![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
78 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
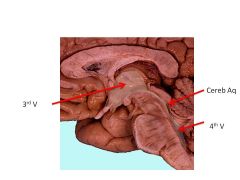
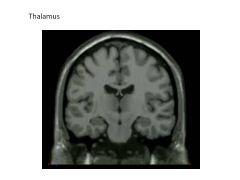
What structure comprises the lateral walls of the third ventricle?
|
Thalamus
|
|
|
What structure forms the floor of the third ventricle?
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
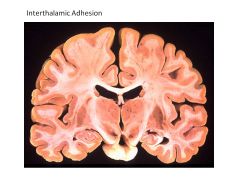
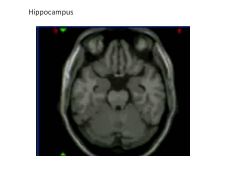
What structures comprise the Limbic System?
|
Hippocampus
Fornix Amygdala Cingulate Cortex |
|
|
If you couldn't see the hypothalamus on a coronal section, what structure of the Limbic System would you expect NOT to see?
|
Amygdala
|
|
|
What gross changes in the brain can you expect to see in a patient with Alzheimer's Disease?
|
Deteriorated cortex, enlarged ventricles (deteriorated areas fill with CSF)
|
|
|
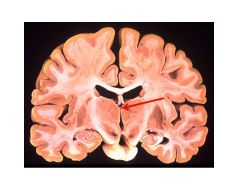
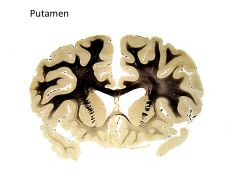
What structures comprise the basal ganglia?
|
Globus Pallidus
Caudate Putamen |
|
|
What is the role of the basal ganglia? What division of the nervous system does it fall under?
|
Role: Motor control
Division: Telencephalon |
|
|
What structures in the Basal Ganglia are affected by Parkinson's Disease?
|
Caudate and Putamen (these are where dopamine secreted by SN in midbrain acts)
|
|
|
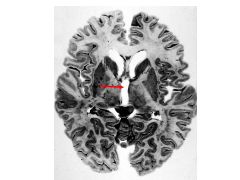
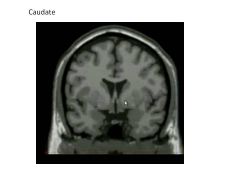
What structure comprises the lateral wall of the lateral ventrical?
|
Caudate (follows it from anterior horn to temporal horn)
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
Location of nucleus accumbens. Role?
|
Where caudate meets putamen.
Role: pleasure, reward, mood, placebo effect |
|
|
Role of caudate.
|
Memory (higher thinking; higher motor control)
|
|
|
What regions of fibers must a corticospinal axon pass through to get from the cerebral cortex to the pons?
|
Corona Radiata
Internal Capsule Cerebral Peduncle IN THAT ORDER |
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
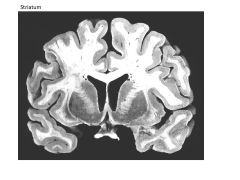
|

|
|
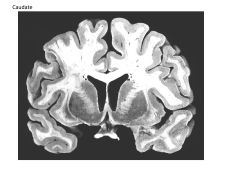
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
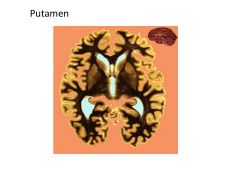
|

|
|

|

|
|
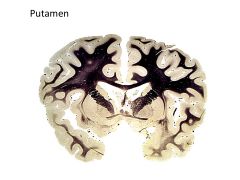
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|

