![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
self fulfilling prophecy
|
a perceptual process in which our expectations to another person causes that person act more consistently with those expectations
|
|
|
self fulfilling prophecy cycle
|
eexpectation formed affection supervisor behaviour
supervisors affection employee behaviour employee matches expectation |
|
|
self–fulfilling prophecy is strongest 4pt
|
when1: at the beginning of the relationshipwhen several people have similar expectation
when employees has low input cost when there is a need to develop and preserve positive and yet realistic expectations |
|
|
other perceptual effects4
|
1 Halo effect: form a general impression of others from one trait/ behaviour (distorts our perception of person's other traits /behaviour
2:false– consensus effect: over estimate others has similar beliefs or traits like ours. 3. primacy effect: forming perception of others( categorization based on first information we receive about them . first impression is difficult to change 4.recency effect.: most recent information dominates perception. |
|
|
iimproving perceptions
|
1. awareness of biases2. improving self awareness.: i.e. : beliefs, attitudes. test for biases and use johari window
3. meaningful interaction: cased on contact hypothesis : more interaction, less prejudiced equal status engaged in a meaningful task |
|
|
glocal mindset abilities: 4
|
ability to understand and respect other views/ practices around the world
empathize and act effectively across cultures. ability to process complex information about novel environment ability to comprehend and re concise intercultural matters with multiple levels of thinking |
|
|
ddeveloping global mindset
|
improve self awareness
compare mental models with other culture develop better knowledge of people and cultures– especially through immersion |
|
|
self fulfilling prophecy
|
a perceptual process in which our expectations to another person causes that person act more consistently with those expectations
|
|
|
self fulfilling prophecy cycle
|
eexpectation formed affection supervisor behaviour
supervisors affection employee behaviour employee matches expectation |
|
|
self–fulfilling prophecy is strongest 4pt
|
when1: at the beginning of the relationshipwhen several people have similar expectation
when employees has low input cost when there is a need to develop and preserve positive and yet realistic expectations |
|
|
other perceptual effects4
|
1 Halo effect: form a general impression of others from one trait/ behaviour (distorts our perception of person's other traits /behaviour
2:false– consensus effect: over estimate others has similar beliefs or traits like ours. 3. primacy effect: forming perception of others( categorization based on first information we receive about them . first impression is difficult to change 4.recency effect.: most recent information dominates perception. |
|
|
iimproving perceptions
|
1. awareness of biases2. improving self awareness.: i.e. : beliefs, attitudes. test for biases and use johari window
3. meaningful interaction: cased on contact hypothesis : more interaction, less prejudiced equal status engaged in a meaningful task |
|
|
glocal mindset abilities: 4
|
ability to understand and respect other views/ practices around the world
empathize and act effectively across cultures. ability to process complex information about novel environment ability to comprehend and re concise intercultural matters with multiple levels of thinking |
|
|
ddeveloping global mindset
|
iimprove self awareness
compare mental models with other culture develop better knowledge of people and cultures– especially through immersion |
|
|
cognitive dissonance
|
emotional experience caused by a perception that our belie, feelings and behaviour are in congruent( not consistent ) with each other
|
|
|
¡Inconsistencygenerates
|
emotions that motivate us to increase consistency. Instead we reduce dissonance by changing our belifs/feelings about our attitude ¡” something inconsistency with our emotions and attitudes may trigger us to change
|
|
|
¡how emotions influence attitudesand behaviour:
|
¡When our feelings are influenced by cumulative/numerous emotional episodes(e..g. we often experience numberous emotional fellings when something+or –happens) ¡When we ‘listen in ‘ on our emotions, and sometimes we allow them to influence our cognitive logical reasoning
|
|
|
¡When there is a confilct between cognitive and emotional processes:
|
they sometimes disagree with each other(e.g. something you feel isn’t right though you sometimes do not use your logical reasoning) ¡Q which one should we pay much attention to ? ¡Follow our gut feelings or allow ourselives enough time to use our cognitive logical reasoning ! ¡
|
|
|
Emotions also directly affect behavior
|
(ie facial expressions – at workplace working as reception)
|
|
|
emotional labour
|
effort, planning and control needed to express organizationally desired emotions during inter personal transaction
|
|
|
Higherin jobs requiring
|
¡Frequent/lengthyemotion display¡Varietyof emotions display¡Intenseemotions display
|
|
|
emotional labour challenges 4
|
difficult to accurately display expected emotions
to hide emotional dissonance––conflict between tre and required emotions |
|
|
emotional labour solutions
|
perceive emotional labour as professional skill
egg in dee[ acting not surface acting |
|
|
managing work related stress 5
|
¡Removethe stressor¡Minimize/removestressors¡Work/lifebalance initiatives¡
Withdrawfrom the stressor¡Vacation,rest breaks Changestress perceptions¡Positiveself–concept, humour¡ Controlstress consequences¡Healthylifestyle, fitness, wellness ¡Receivesocial support |
|
|
emotional intelligence model
|
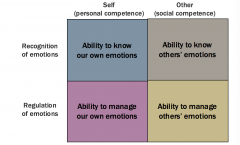
//fce-study.netdna-ssl.com/2/images/upload-flashcards/01/25/79/18012579_m.png
|
|
|
emotional intelligence hierarchy
|
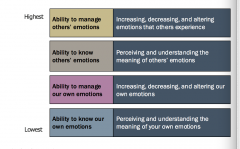
//fce-study.netdna-ssl.com/2/images/upload-flashcards/01/25/88/18012588_m.png
|
|
|
EI
|
is associated with better relations,emotional labour, leadership, social decisions, job interview, knowledge sharing
It can be learned through training coaching practice feed back it increase with age |
|
|
job satisfaction
|
a persona evaluation of his or her job and work context
an appraisal of the perceived job characteristics, work environment , and emotional experience at work |
|
|
EVLN
|

//fce-study.netdna-ssl.com/2/images/upload-flashcards/01/26/18/18012618_m.png
|
|
|
organizational commitment |
Affective commitment : emotional attachment to identifuaction with and involvement in an orgaization |
|
|
continuance commitment |
¡Continuancecommitment: calculative attachment to an organization.¡Canbe seen through “affective commitment” : refers to emotional attachment to ,identification with and involvement in an organizaiton¡Employees stasbecause a no other chioce¡Ortoo expenisveto quit |
|
|
Building affective commitment |

|
|
|
Stress |
Adaptive response to situationas perceived as challenging or threaten ing to well being -prepares us to adapt to hostile or noxious dangers envirnmenttal conditions Eustress+ vs dis tress- |
|
|
consequences of distress!; |
physiological: cardiovacular diseasehypertension, headaches behavioural : work performannce, accidenct, absenteeism, aggression, poor decision psycological:dissatisfaction, moodiness, depression, emotional fatigue |
|
|
common work palce stressors |
harassemnt an incivility work overload low task control . lack of work autonomy |
|
|
experience less stress and or negative outcomes when they have |
better healthy appropriate stress coping strategies personality , lower neuroticism and higer extraversion positive self concept lower work aholism |
|
|
managing work related stress |
remove , withdraw, change stresss perceptionsn positive self concept control stress consequences: healthy receive social support |
|
|
types of emotions |

|
|
|
attitude vs emotions |

|
|
|
EI model |
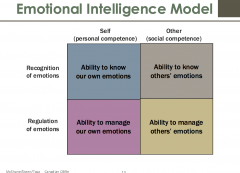
|

