fission? |
When a nucleus decays into daughter nuclei and releases energy |
|
|
What’s the problem with nuclear waste from fission? |
- waste products are still unstable isotopes and decaying (uranium 238) - therefore needs to be cooled, stored until less radioactive , then disposed of safely |
|
|
What needs to happen for fusion to occur |
Particles need enough energy to overcome electrostatic force Must be close enough for SNF to hold them together (3fm) |
|
|
Why wont low energy nuclei fuse? |
Electrostatic force means they’ll repel |
|
|
What is binding energy |
Energy needed to separate a nucleus into its constituents |
|
|
How to find change in energy when you know mass defect? |
∆E (MeV)= mass defect (u)x 931.5 |
|
|
What is equation with binding energy and mass defect |
Binding energy / mass defect = 931.5 |
|
|
What is mass defect |
The change in total mass when fusing or separating nuclei constituents |
|
|
What equation gives the relationship between R and A |
R= R0A^(1/3) |
|
|
How to find average binding energy? |
Binding energy / nucleon number |
|
|
What nucleus is most stable and has highest average bindign energy per nucleon |
56 Fe , iron |
|
|
How to find energy released by fission given masses of products and reactants? |
Turn masses into energy and find the change in energy |
|
|
What equation gives radius of a nucleus using closest approach? |
R = 1/4πε0 x Qq/V V = electric potential energy |
|
|
What is R0 |
A constant (roughly = 1.4fm) Allows comparing of two nuclei R0 = R/A^(1/3) R1/A1^(1/3) = R2/A2^(1/3) |
|
|
What order of magnitude is the radius of a typical nucleus |
X10 ^-15, Fm |
|
|
How can you tell density of a nucleus is so big |
Density = m / v Most mass of atom is stored in nucleus Density of a nucleus roughly = mass of atom / volume of a nucleus |
|
|
What makes a nucleus radioactive |
When it is unstable and so decays , emitting ionising radiation |
|
|
What are the 4 types of ionising radiation? |
Alpha Beta Beta plus Gamma |

