![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How does sensory and motor organization differ in the brainstem and spinal cord? (2 ways)
|
SC: Continuous distribution of motor and sensory nerves
Sensory afferent is dorsal Motor efferent is ventral BS: Discontinuous distribution Sensory afferent is lateral Motor efferent is medial |
|
|
What are the special senses?
|
Signals specific to the head (vision, taste, hearing, balance)
|
|
|
Somatomotor vs Branchiomotor
Provide examples. |
Somato: somite origin (extraocular muscles, intrinsic muscles of tongue)
Branchio: gill arch origin (anything in head; some of neck) |
|
|
Alternate term for visceromotor.
Type of outflow? |
Visceromotor = General Visceral Efferent
Parasympathetic outflow; preganglionic outflow |
|
|
Alternate term for somatomotor.
|
General Somatic Efferent (GSE)
Also innervated by spinal nerves |
|
|
Alternate term for branchiomotor.
|
Special Visceral Efferent
Even though it's visceral, it's under voluntary control (not autonomic); unique to head; only innervated by cranial nerves |
|
|
CN I
Somatic Branchio Viscero Sensory |
Olfactory
Sensory: Olfactory |
|
|
CN II
Somatic Branchio Viscero Sensory |
Optic
Sensory: Vision |
|
|
CN III
Somatic Branchio Viscero Sensory |
Oculomotor
Somatic: Extraocular Eye Muscles Viscero: Parasympathetic for eye (ciliary muscles for lens adjustment) |
|
|
CN IV
Somatic Branchio Viscero Sensory |
Trochlear
Somatic: Superior oblique (eye muscle) |
|
|
CN V
Somatic Branchio Viscero Sensory |
Trigeminal
Branchio: muscles of mastication Sensory: face, head skin, mucosa, dura |
|
|
CN VI
Somatic Branchio Viscero Sensory |
Abducens
Somatic: Lateral rectus |
|
|
CN VII
Somatic Branchio Viscero Sensory |
Facial
Branchio: Facial muscles, stapedius (stabilizes stapes) Viscero: Salivary glands, lacrimal gland Sensory: Taste, skin behind ear |
|
|
CN VIII
Somatic Branchio Viscero Sensory |
Auditory N
Sensory: Auditory, vestibular |
|
|
CN IX
Somatic Branchio Viscero Sensory |
Glossopharyngeal
Branchio: Stylopharyngeus (swallowing) Viscero: Salivary gland Sensory: Taste, carotid sinus/body, pharynx, skin (ear) |
|
|
CN X
Somatic Branchio Viscero Sensory |
Vagus
Branchio: Larynx Viscero: Neck, thorax, abdomen Sensory: Visceral, pharynx, larynx, thorax, abdomen |
|
|
CN XI
Somatic Branchio Viscero Sensory |
Spinal Accessory
Somatic: SCM Branchio: Larynx |
|
|
CN XII
Somatic Branchio Viscero Sensory |
Hypoglossal
Somatic: tongue muscles |
|
|
How many motor nuclei does a cranial nerve have?
|
Has one nuclei for every kind of motor information (somatomotor, branchiomotor)
|
|
|
Can a cranial motor nerve have both a somatomotor or branchiomotor component?
|
No (except for spinal accessory)
|
|
|
What is the sulcus limitans?
|
Line that divides sensory from motor information in spine/brainstem
|
|
|
Where are the alar and basal plates located in the brainstem (in relation to each other)?
What kind of information does each contain? |
Alar: Lateral; sensory
Basal: Medial; motor |
|
|
What type of cranial nerve nuclei are common to both the spine and brainstem? Which are not?
How do they differ in location? |
Brainstem and SC both have somatomotor, visceromotor, and sensory nerve nuclei. These are all located adjacent to the 4th ventricle (in the brainstem).
Brainstem also has unique branchiomotor nucleus, which is furthest from ventricle (near olive). |
|
|
What cranial nerve is the Edinger-Westphal nucleus associated with? Information type?
|
CN III (oculomotor)
Visceromotor |
|
|
What cranial nerve is the nucleus ambiguus associated with? Information type?
|
CN IX (glossopharyngeal), X (vagus), XI (spinal accessory)
Branchiomotor |
|

|
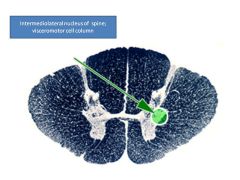
|
|

|

|
|

|

|

