![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What structures comprise the PNS and CNS?
|
PNS: Cranial Nerves (peripheral nerves attached to brain); Spinal Nerves (Peripheral Nerve attached to spinal cord)
CNS: Brain, Brainstem, Cerebellum, Spinal Cord |
|
|
|
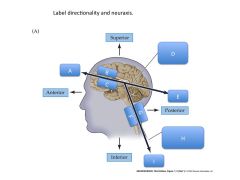
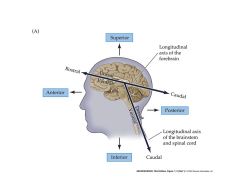
What structures are contained within the telencephalon?
|
Cerebral cortex and subcortical white matter
Basal ganglia Basal forebrain nuclei (FOREBRAIN) |
|
|
|
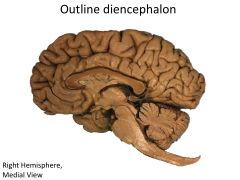
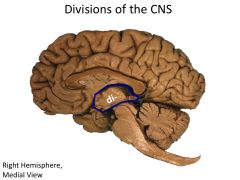
What structures are contained within the diencephalon?
|
Thalamus
Hypothalamus Epithalamus THALAMIC NUCLEI :) (FOREBRAIN) |
|
|
|
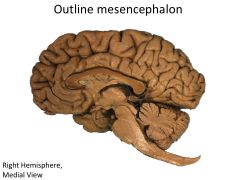
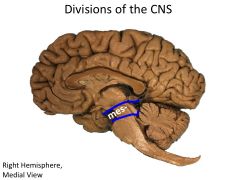
What structures are contained within the mesencephalon?
|
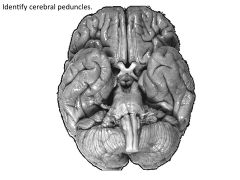
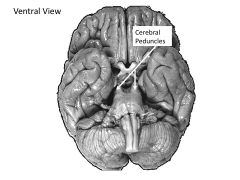
Cerebral peduncles
Midbrain |
|
|
|
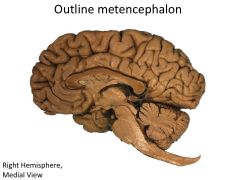
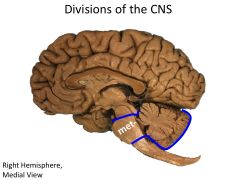
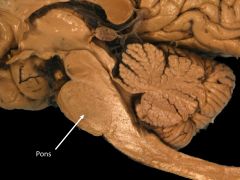
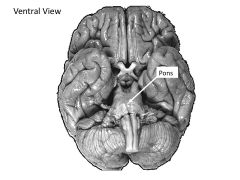
What structures are contained within the metencephalon?
|
Pons
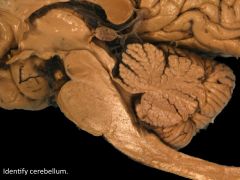
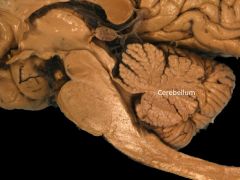
Cerebellum (HINDBRAIN) |
|
|
|
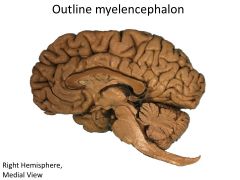
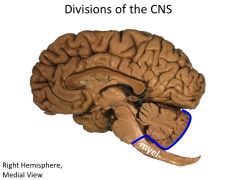
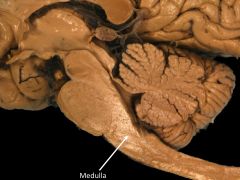
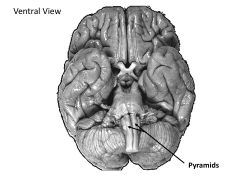
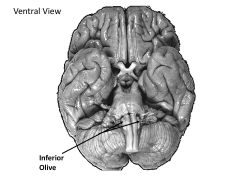
What structures are contained within the myencephalon?
|
Medulla
|
|
|
|
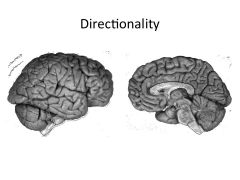
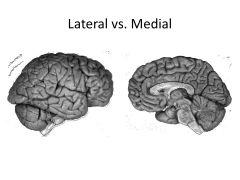
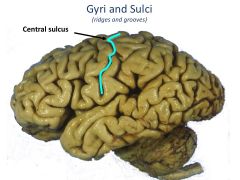
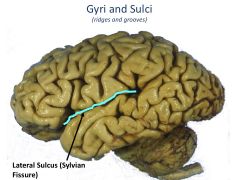
Gyrus vs Sulcus
|
Gyrus is a ridge
Sulcus is a groove |
|
|
|
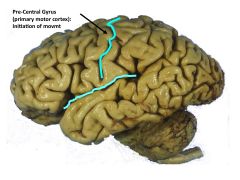
Broadmann's Number(s) for Primary Motor Cortex
|
Precentral Gyrus: Area 4
|
|
|
|
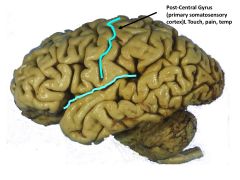
Broadmann's Number(s) for Primary Somatosensory Cortex
|
Postcentral Gyrus: 1, 2, 3 (SENSORY STRIP)
|
|
|
|
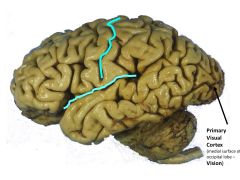
Broadmann's Number(s) for Visual Cortex
|
17
|
|
|
|
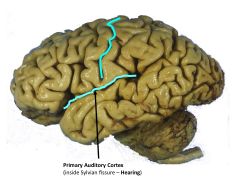
Broadmann's Number(s) for Auditory Cortex
|
41
|
|
|
|
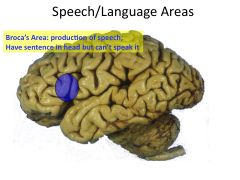
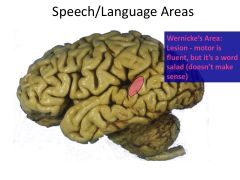
With regard to speech/language, how do left and right hemisphere lesions differ?
|
Left Lesion: Aphasia (problems producing speech)
Right Lesion: Neglect (no awareness or attention to one side of body) |
|
|
|
Going from lateral to medial, list the major structures controlled by the primary motor and primary somatosensory cortices.
|
Most lateral third: Face
Then Hand Most medial third: trunk, leg |
|
|
|
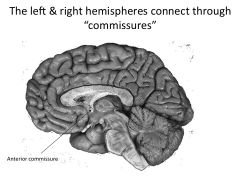
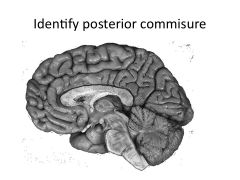
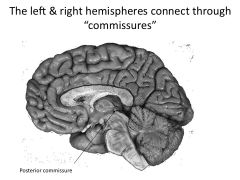
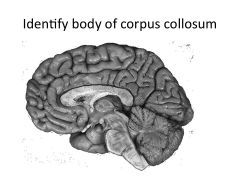
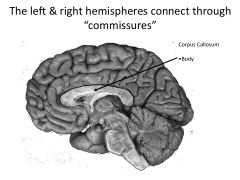
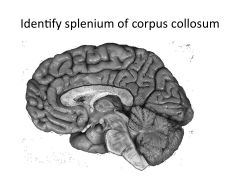
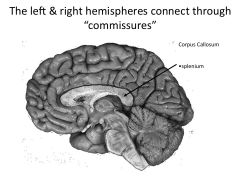
What is a commisure?
|
Structures that connect left and right hemisphere
|
|
|
|
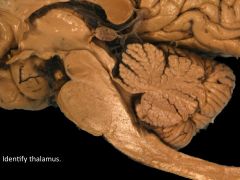
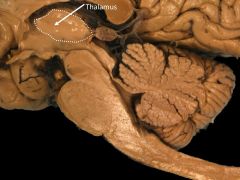
Function of thalamus.
|
Grand Central Station for sensory information (except olfaction)
|
|
|
|
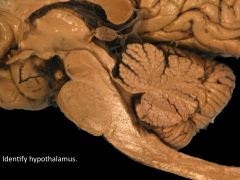
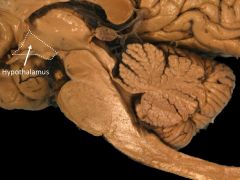
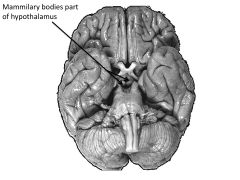
Function of hypothalamus.
|
Feeding (hunger AND thirst), fighting, fleeing, mating
|
|
|
|
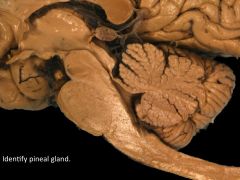
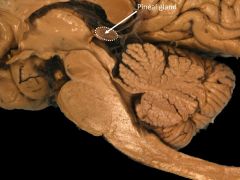
Functnon of pineal gland.
|
secretes melatonin at night onset to make you sleepy
|
|
|
|
Function of posterior pituitary.
|
Secretes hormones including oxytocin and vasopressin
|
|
|
|
Roots and vertebrae numbers for:
Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral |
Cervical: 8 roots, 7 vertebrae
Thoracic: 12, 12 Lumbar: 5, 5 Sacral: 5, 5 |
|
|
|
Where is a lumbar puncture performed?
|
Between L4 and L5
|
|
|
|
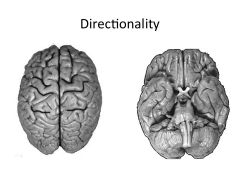
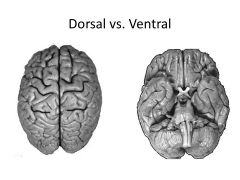
How do dorsal and ventral horns differ in terms of information sent/received?
|
Dorsal: Sensory Afferent
Ventral: Motor Efferent It's always the SAME |
|
|
|
Which region of gray matter of the ventral horn has motor output to the trunk?
|
Medial
|
|
|
|
Which region of gray matter of the ventral horn has motor output to the limbs?
|
Lateral
|
|
|
|
How would you differentiate between cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine cross-sections?
|
Cervical: Closest to brain, lots of white matter (ovoid shape); limbs in this region so gray matter will form true horns
Thoracic: No limbs, no horns formed by grey matter (fewer neurons going to limbs, less grey matter needed) Lumbar: Limbs present, have true horns; but further from brain so less white matter (more circular) |
|
|
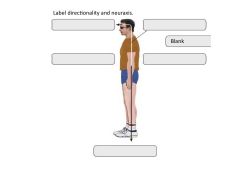
Sheets of tightly packed cells that line organs and body cavities.
|
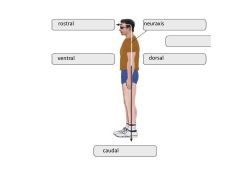
epithelial tissue
|
40.2
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
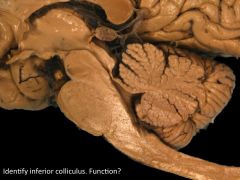
|
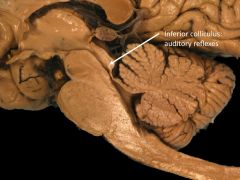
|
|
|
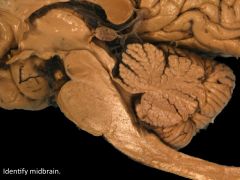
|
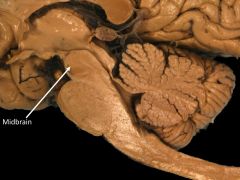
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Epithelia that secrete chemical solutions.
|
glandular epithelia
|
40.2
|
|
|
|
|

