![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What neuron type is found in the cerebellum?
|
Purkinje Cells
|
|
|
Describe the shape and structure of dendrites.
|
Dendrites: tapered (get thinner), branch at ACUTE angles; integrate signal
|
|
|
How does dendrite length affect signal transduction?
|
The longer the dendrite, the greater the signal decrements
|
|
|
In terms of signal propagation, how is plasticity achieved?
|
Signals can propagate backwards (from soma to dendrite)
|
|
|
How is the cerebral cortex 'laminated'?
|
It has 6 layers
|
|
|
Structures Nissl can stain?
|
stains somas of neurons/glial cells (proteins)
|
|
|
Structure Golgi can stain?
|
Entire neuron
|
|
|
Size of a dendritic spine?
|
About 1 micron
|
|
|
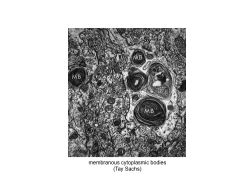
Mechanism of Tay-Sachs
|
Accumulation of membrane in dendrites, can't conduct information, results in MR, Death (enlarged dendritic processes; aka MEGANEURITES)
|
|
|
What effect would lack of nutrition during development have on dendrites?
|
Growth restriction; dendrites won't receive information because can't reach!
|
|
|
What effect does estradiol have on dendrites? What else could cause this?
|
Irregular spines (loss of spines, more spread out along dendrites)
Also caused by other hormones, aging, MR, FRAGILE X |
|
|
Describe the shape and structure of axons.
|
NOT tapered, branch at right angles, no spines
|
|
|
Give an example of a neuron that has a large diameter and is myelinated.
Give an example of a neuron that has a smaller diameter. How do they differ? |
Large diameter and myelin = Fast conducting, ex: PROPRIOCEPTORS
Small diameter = Slow conducting; carry slow (burning) pain, temperature |
|
|
List two ways that Schwann Cells differ from Oligodendrocytes.
|
Oligos are in CNS; one oligo can form many layers of myelin
Schwann Cells are in PNS; one Schwann cell per layer of myelin |
|
|
Where is the highest concentration of sodium-channels found on a neurons? Why is this important?
|
Found on axon hillock; when depolarized fires an IMPULSE which is propagated UNDECREMENTED
|
|
|
How does action potential propagation differ among myelinated and unmyelinated axons?
|
Myelinated: Saltatory; fast (AP propagates across Nodes of Ranvier); Faster
Unmyelinated: depol occurs locally, creeps down membrane, doesn't 'jump'; Slower |
|
|
List two ways that C-fibers differ from A-delta fibers
|
A-delta: FAST pain fibers; medium thickness
C-fibers: SLOW pain fibers; thin axons (dull, aching pain) |
|
|
What is the mechanism of onset of Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
|
AKA Acute Inflammatory Demyelinating Neuropathy
Due to demyelination in PERIPHERAL axons |
|
|
What is the mechanism of onset of Multiple Sclerosis?
|
Demyelinatin in CNS
|
|
|
What is the effect of cross-talk in demyelinated axons?
|
Message leaks out and is no longer localized
|
|
|
Fast acting excitatory NT
|
Glutamate
|
|
|
Fast acting inhibitory NT
|
GABA
|
|
|
Modulatory NTs
|
DA
ACh NE Serotonin |
|
|
Briefly describe the electrochemical events of a GABA-a-like synapse.
|
IPSP!
Ca2+ in PreSyn GABA fuse, release, bind Cl- enters PostSyn (HYPERPOL) |
|
|
Define receptor divergence.
|
A single NT can activate multiple receptors (have multiple effects)
|
|
|
Describe the three classes of GABA receptors.
|
GABA a: Cl- channels (ligand)
GABA b: K+, Ca2+ (G-prot) GABA c: Cl- (ligand gated) |
|
|
Effect of glycine?
|
Inhibitory; Cl- (ligand)
|
|
|
What can the modulatory sites of GABA a receptors bind? Effect of their binding?
|
EtOH
Benzodiazepines Barbiturates Neurosteroids Result in greater sedative (Depressive) effect; Potentiate GABA |
|
|
Field Potential VS Action Potential
|
Field Potential: Electrical events in dendrites (Slow); reflect INPUT
AP's: axons, spikes (Fast); reflect OUTPUT |
|
|
How do excited EEG waves differ from relaxed waves? How would these waves look in seizures?
|

Excited waves are less synchronous (much smaller spikes)
Relaxed waves are more synchronous (bigger spikes) Waves would go from asynchronous to VERY synchronous |
|
|
What is the major form of coding in the brain?
|
Spikes (outgoing message); frequency of firing is a possible code
|
|
|
Approximately how big is a soma?
|
~30 microns
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|

