![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
__________ is the most common of genital ambiguity.
|
Virilizing congenital adrenal hyperplasia
|
|
|
What is congenital adrenal hyperplasia?
|
Inherited autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in genes involved with adrenal steroidogenesis leading to deficient cortisol production/synthesis**
|
|
|
What enzyme deficiency characterizes congenital adrenal hyperplasia? What effect does this have on hormone levels?
|
21-hydroxylase deficiency -->
testosterone build up Less cortisol-->ACTH hypersecretion and CRH-->Adrenal glands become hyerplastic HIGH ACTH HIGH CRH LOW CORTISOL!!! |
|
|
What is the net effect of congenital adrenal hyperplasia?
|
Excess testosterone-->prenatal virilization of girls
Rapid somatic growth with early epihpyseal fusion in both boys and girls |
|
|
Why do females with CAH virilize and have normal mullerian structures (internal genitalia)?
|
Girls with 21-OHase still lack Anti-Mullerian Hormone synthesized by sertoli cells of testes
|
|
|
What are genital symptoms of CAH in boys?
|
Hyperpigmentation of scrotum (excess ACTH acting on melanocyte receptors), and sometimes bigger penises
|
|
|
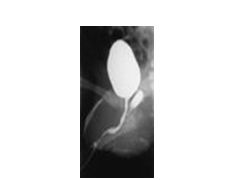
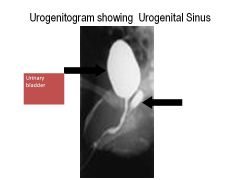
What is a urogenital sinus?
|
When female only born with one opening (shared for urethra and vagina)
Can detect with urogenitogram--helps localize mullerian structures |
|
|
What are the two types of classical 21-OHase deficiency?
Which is most common? How do they differ? |
Salt-wasting: 60-75%
Simple-virilizing: 25% (adequate aldosterone bc have 1-2% of 21-OHase activity which is sufficient for aldosterone production) Both have low cortisol! |
|
|
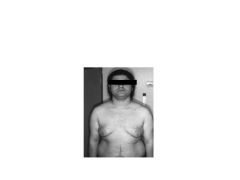
Classic vs Non-Classic CAH
|
Degree of enzyme def
Classical: lack cortisol AND aldosterone (ambiguous genitals, fast growth, early puberty) Non-Classic: have functioning 21-OHase (up to 50% enzyme activity), NOT salt wasting Mildly affected (Common in Ashkenazi Jews) NO AMBIGUOUS GENITALS! Syx: hirsutism, acne, premature puberty, irregular menses |
|
|
Diagnose:
4 year old female with premature pubic hair, rapid growth, prepubertal testes |
Simple-virilizing CAH
|
|
|
Diagnose:
4 year old female with premature pubic hair, hirsutism, acne, menstrual irregularity, infertility |
Non-classic CAH
|
|
|
How would you diagnose CAH?
What lab values would you use to differentiate between salt-wasting, simple virilizing, and non-classical CAH? |
60-minute response to synthetic ACTH, measure 17-OHP (built up with 21-OHase def)
Salt-wasting/Simple virilizing: 10K-100K Non-classical CAH: 1500-10K |
|
|
How do boys with salt-wasting CAH present?
Describe metabolite and renin levels. |
No genital ambiguity so gets missed at birth, but then:
Failure to thrive: Not enough aldosterone: Hyponatremia Excreting potassium, so retaining K+: HYPERkalemic Retaining Hydrogen ions: metabolic acidosis Plasma renin HIGH Cortisol is low even though patient is DYING (not good. should go up with stress) |
|
|
How do boys present with simple virilizing CAH?
|
Precocious puberty: pubic hair, small testes, penile enlargement at young age (~5 years of age)
|
|
|
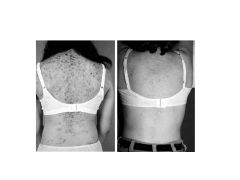
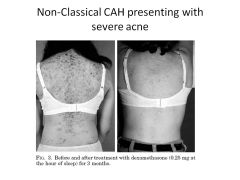
How do girls present with non-classical CAH?
|
Precocious puberty (pubic hair)
ACNE No breast development Height 50th-75th percentile (FAST GROWING) |
|
|
Why would precocious puberty be alarming?
|
Testosterone-->E2-->SEAL growth plates
|
|
|
What treatment is used for CAH? What would over/undertreatment result in?
|
CORTISOL
Overtx: growth retardation Undertx: epiphyseal closure-->short stature (low cortisol-->high androgens) |
|
|
What is the treatment for salt-wasting CAH? How is treatment monitored?
|
Hydrocortisone
Fludrocortisone NaCl tablet Tx monitored by measuring 17-OHP |
|
|
What is the mechanism of prenatal treatment of CAH?
|
Dexamethasone taken by mother, not degraded by placenta, and suppresses fetal ACTH to limit testost production.
(Stop if fetal DNA is boy or if girl unaffected by fetal ACTH) |
|
|
Substantial risk of sex misassignment occurs with ___________.
|
Classical CAH
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

