![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
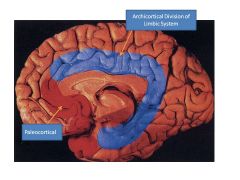
What structures comprise the archicortical division of the limbic system?
Role? |
Archicortical:
Hippocampus, Cingulate Gyrus, Papez Circuit Modulates sensory processing, encoding of information, attentional control |
|
|
What structures comprise the paleocortical division of the limbic system?
Role? |
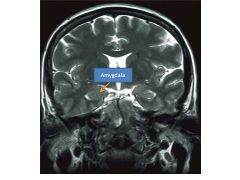
Paleocortical division contains the amygdala and its connections to the basal forebrain and hypothalamus
Tags emotions to sensory stimuli, modulates fear/emotional responses and memories, integrates affect/drives, ESSENTIAL for emotional processing |
|
|
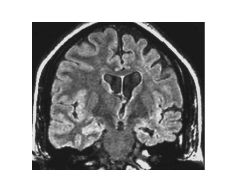
What is cortical and hippocampal atrophy symptomatic of?
|
AD
|
|
|
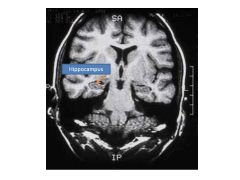
Results of damage to the hippocampus?
|
Damage hippocampus:
Impaired episodic memory (memory of autobiographical events) Disturbance of attention |
|
|
Effects of lesion to anterior nucleus of thalamus?
|
Confusion, memory loss (produces effects similar to that of hippocampal lesions)
|
|
|
Function of cingulate gyrus?
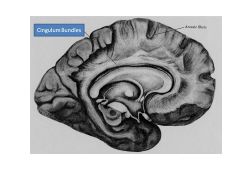
Reason for lesioning cingulum bundles? |
Role: Emotional behavior
Lesion Cingulum Bundles to treat refractory pain/OCD (refractory = treatment resistent) |
|
|
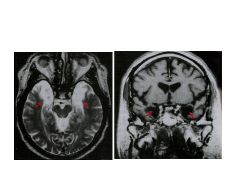
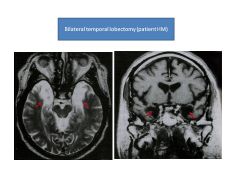
Significane of patient HM.
|
b/l temporal lobectomy cured seizures, but was no longer able to form memories
|
|
|
What does the stria terminalis connect?
|
Amygdala to basal forebrain
|
|
|
What does the ventral amygdalofugal pathway connect?
|
Amygdala to hippocampus
|
|
|
Effect of stimulating lateral hypothalamus?
|
Aggression, voracity, hypersexual
|
|
|
Effect of stimulating ventromedial nucleus?
|
Placid, early satiety
|
|
|
Why would a seizure in the amygdala result in auditory hallucinations and limb spasticity?
|
Abnormal electrical activity in the amygdala can evolve to surrounding areas (cortex)
|
|
|
What is a complex seizure? Cause?
|
Electrical activity spreads to hippocampus and patient no longer remembers events of seizures (complex seizure); patient is unaware/unresponsive
|
|
|
What does the fornix connect?
|
Hippocampus to mammallary bodies
|
|
|
What is the only primary sensory input to the amygdala?
|
Olfaction
|
|

|
|
|
|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|

|

|

