![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
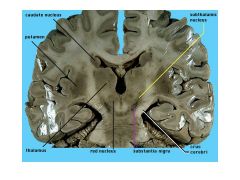
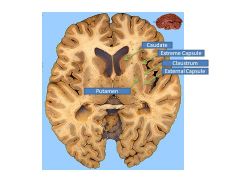
What structures comprise the basal ganglia?
Which of these comprise the striatum? |
BG:
Caudate Putamen Nucleus Accumbens Globus Pallidus SN Subthalamic N Caudate, Putamen, N Accumbens = Striatum |
|
|
What is the function of the cellular bridges in the basal ganglia?
|
Connect the caudate and putamen
|
|
|
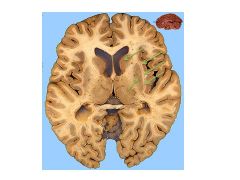
What structure atrophies in Hungtington's Disease?
|
Caudate nucleus
|
|
|
What effect do the indirect and direct pathways of the basal ganglia have on cortical activity?
What neurotransmitter allows for their balance in activity? |
Indirect: inhibitory
Direct: excitatory NT: DA |
|
|
Draw the basal ganglia circuit.
|
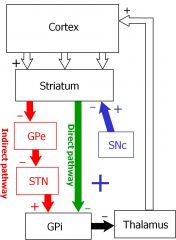
|
|
|
What is the effect of the SN pars reticulata on the thalamus?
|
Inhibitory
|
|
|
Dyskinesia vs Dystonia
|
Dyskineia: abnormal and involuntary movement
Dystonia: abnormality of tone, posture, position |
|
|
What is chorea?
|
dancing movements (Huntington's Dz)
|
|
|
What is athetosis?
|
Twisting movements of limbs, trunks
|
|
|
What is torticollis?
|
Wry neck
|
|
|
Give an example of a hypokinetic disorder, and a hyperkinetic disorder.
|
Hypokinetic: PD
Hyperkinetic: HD |
|
|
What is akinesia?
|
disorder of movement initiation
|
|
|
What changes occur in the basal ganglia during the development of Parkinson's Disease?
|
Dopaminergic neurons of SN pc die
|
|
|
What is hemiballismus? How does it occur?
|
Wild flinging movements, usually unilateral.
Cause: lesion subthalamic nucleus-->decreased excitation of GPi; thus less inhibition of thalamus |
|
|
How do the symptoms of Huntington's Disease change with time?
|
Initially hyperkinetic (chorea)
In late stages, rigid, hypokinetic Parkinsonian state (Severe neuropsychiatric disturbances, progressive dementia) |
|
|
|
|
|
|

